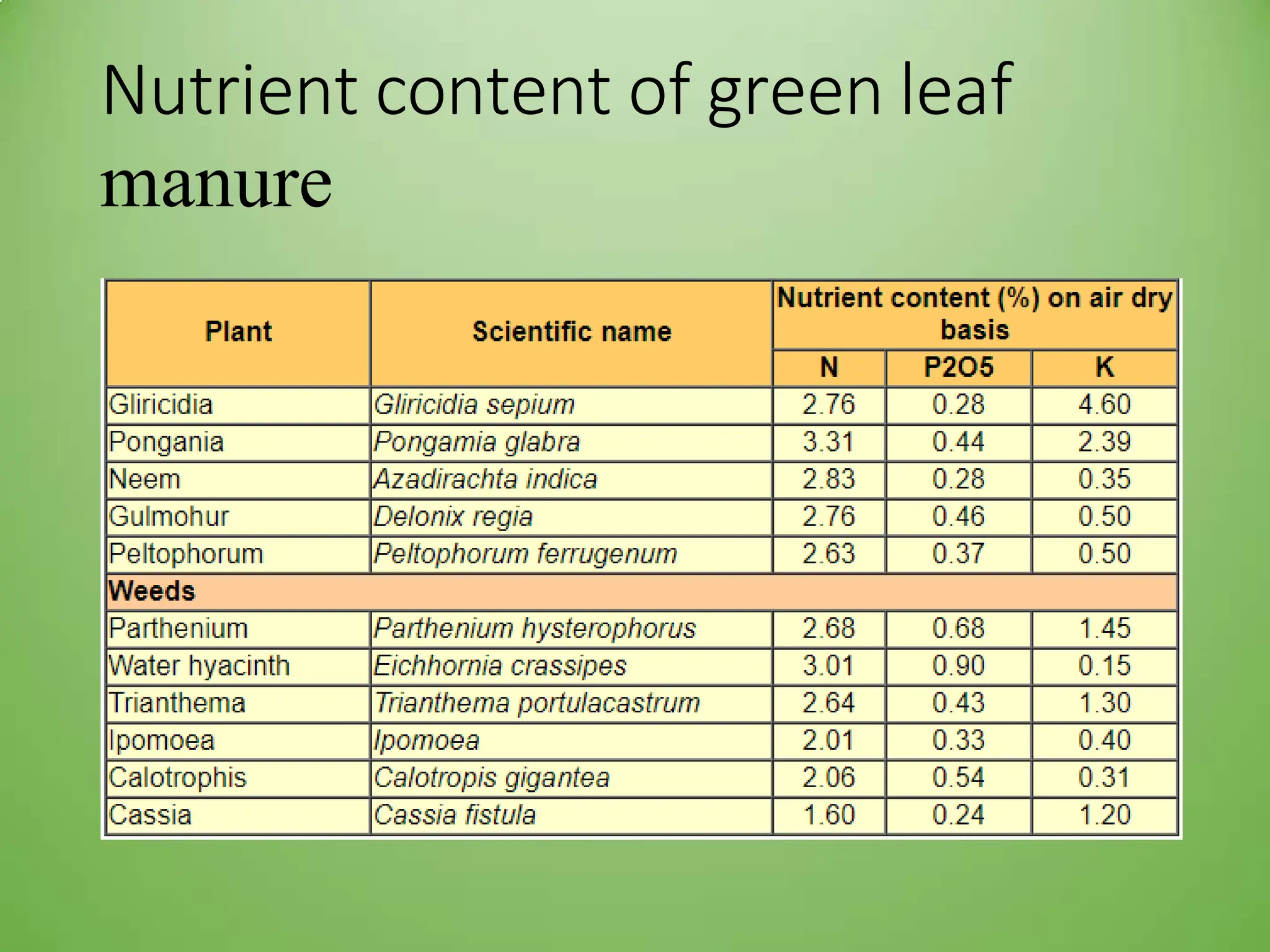
Green manuring is the practice of plowing green plant materials into the soil to improve soil structure and fertility. There are two types of green manuring: green leaf manuring, which involves collecting and incorporating leaves and twigs from outside sources, and green manuring in situ, which involves growing and plowing under leguminous crops. Green manuring contributes nitrogen to the soil, prevents nitrogen loss, improves soil structure and water retention, and can reclaim saline or alkaline soils. Common green manure crops include sunn hemp, dhaincha, sesbania, and clusterbeans, as they are fast-growing legumes that decompose quickly and add nutrients to the soil without competing with main crops.