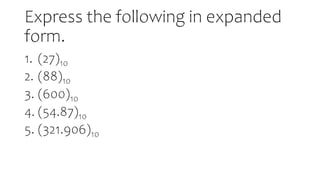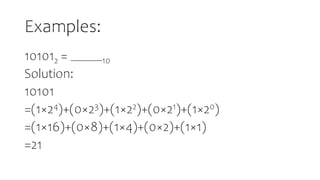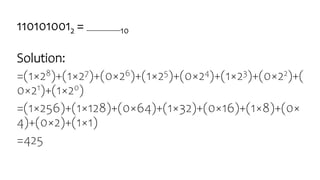The document discusses different number systems including decimal, binary, octal, and hexadecimal. It provides details on:
- What defines a number system and how they are used to represent quantities
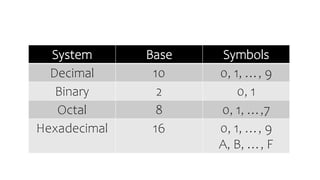
- The base or radix of a system determines the number of unique symbols used
- Decimal uses base-10 with symbols 0-9 and is widely used. Binary uses base-2 with only symbols 0 and 1.
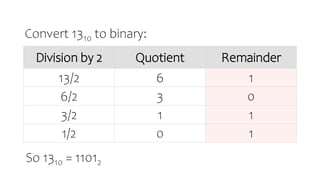
- Methods for converting between decimal and binary are presented using division and remainder.