Embed presentation
Download to read offline




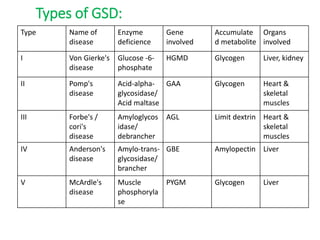
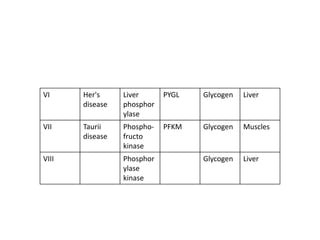



Glycogen storage diseases are a group of metabolic disorders caused by enzyme deficiencies that affect glycogen synthesis or breakdown in the liver and/or muscles. The main symptoms include low blood sugar, liver enlargement, slow growth, muscle weakness, and breakdown of muscle fibers. Diagnosis involves biopsy, blood and urine tests, and MRI scans. There are several types of glycogen storage diseases categorized by the specific enzyme deficiency and accumulated metabolite. Treatment focuses on maintaining blood glucose levels through nasogastric infusion, medications to manage symptoms, dietary changes, and in severe cases, organ transplantation.







