This document provides examples and explanations of different methods for counting outcomes of experiments:
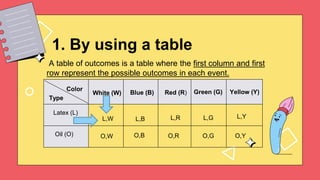
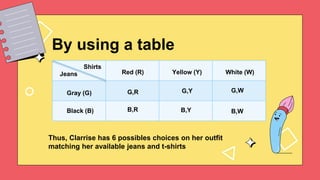
1. Tables can be used to systematically list all combinations of outcomes in experiments with multiple variables.
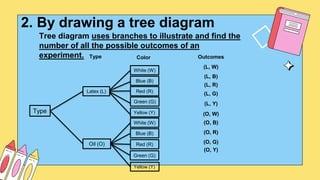
2. Tree diagrams visually illustrate the branching possibilities in an experiment.
3. Systematic listing ensures all outcomes are included without omissions or duplicates.
4. The fundamental counting principle of multiplying the number of possible outcomes in each variable provides the total without explicit listing.