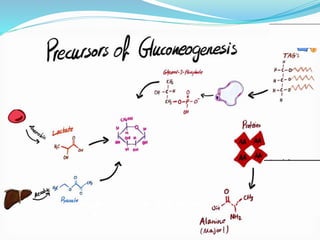
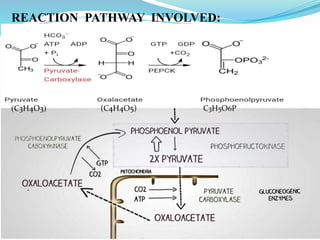
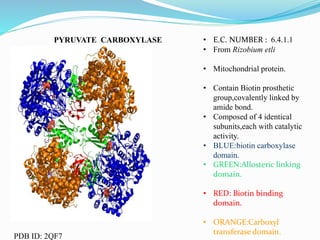
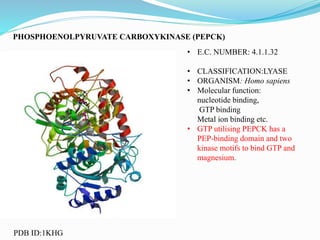
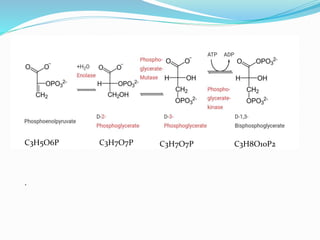
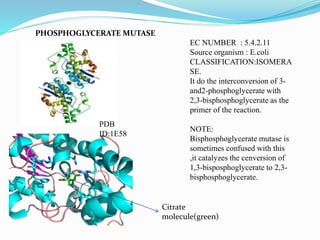
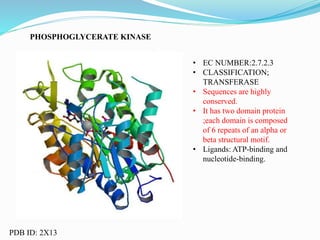
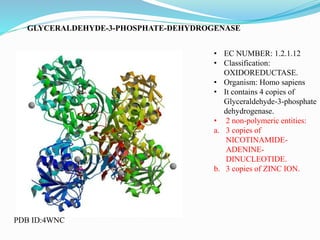
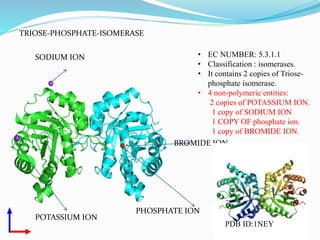
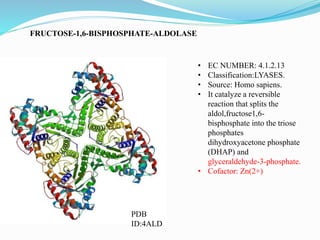
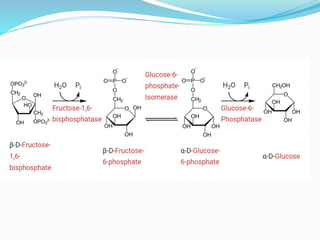
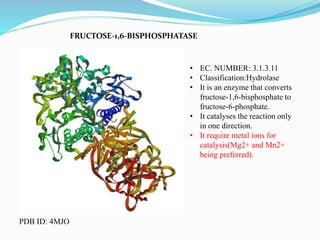
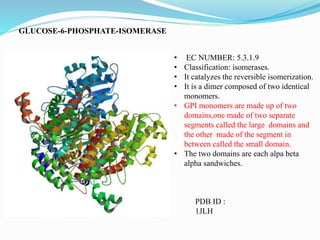
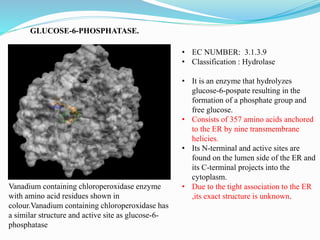
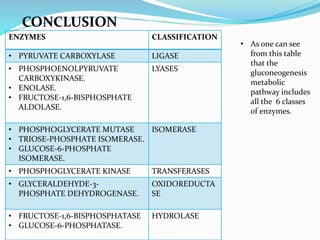
This document presents information on the enzymes involved in the metabolic pathway of gluconeogenesis. It discusses 12 key enzymes by name, EC number, classification, source organism, and molecular structure. The enzymes catalyze critical reactions in converting non-carbohydrate precursors into glucose and include ligases, isomerases, transferases, oxidoreductases, and hydrolases. The shapes and structures of the enzymes are tailored to their specific functions in gluconeogenesis.