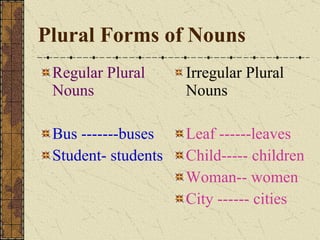
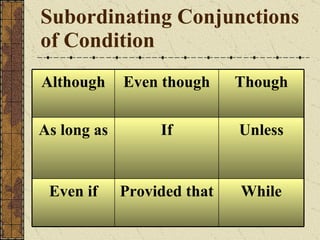
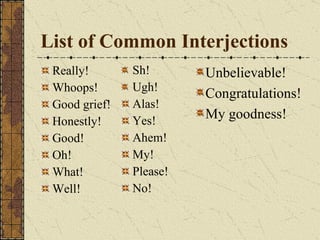
The document provides a comprehensive overview of grammatical components, defining sentences, nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. It explains their roles within sentences, their kinds, and provides examples for each category. The material serves as a grammar workshop resource aimed at enhancing language skills.