This document is a Spanish grammar book that provides an overview of various grammar topics in 9 chapters:
1) Subjunctive in adjective clauses
2) Tu commands
3) Nosotros commands
4) Past participles used as adjectives
5) Present perfect
6) Past perfect
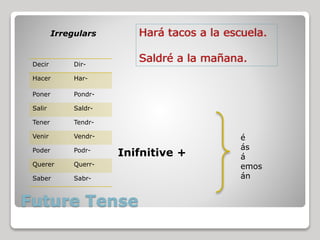
7) Future tense
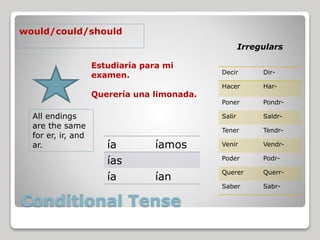
8) Conditional tense
9) Past subjunctive
Each chapter explains the formation and use of the grammar points covered in that section, along with examples. The document serves as a reference for different aspects of Spanish grammar.