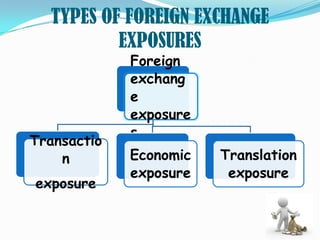
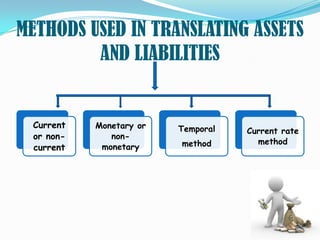
Foreign exchange risk, also known as currency risk, refers to the financial risk posed by unexpected changes in exchange rates. It affects investors and businesses involved in international trade or foreign investments. There are three main types of foreign exchange exposure: transaction, economic, and translation. Transaction exposure involves existing foreign currency transactions, economic exposure impacts future cash flows and firm value, and translation exposure affects financial reporting due to exchange rate movements between periods. Companies can use hedging strategies like forward contracts, options, and money market operations to eliminate or reduce foreign exchange risk.