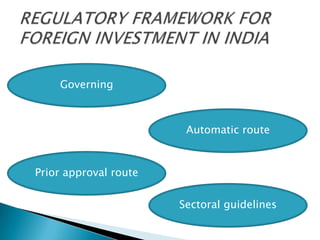
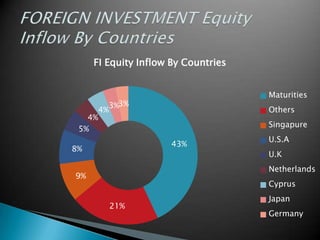
Foreign investment refers to capital flows between nations for significant ownership stakes in domestic companies or assets. There are three main options for foreign investment: equity acquisitions, loans, and profit reinvestment. Foreign capital is needed for economic growth when domestic capital is inadequate and capital markets are developing, as it brings technical skills, experience, and scarce productive factors. Foreign investment is governed by regulations and allowed in most sectors except atomic energy, agriculture, lotteries, and plantations.