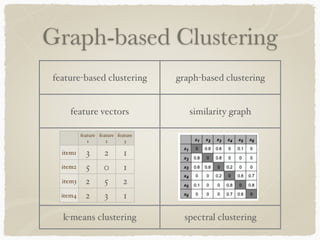
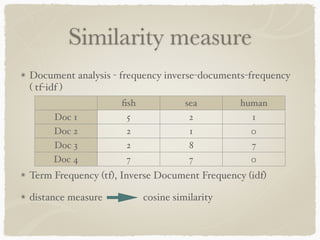
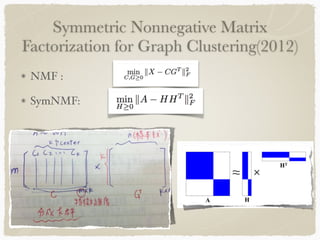
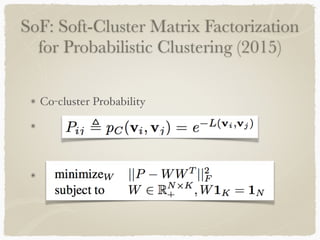
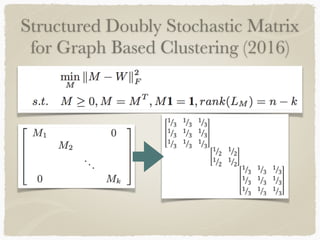
Graph-based clustering uses similarity graphs instead of feature vectors, representing data as a graph where nodes are data points and edges represent similarity. It can handle any data type as long as similarities are defined, and is useful for high-dimensional data by reducing dimensionality. However, computing similarities between all pairs of data points is computationally expensive. Survey papers discussed algorithms like spectral clustering and modularity optimization. Applications include document analysis, social networks, and recommendation systems. Future work includes determining optimal cluster numbers, scaling to large data, and handling directed graphs.