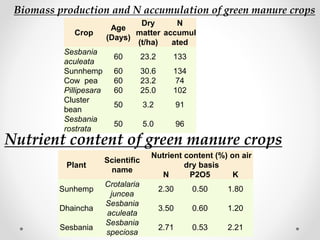
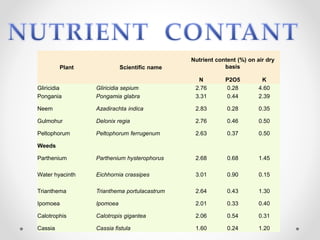
Green manure refers to undecomposed plant material grown and then incorporated into soil. It is obtained by growing leguminous green manure crops or collecting plant materials from wastelands. Important green manure crops include sunnhemp, dhaincha, and sesbania which accumulate substantial amounts of nitrogen and dry matter. Green manuring improves soil structure, increases water holding capacity, and decreases erosion by providing ground cover and bringing nutrients up from lower soil layers.