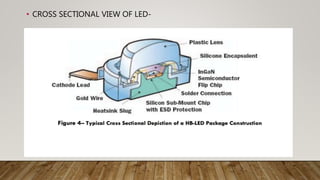
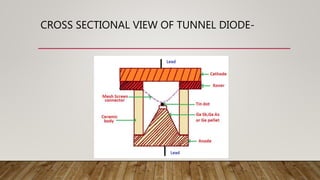
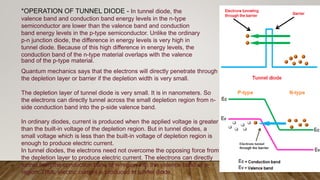
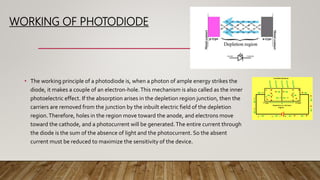
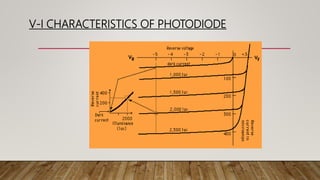
LEDs emit light when activated by electricity due to a phenomenon called electroluminescence. The color of light emitted depends on the semiconductor material used - gallium arsenide produces infrared, gallium arsenide phosphide produces red or yellow, and gallium phosphide produces red or green. Tunnel diodes use the quantum mechanical effect of tunneling to produce electricity with a small voltage, and are used for fast switching, oscillation, and amplification. Photodiodes convert light into an electrical current when photons are absorbed, with the current flowing in the reverse direction of a regular diode. They are used to detect light properties and in optical devices.