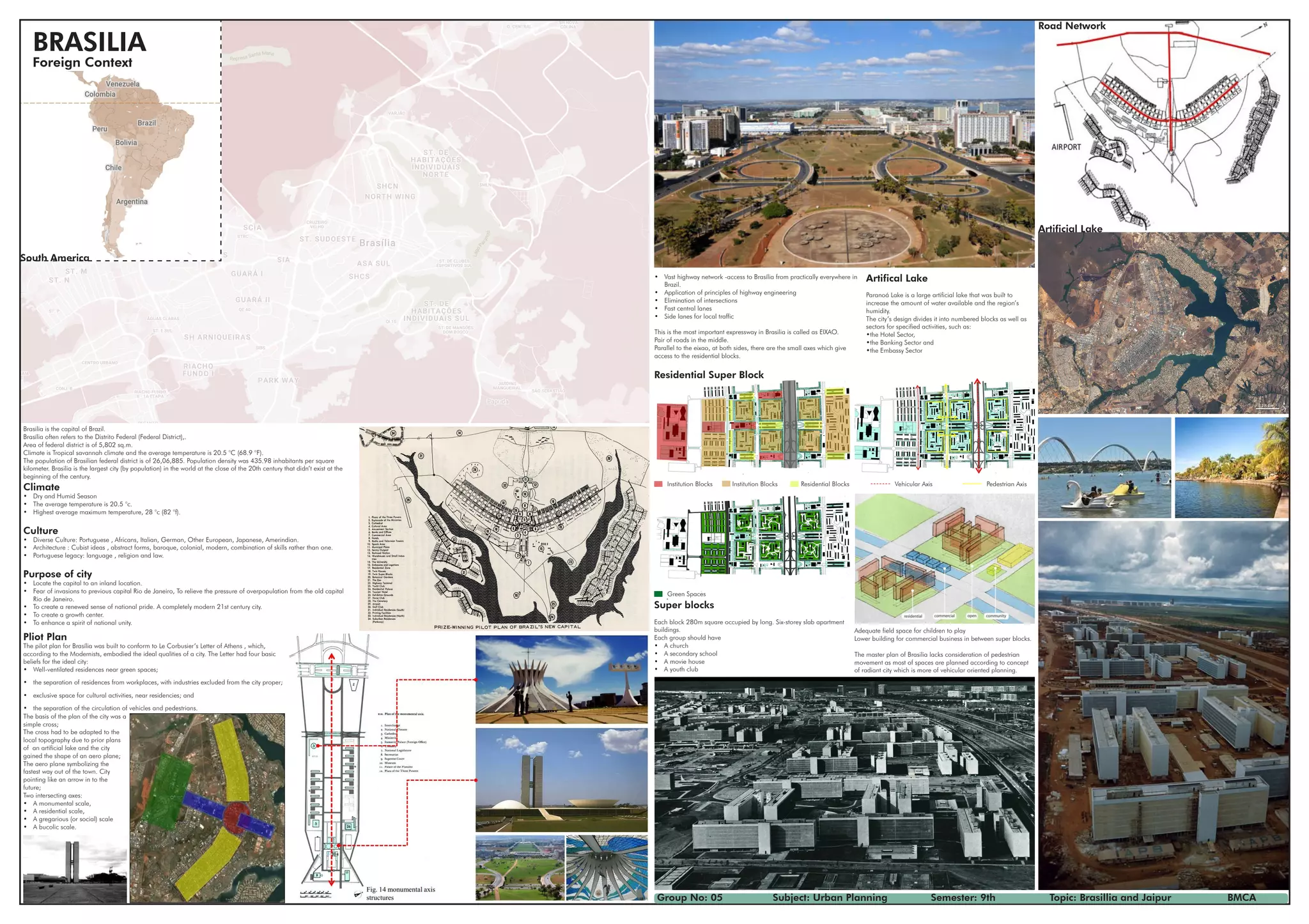
Brasilia is the capital city of Brazil, located in the Distrito Federal region. It was planned and constructed in the mid-20th century as a new planned city to replace Rio de Janeiro as the capital. Brasilia has a tropical savannah climate with an average temperature of 20.5 degrees Celsius. The population is over 2.6 million people with a density of around 435 inhabitants per square kilometer, making it one of the largest cities built in the 20th century. The city was planned with distinct sectors for different functions and an emphasis on separating vehicles and pedestrians.