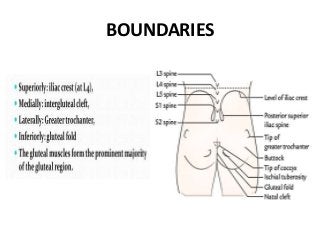
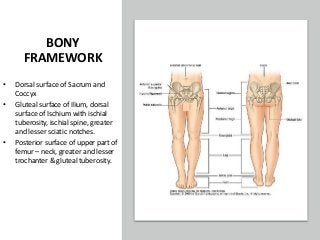
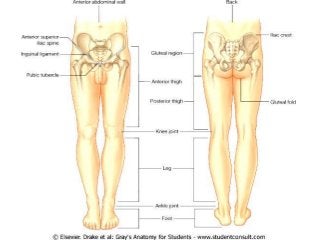
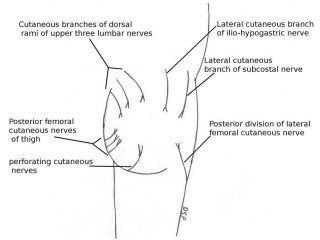
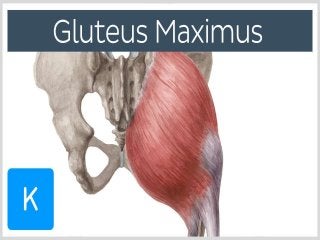
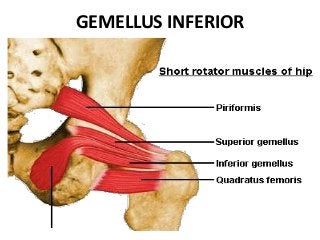
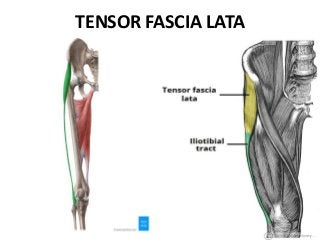
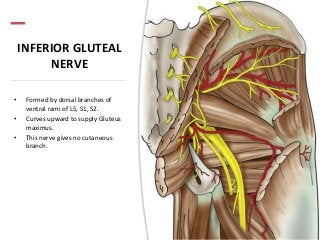
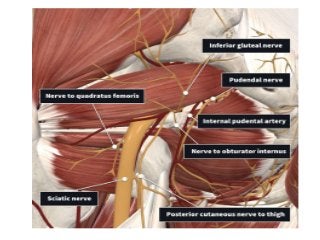
The gluteal region is bounded by the sacrum, coccyx, ilium, ischium and femur. It contains the gluteus maximus, medius and minimus muscles. Other structures include the piriformis, obturator internus and quadratus femoris muscles. The region has a superficial and deep fascia. It is supplied by the superior and inferior gluteal nerves and vessels. The sciatic nerve also passes through the region.