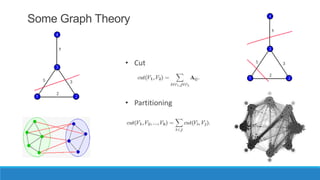
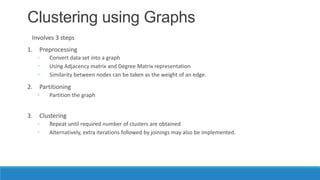
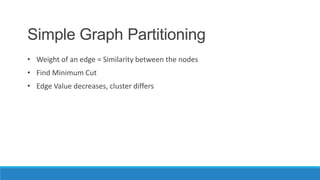
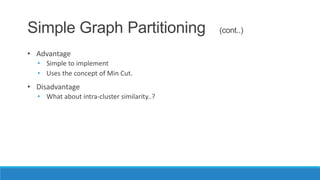
This document discusses using graph-based approaches for gene expression clustering. It describes representing gene expression data as graphs, with genes as vertices and edge weights representing similarity. It covers partitioning graphs into clusters using simple graph partitioning that finds minimum cuts, and spectral graph partitioning that uses the eigenvectors of the graph Laplacian matrix. Spectral partitioning is shown to provide better, more qualitative clusters than simple partitioning. The document provides an overview of key graph theory concepts used in these clustering methods like cuts, partitioning, degrees, and Laplacian matrices.






![Spectral Graph Partitioning
Input : Graph G<V,E>
Output: Graphs G1< V1,E1>, G2< V2,E2>
Create the Laplacian Vector L, of the Graph G.
Calculate the Fiedler Vector F
for each vertex vi in G
if F[i]>0
V1.append(v)
else
V2.append(v)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalupload-130323030500-phpapp01/85/Graph-based-approaches-to-Gene-Expression-Clustering-13-320.jpg)



