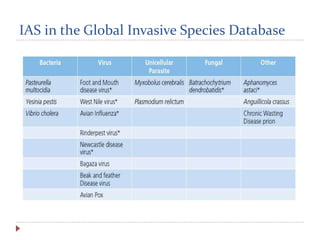
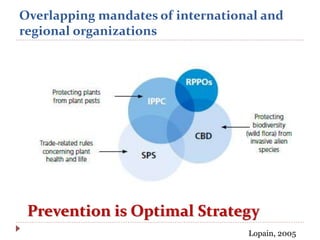
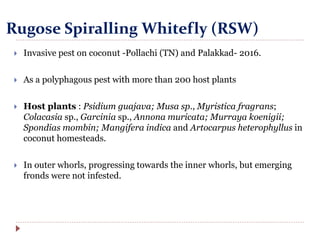
This document discusses the risks of invasive alien species spread through global trade. It defines key terms like invasive alien species, quarantine pest, and outlines the risk analysis process. It notes that increased global trade leads to more potential pathways and habitats for invasives. The effectiveness of existing regulatory systems is limited by low inspection rates. Many species in the Global Invasive Species Database have been introduced through trade and transport. Various international agreements and conventions address preventing invasive species spread, including the Convention on Biological Diversity and International Plant Protection Convention. Managing this threat requires strengthened policies and cooperation across many organizations.