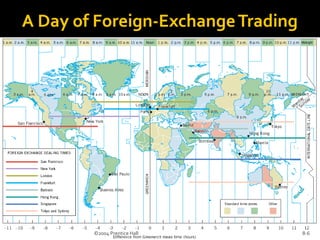
The document discusses foreign exchange management. It begins by defining the foreign exchange market (forex) as a worldwide decentralized market for trading currencies. It then lists some key currencies and their codes. It describes characteristics of the forex market, including that it operates 24 hours a day from locations around the world. It also discusses currency appreciation/depreciation. The document then provides more details on different parts of the forex market including spot markets, forward markets, and derivatives markets. It describes how interbank foreign exchange trading works and participants in the forex market like individuals, banks, and governments.











![Foreign Exchange and Forward ContractsWhat is a forward foreign exchange contract?(An agreement to exchange one currency for another on some date in the future at a price set now [the forward exchange rate]).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/foreignexchangemanagement-110929002933-phpapp01/85/Foreign-exchange-management-13-320.jpg)






