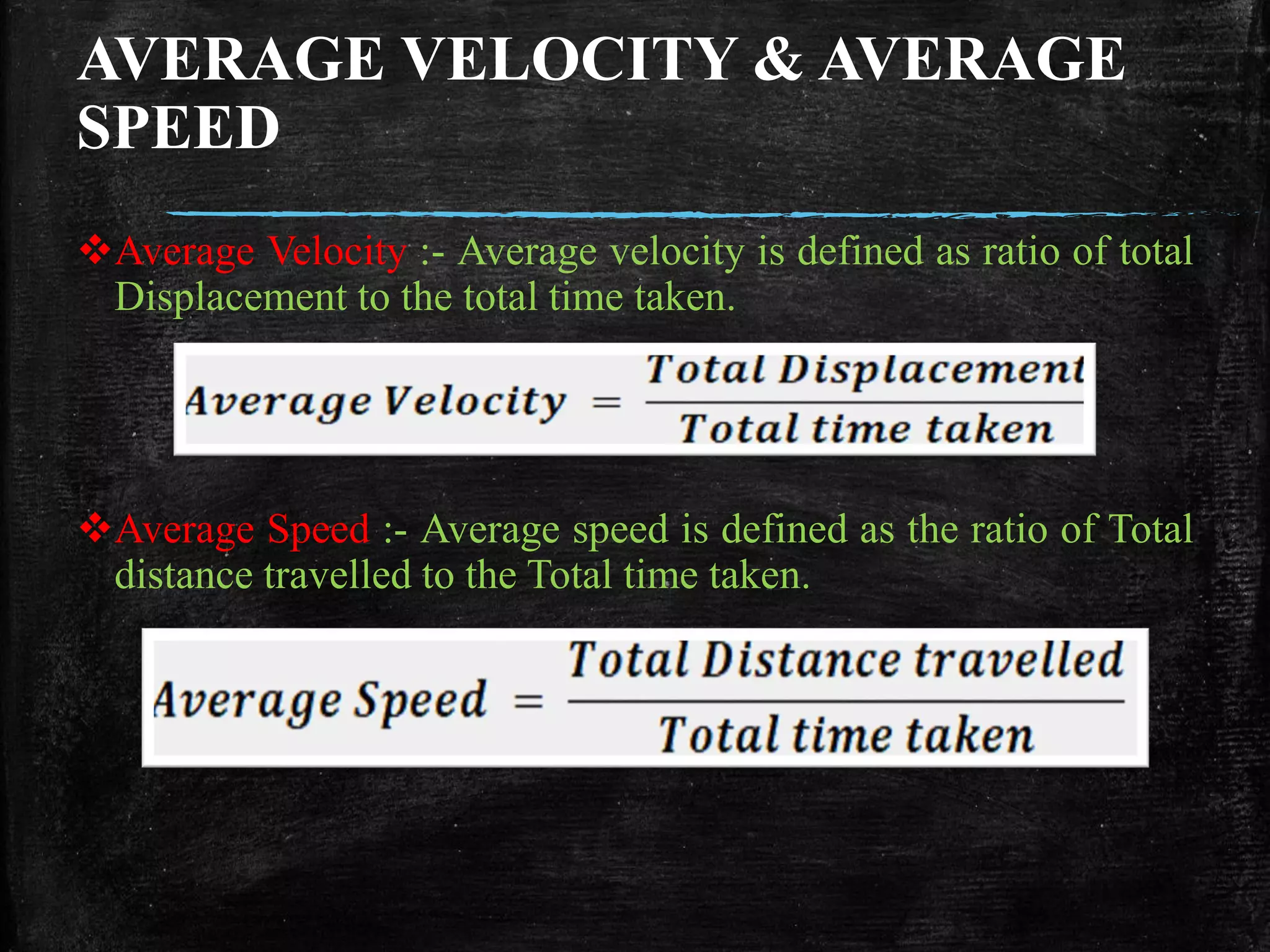
This document provides an overview of motion in a straight line, including definitions of key concepts like position, velocity, acceleration, and different types of motion. It discusses uniform and non-uniform motion, average and instantaneous speed and velocity, and introduces the kinematic equations for uniformly accelerated motion. Key points covered include defining rectilinear, circular and oscillatory motion, position as a coordinate, frames of reference, and formulas for average velocity, acceleration, and solving problems involving motion under constant acceleration.