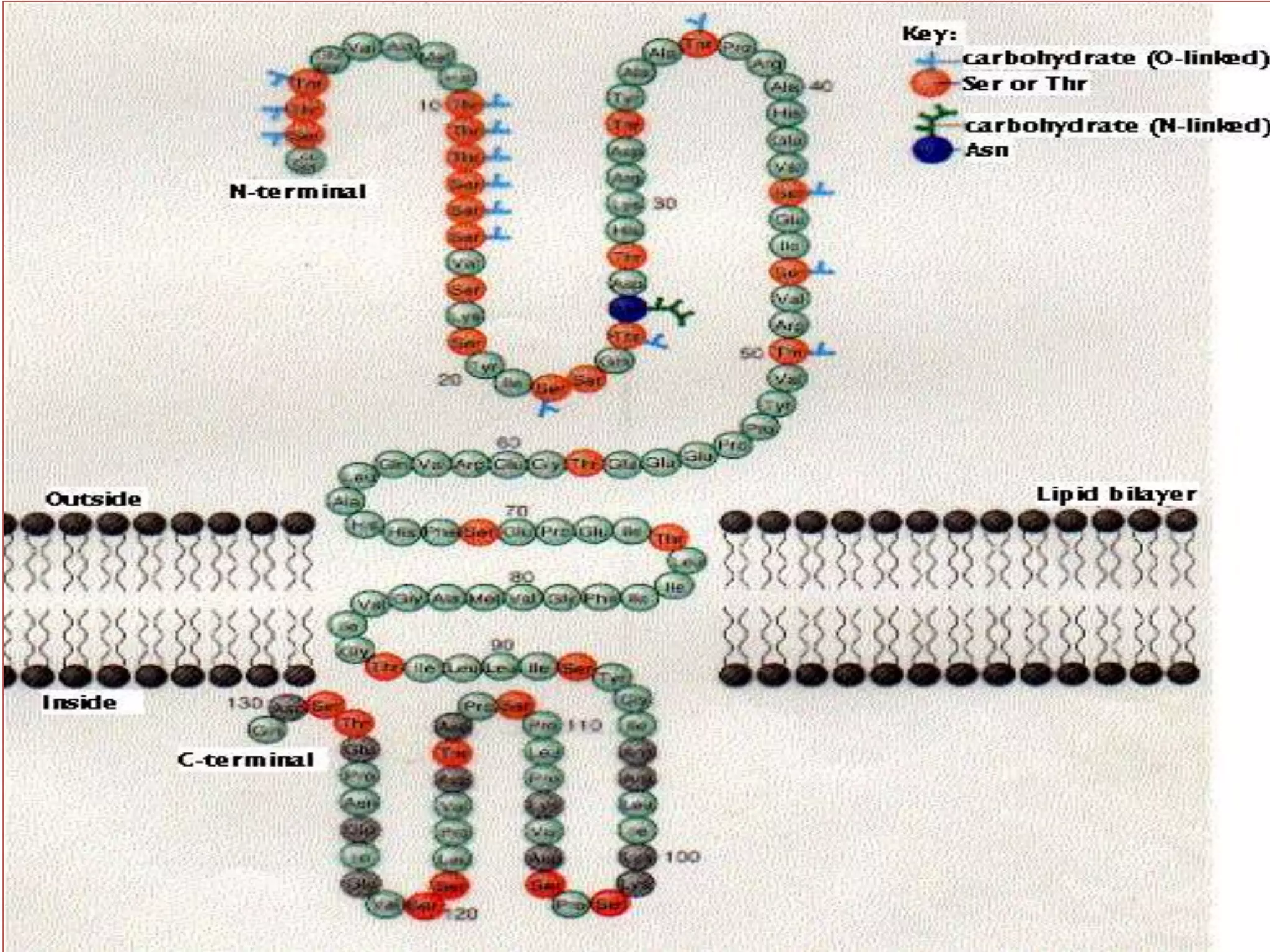
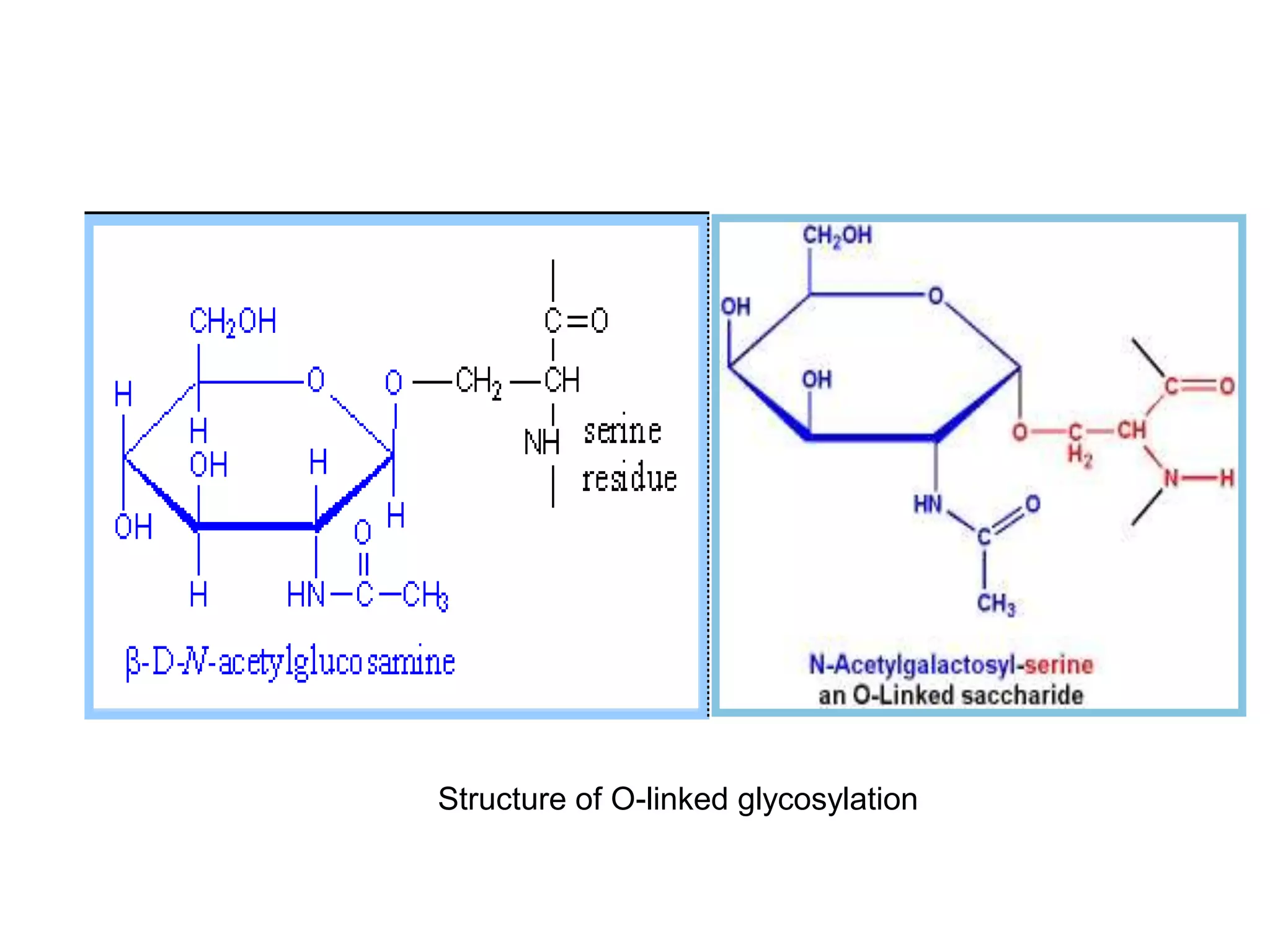
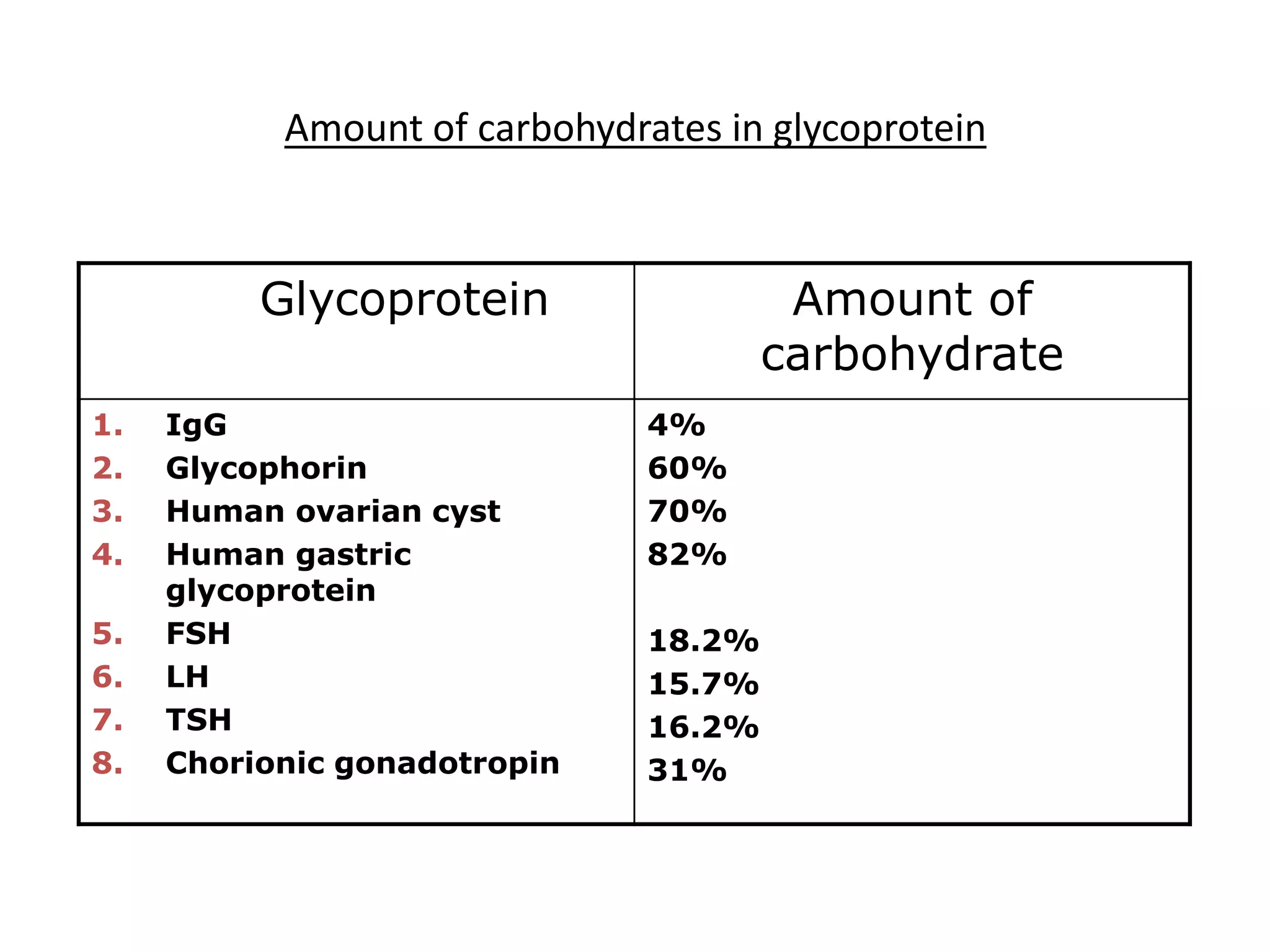
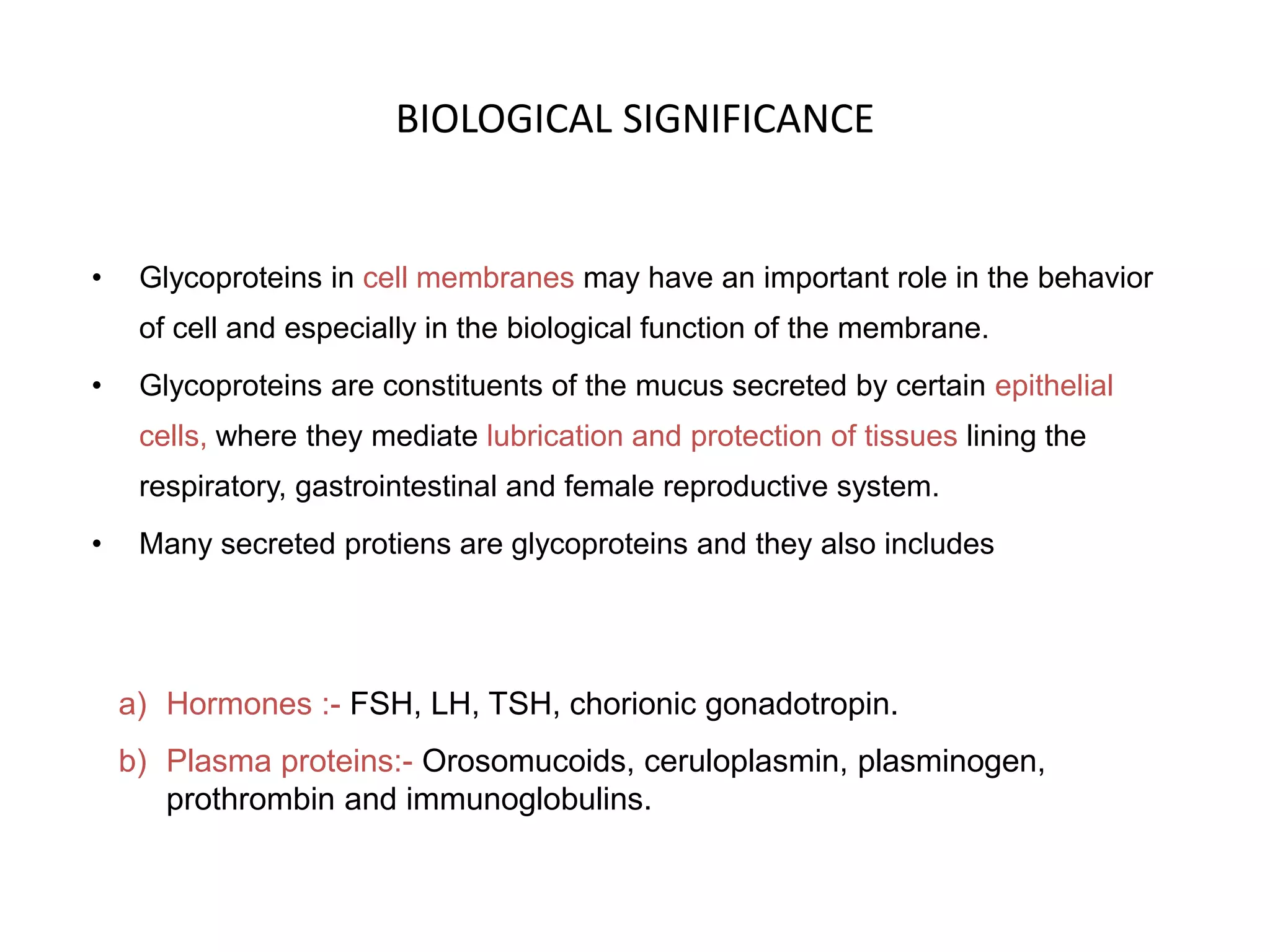
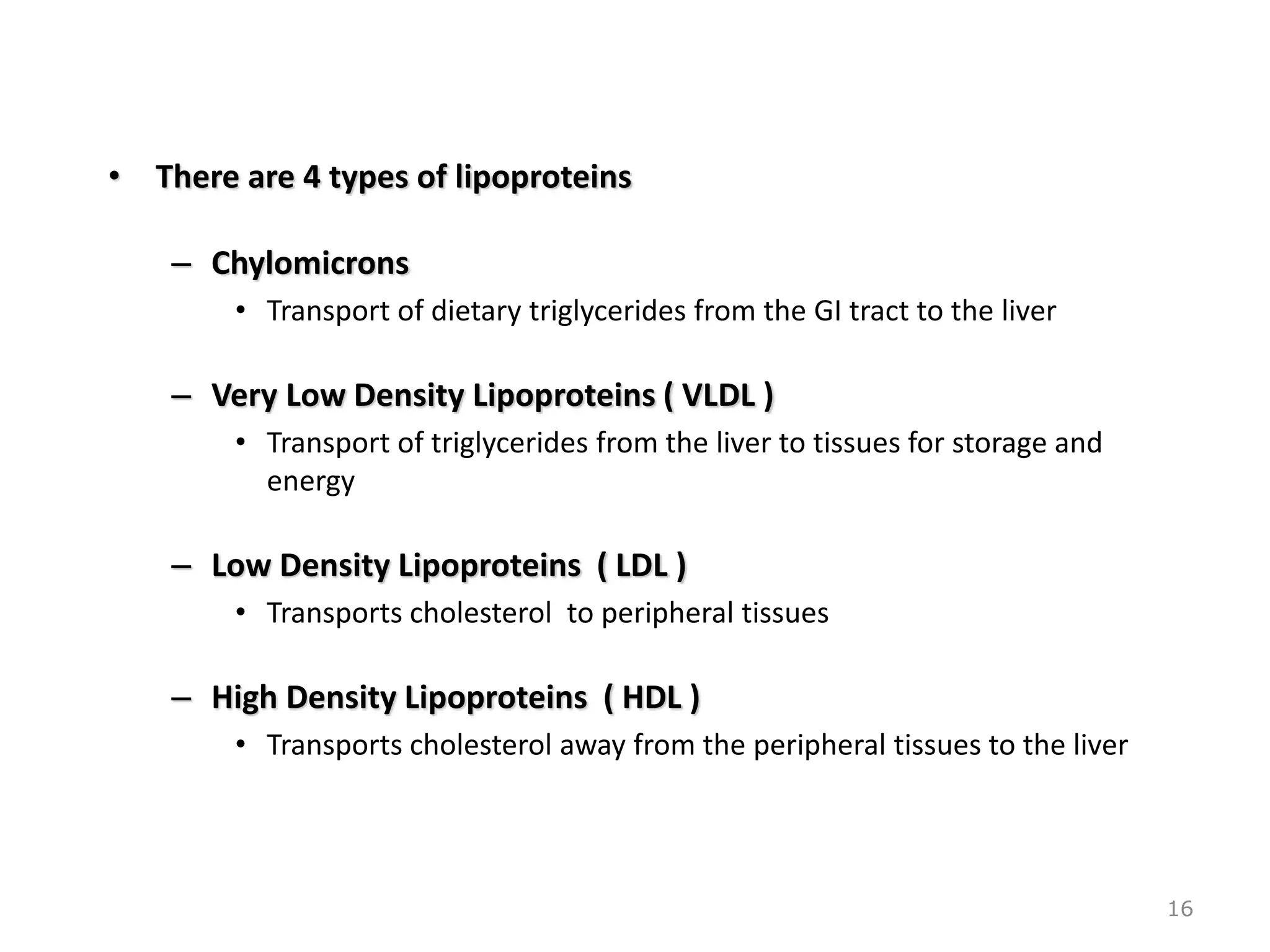
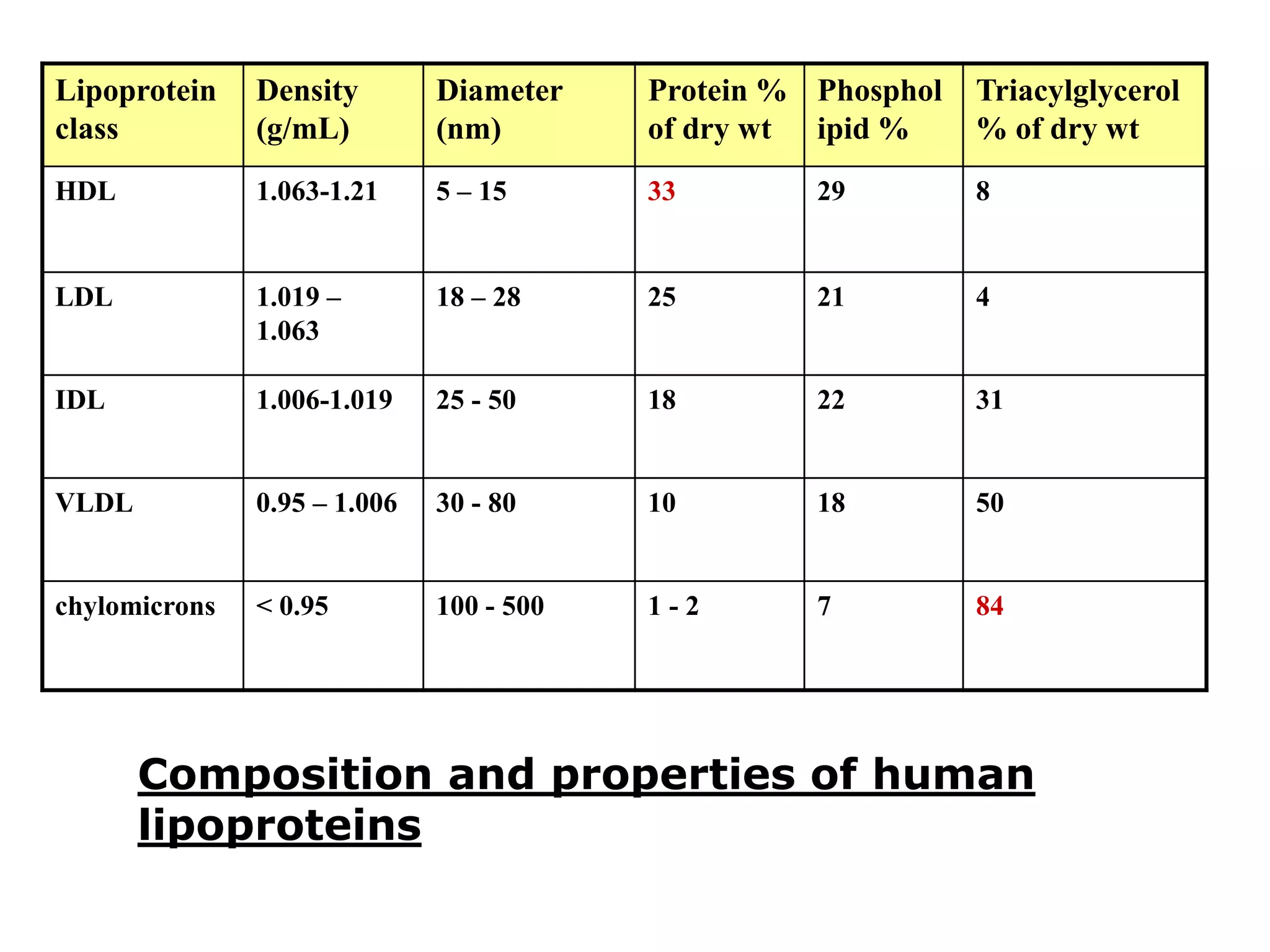
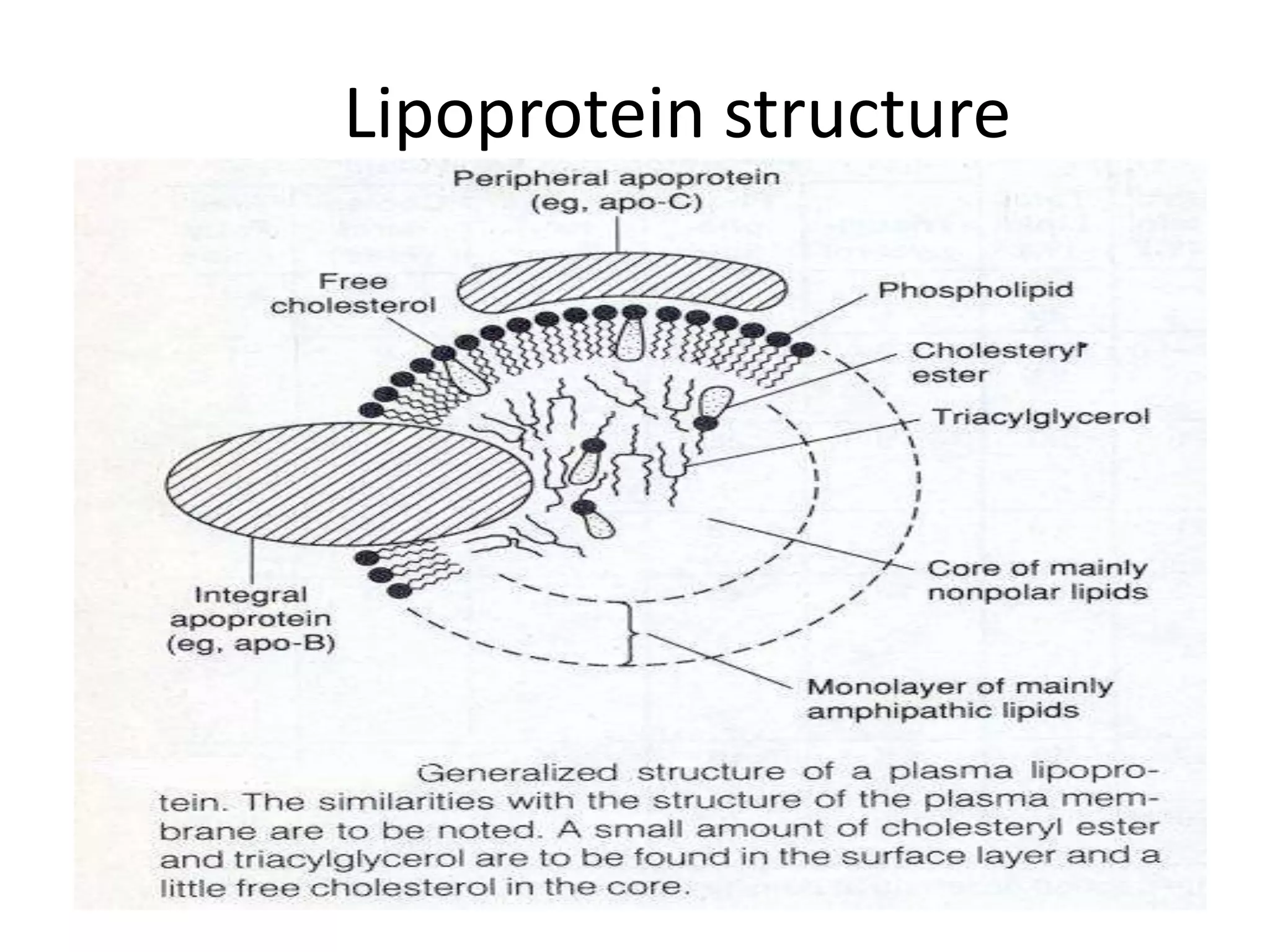
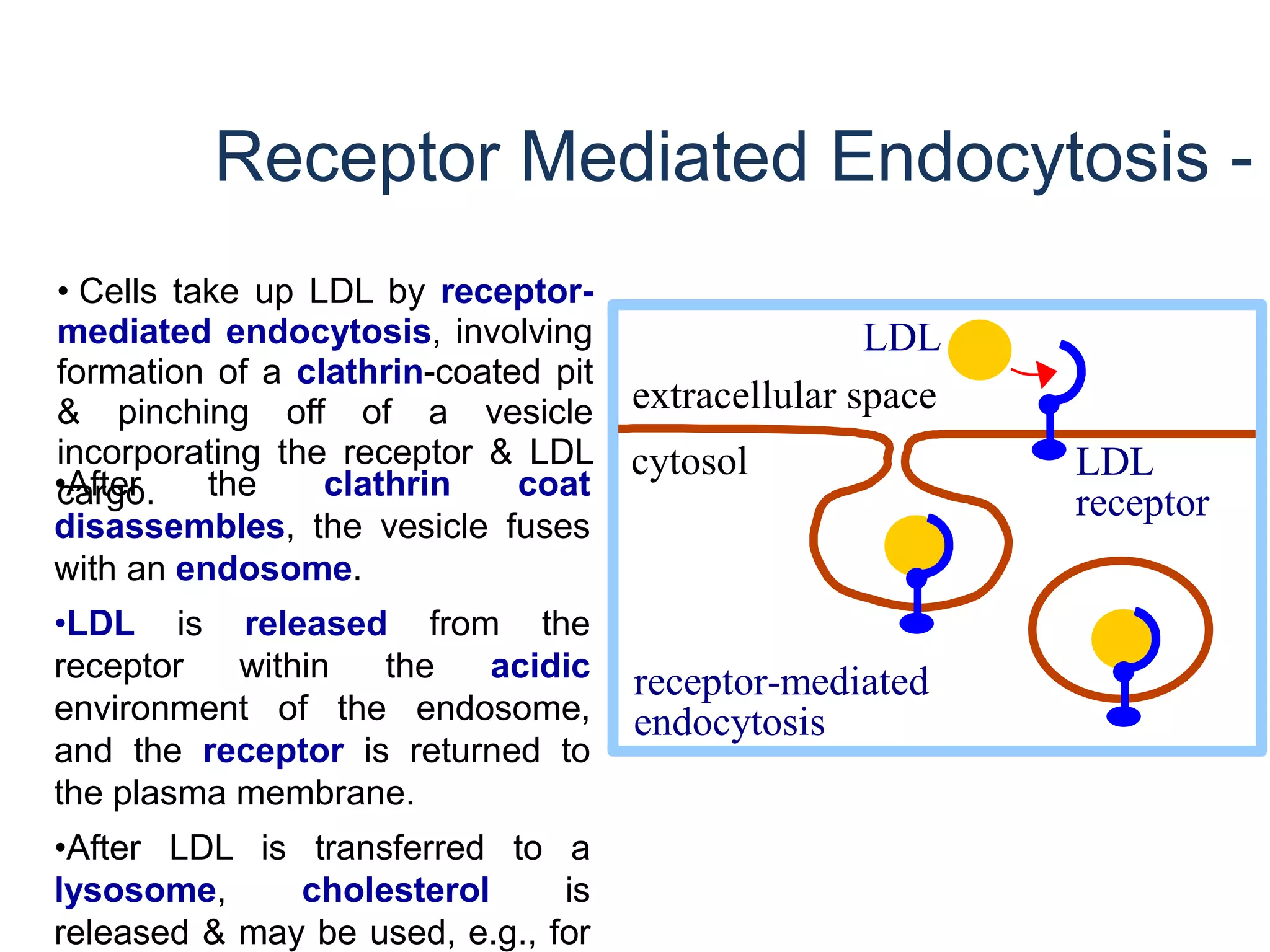
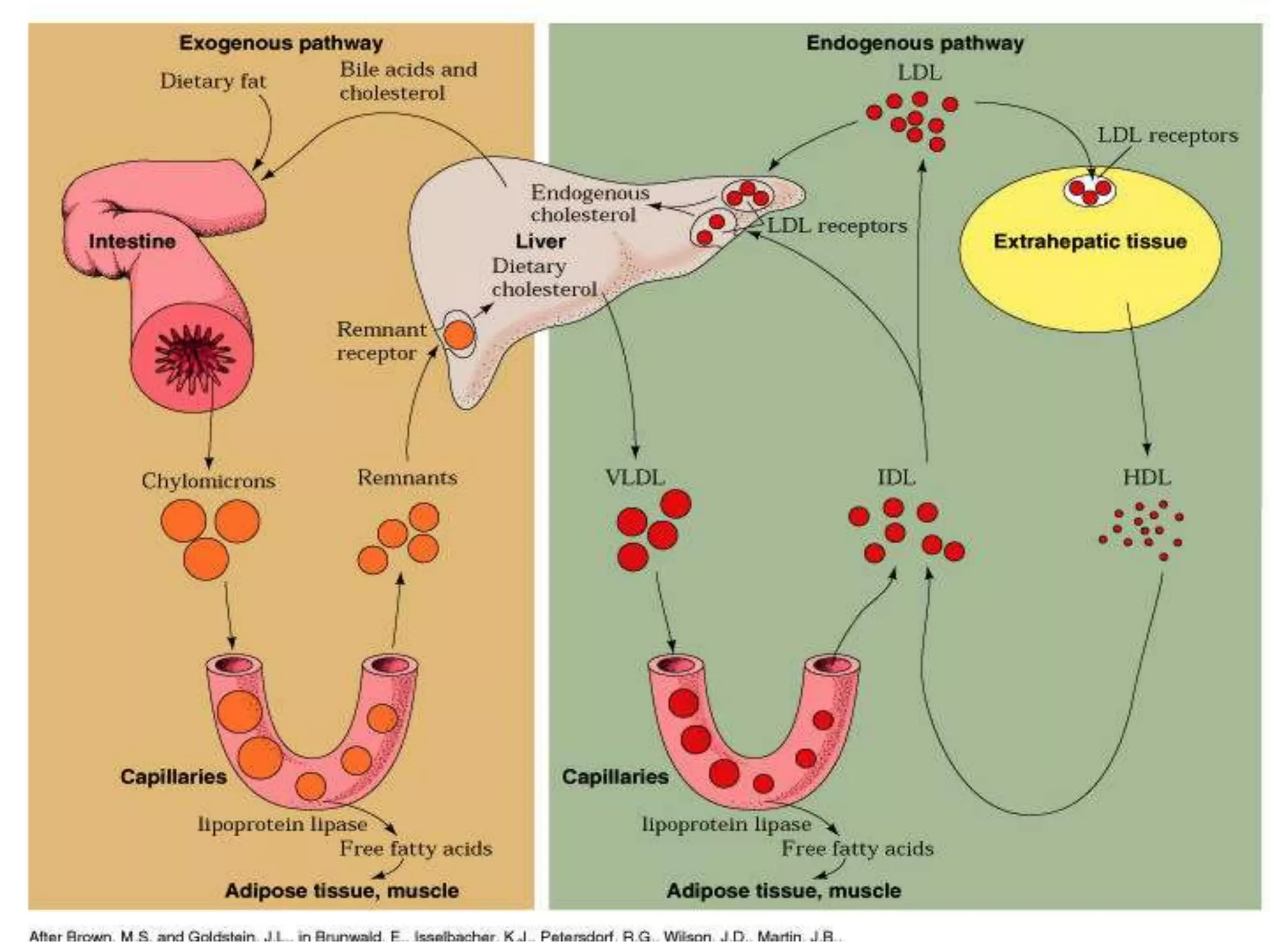
The document discusses the structure and function of glycoproteins and lipoproteins, detailing their definitions, types, and biological significance. Glycoproteins are conjugated proteins that contain carbohydrates, playing crucial roles in cellular functions and membrane stability, while lipoproteins are responsible for transporting lipids in the body. The document emphasizes the importance of studying these biomolecules in relation to various diseases and their metabolic processes.