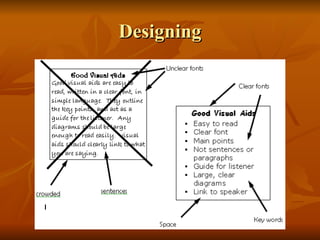
The document provides an overview of a 5-day course on presentation skills from August 27-31, 2006. The objectives are to help participants effectively prepare and deliver presentations through defining objectives and audience, organizing content clearly, designing and using visual aids, and practicing delivery skills. The course will cover preparing an outline and structure, visual aids, rehearsing, and techniques for voice control and handling questions.