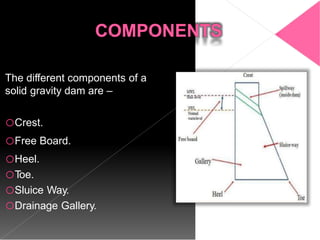
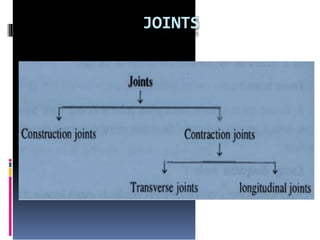
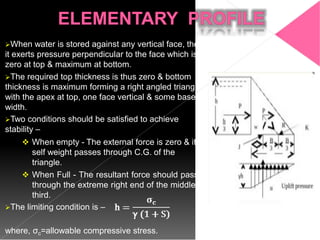
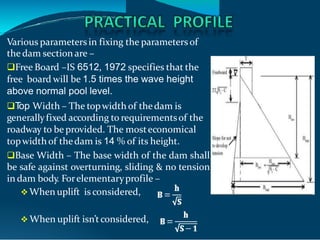
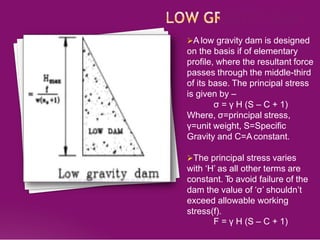
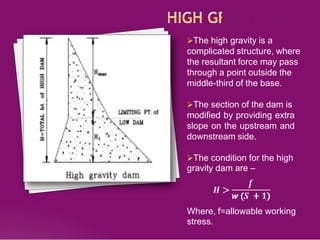
This document discusses the design and construction of gravity dams. It explains that gravity dams resist forces through their massive weight and have vertical or near-vertical faces. The key components, external forces, and methods of stress analysis are described. Failure can occur through sliding, overturning, cracking or crushing, so factors of safety are considered. Joints are used to aid construction and control cracking. High construction costs require stable foundations, but maintenance costs are lower with less water loss.