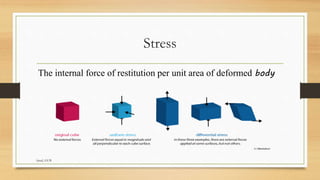
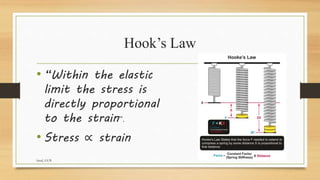
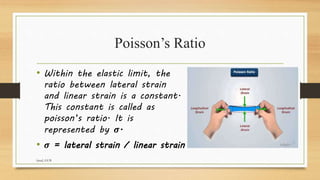
The presentation discusses elasticity, defined as the ability of a deformed material to return to its original shape after deformation. It covers concepts such as Young's modulus, which relates stress and strain, and Poisson's ratio, defining the relationship between lateral and linear strains. The presenter explains different types of strain and properties of elastic and inelastic materials, using examples like springs and rubber bands.