Embed presentation
Download to read offline




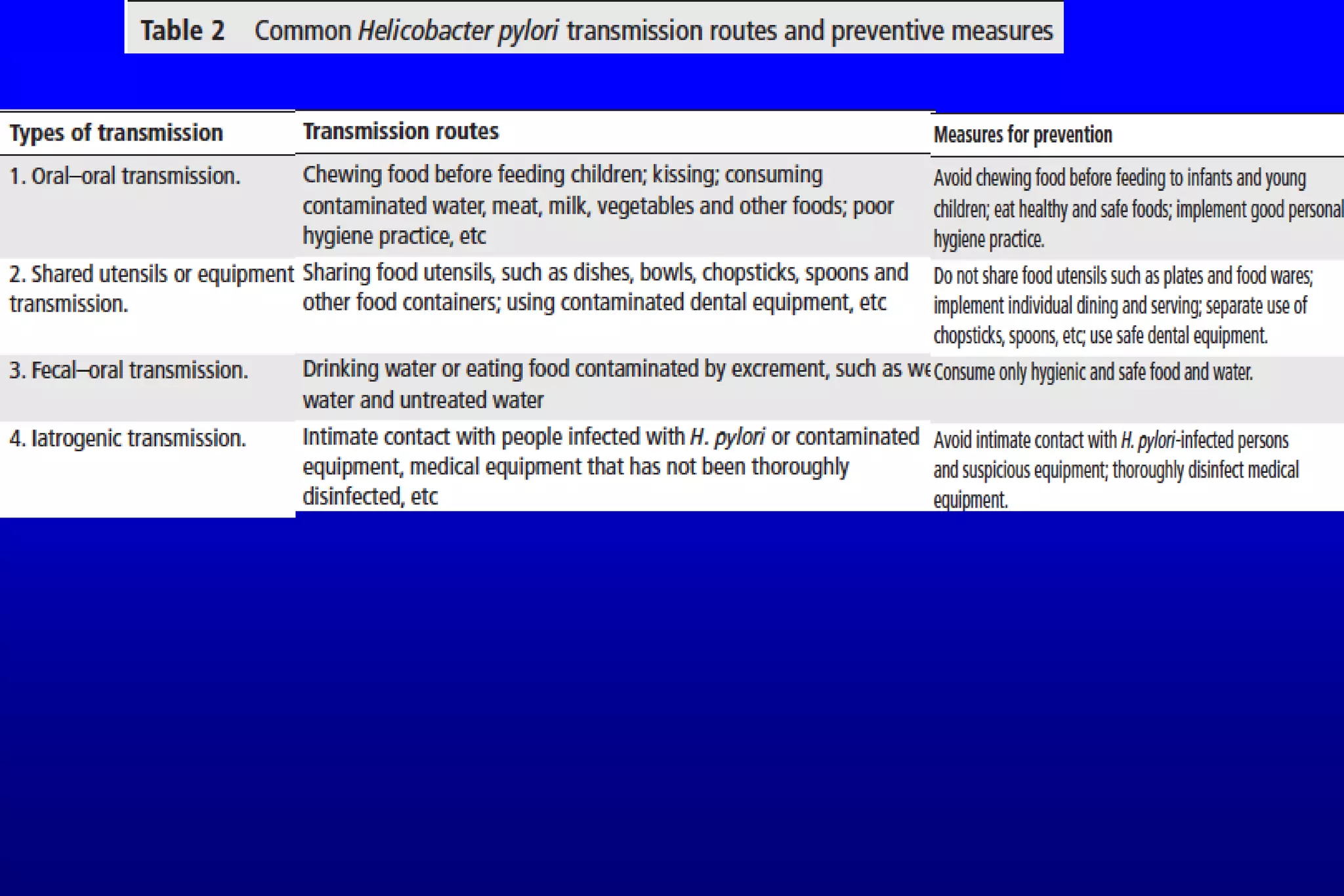
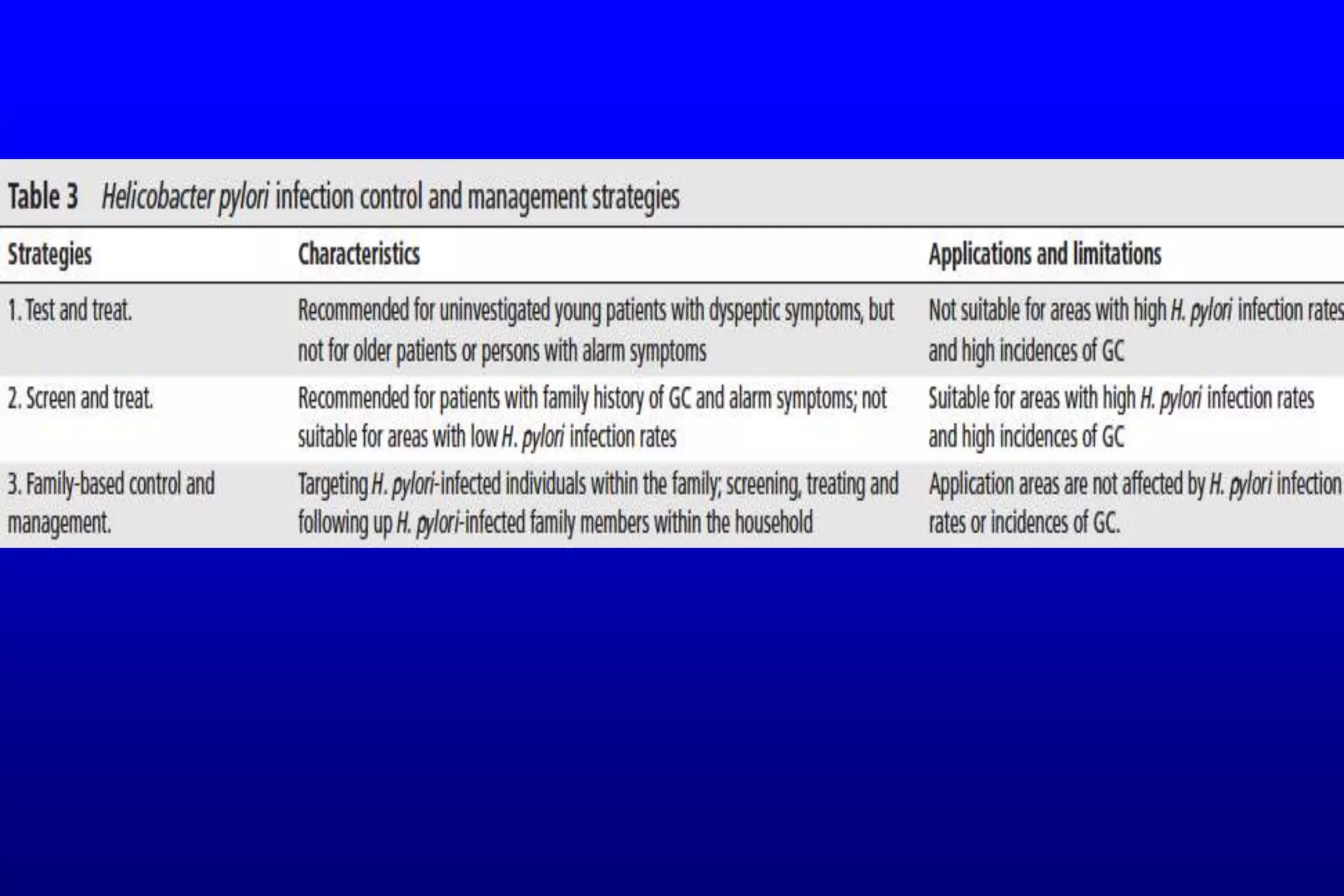
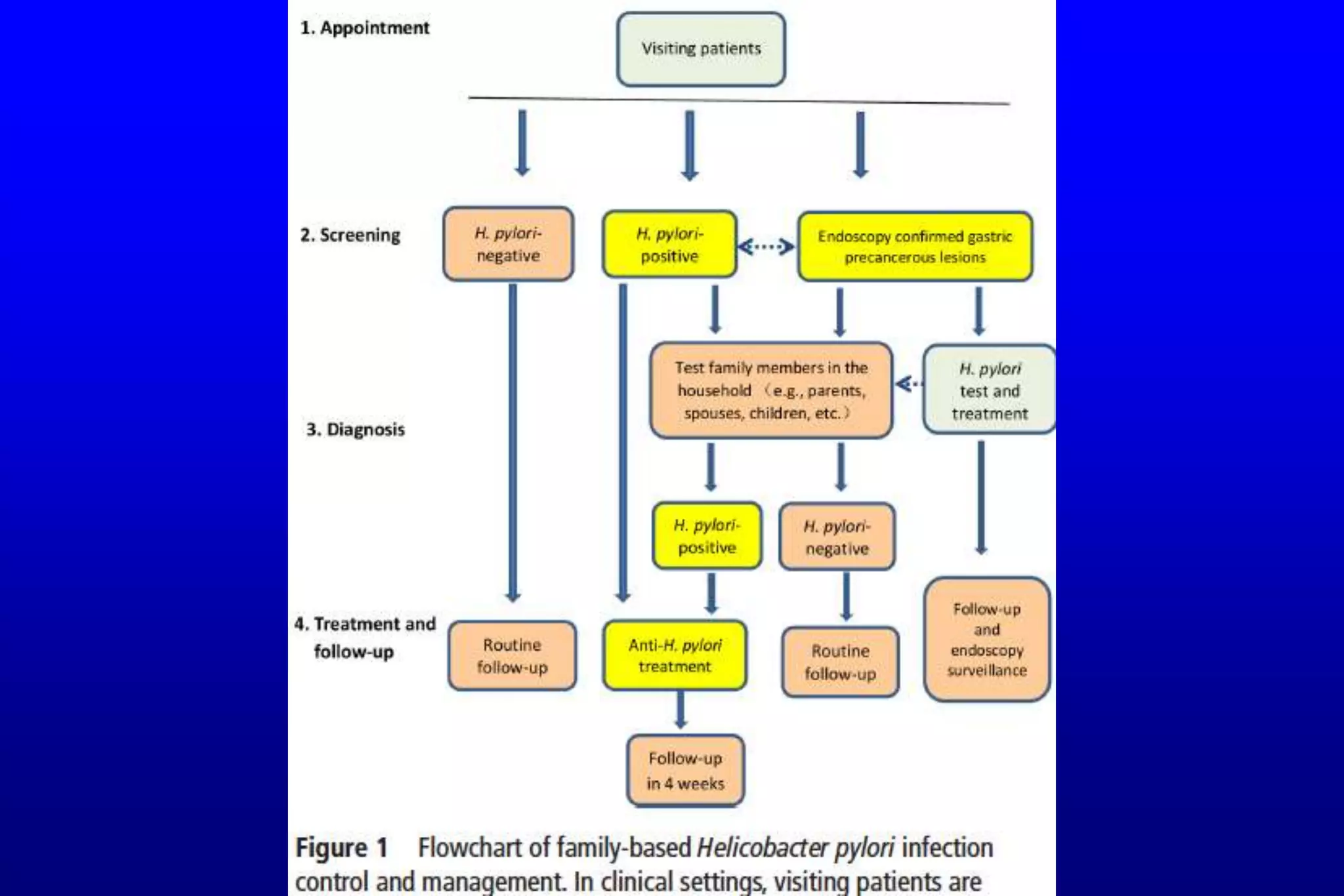
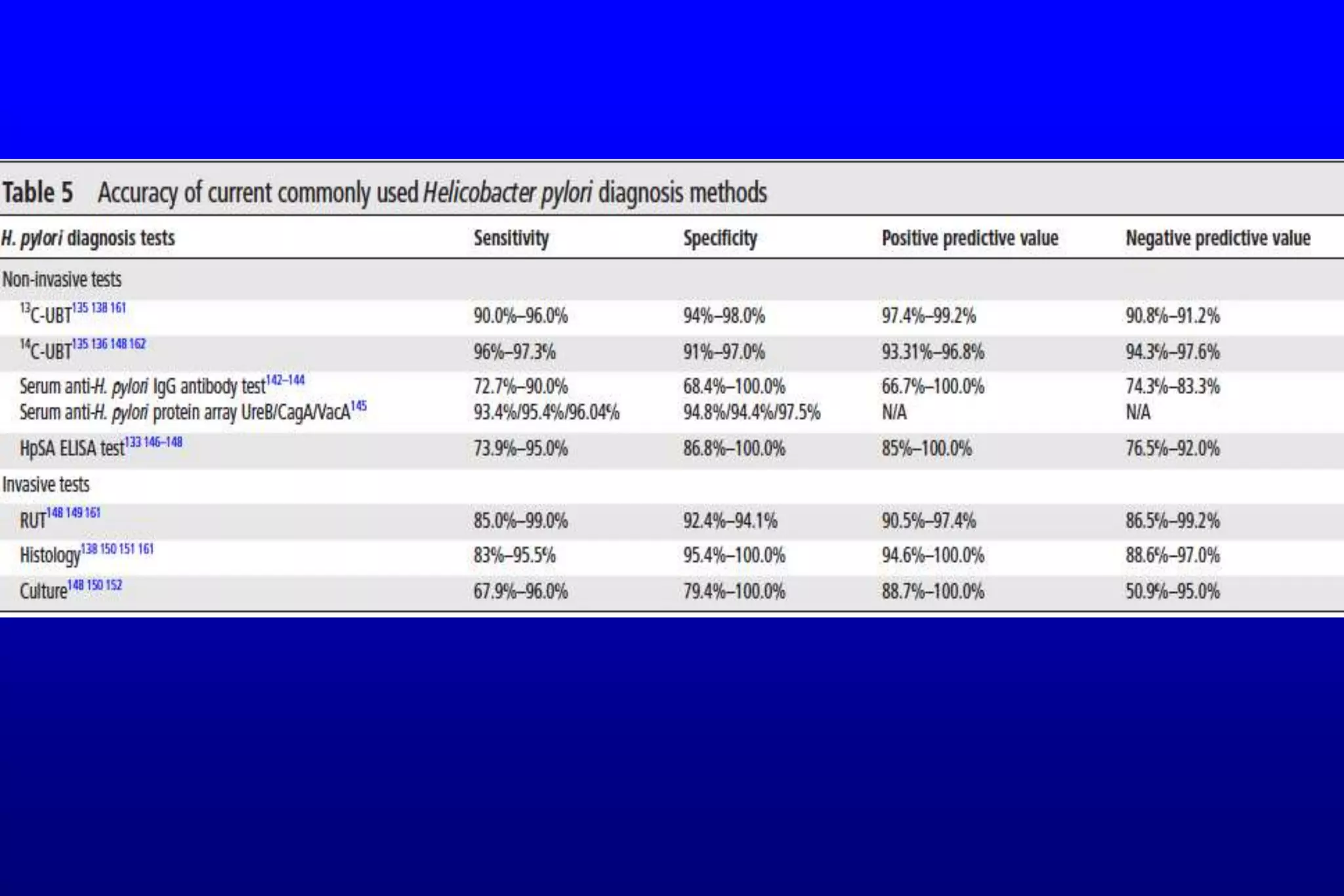
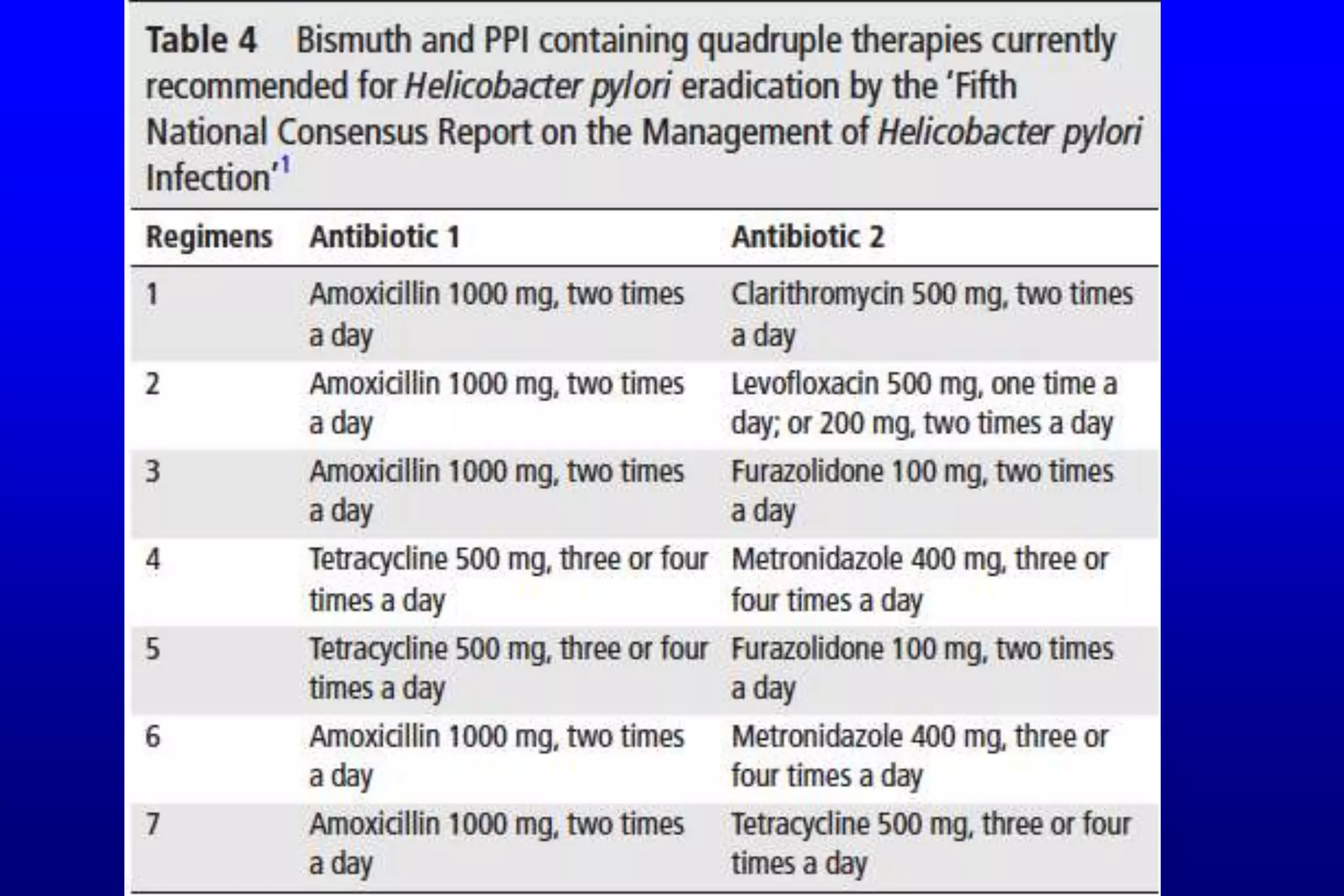

This document summarizes a journal club discussion on strategies for controlling Helicobacter pylori infection. It notes that H. pylori infects over 50% of the world's population and causes various gastrointestinal diseases. A family-based approach to screening and treating H. pylori infection could help block its transmission within families and reduce the infection rate and related diseases more effectively than individual-based testing and treatment. The discussion concludes that a family-focused prevention and eradication strategy would help stop intra-familial spread of H. pylori.









