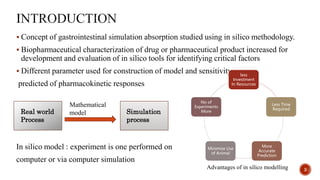
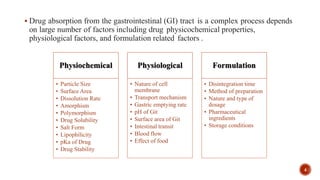
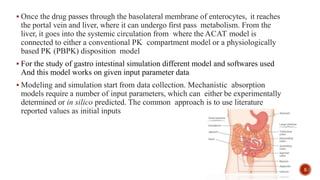
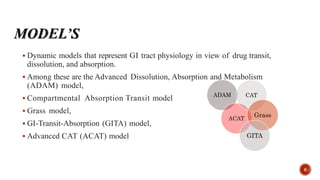
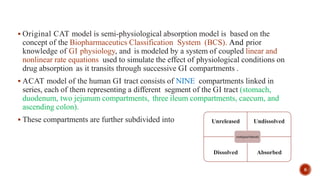
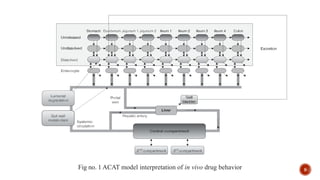
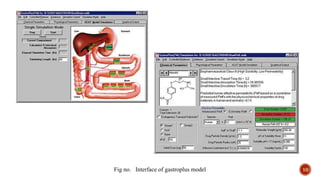
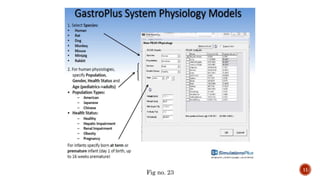
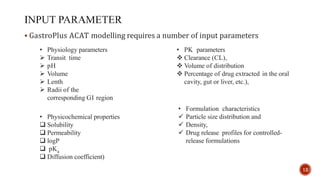
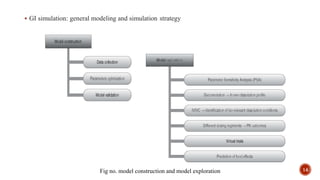
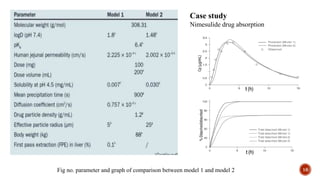
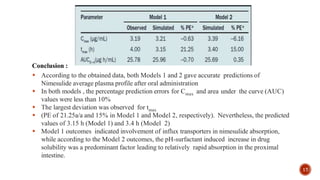
This document discusses the in silico methods used for simulating gastrointestinal absorption and biopharmaceutical characterization to enhance drug development. It details the complexity of drug absorption influenced by physicochemical properties, physiological conditions, and formulations, alongside various computational models and software available for these simulations. The findings stress the importance of accurate input data for meaningful modeling, as well as the impact of food on drug absorption rates.