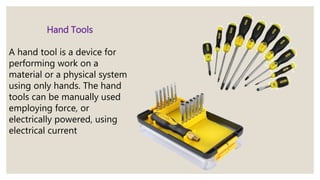
This document discusses tools used in computer hardware servicing. It defines terms related to tools and hardware and categorizes hardware tools into electro-static discharge tools, hand tools, cleaning tools, and diagnostic tools. It provides examples of common tools in each category and their purposes, such as using anti-static wrist straps and mats to prevent electrostatic discharge, screwdrivers and pliers for assembly and disassembly, compressed air and lint-free cloths for cleaning, and multimeters and loopback adapters for diagnostics. The document emphasizes tool selection, safe use, and maintenance to properly service computer hardware.