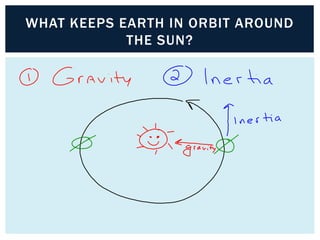
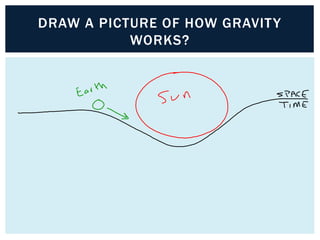
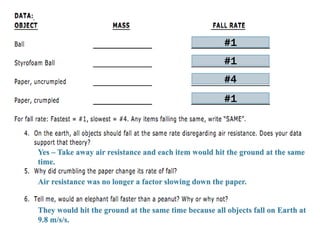
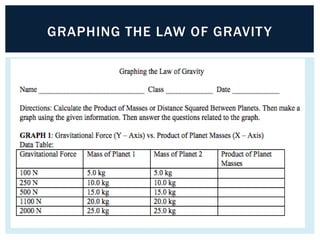
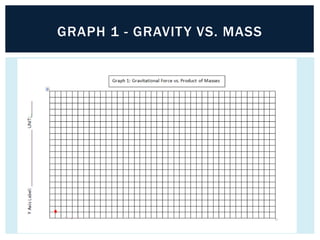
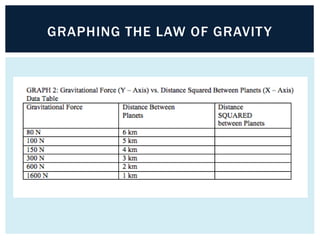
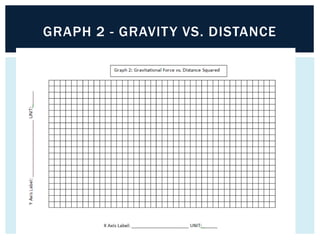
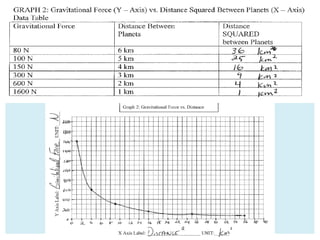
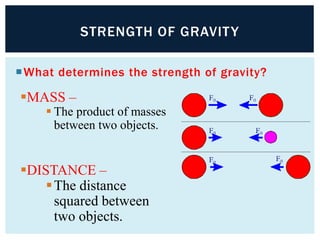
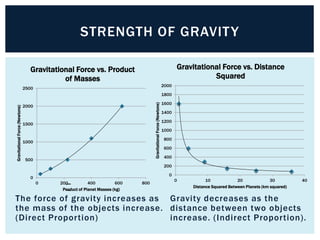
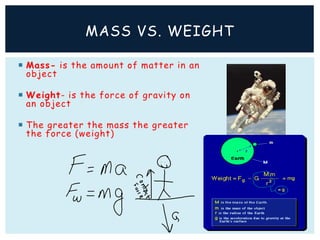
Gravity is the force that keeps Earth and other large celestial bodies in orbit around the Sun. Sir Isaac Newton first hypothesized that the same force of gravity that causes apples to fall to the ground also causes the Moon to orbit Earth. Gravity is caused by the bending of spacetime due to mass. More massive objects cause greater bending. This bending is what we perceive as the force of gravity. Gravity depends on the masses of the interacting objects and the distance between them - the greater the masses and the closer the distance, the stronger the gravitational force. All objects fall at the same rate in a vacuum where air resistance is not a factor.