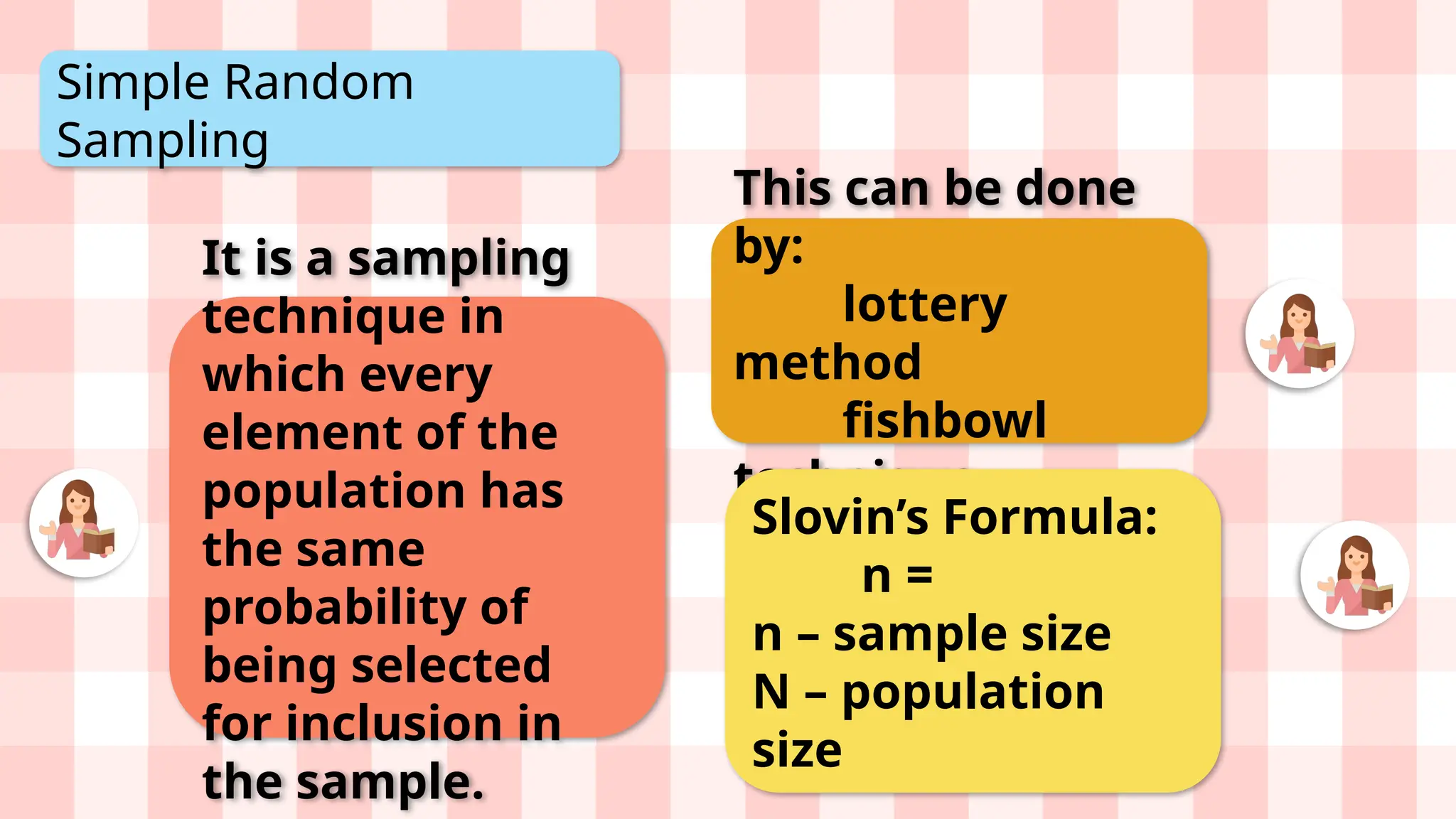
The document covers various random sampling techniques used in research, including simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling. It provides definitions, formulas, and examples to illustrate how to select representative samples from a population. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of sampling in obtaining unbiased results without the impracticality of surveying the entire population.