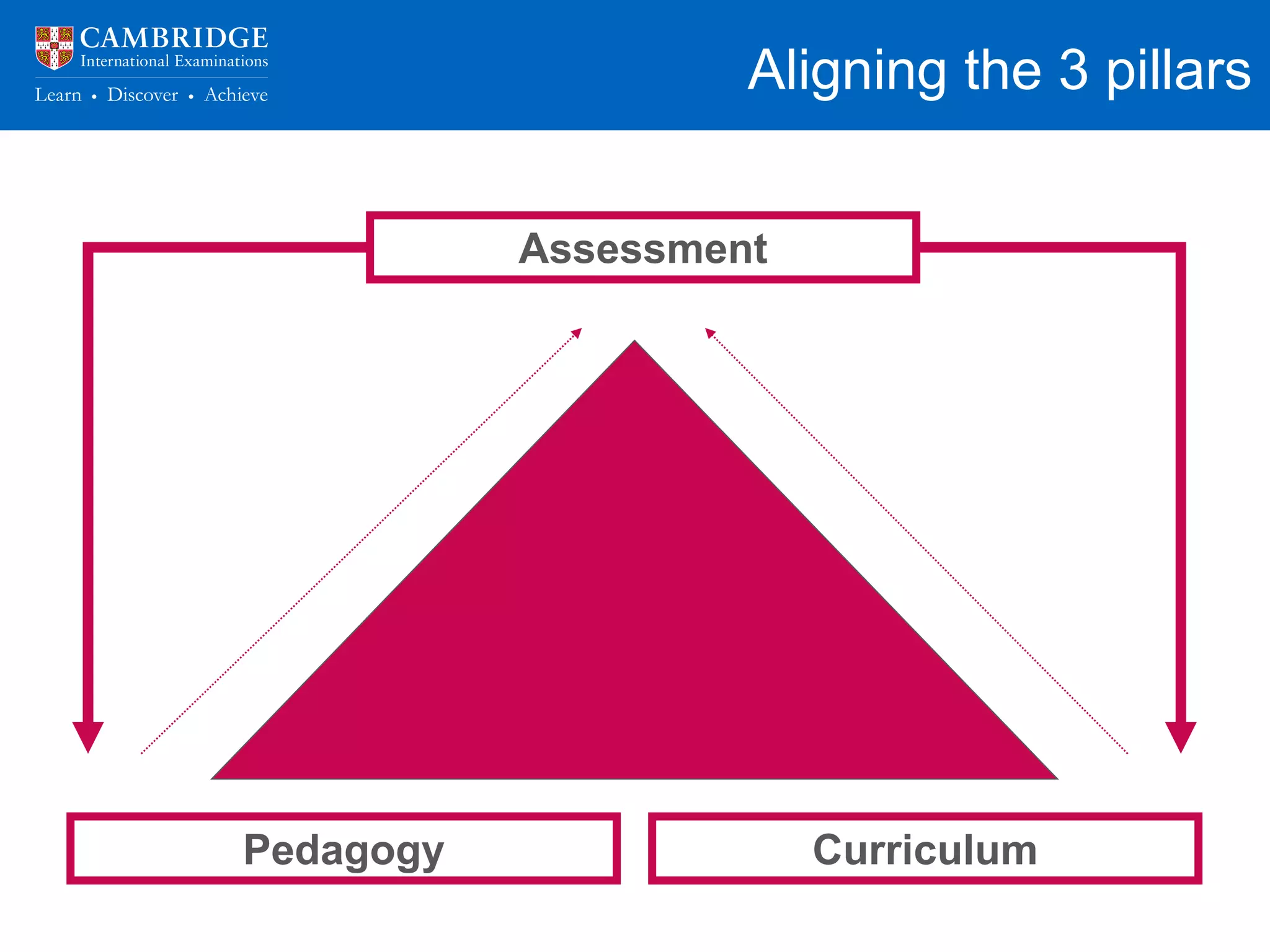
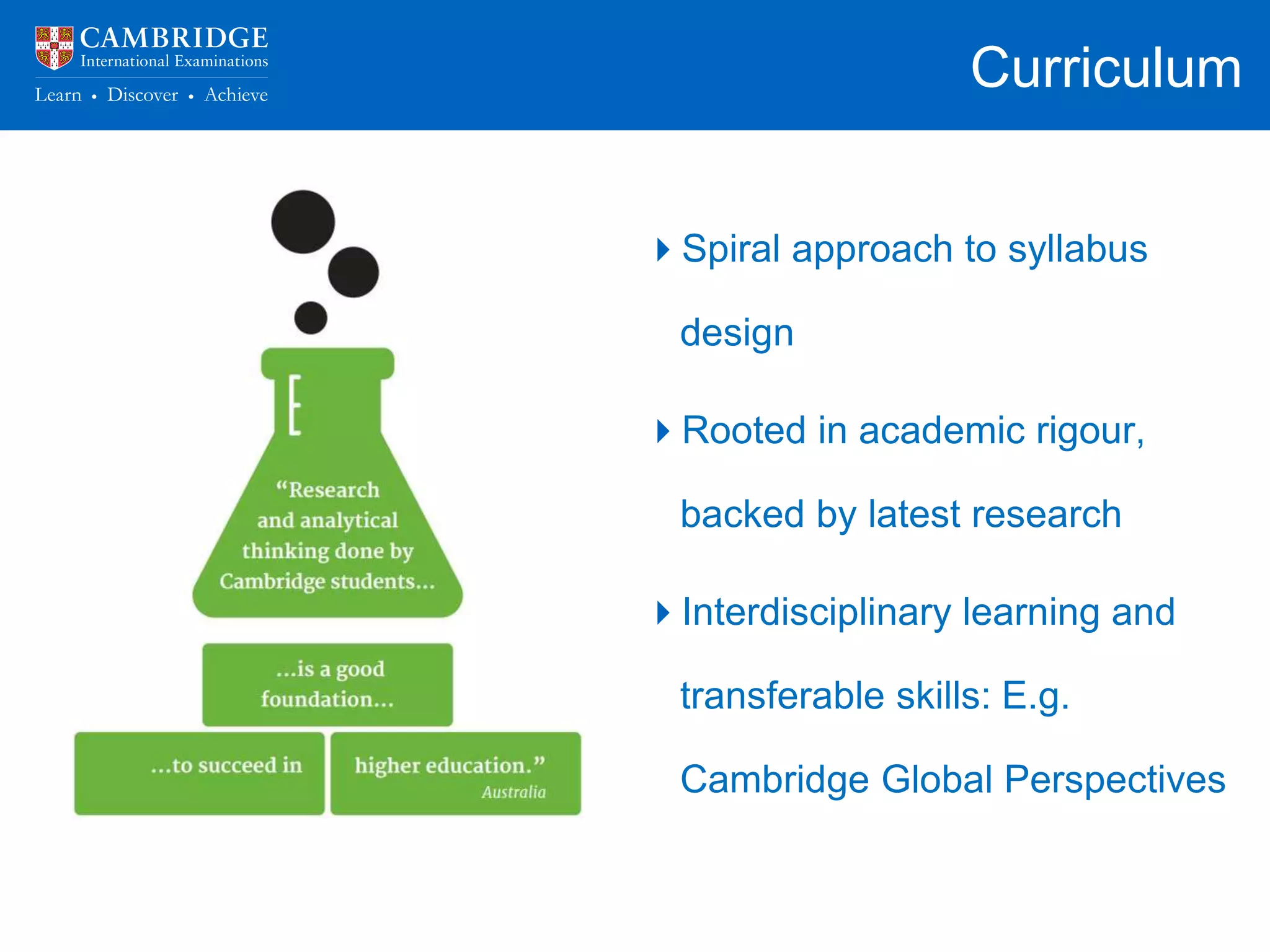
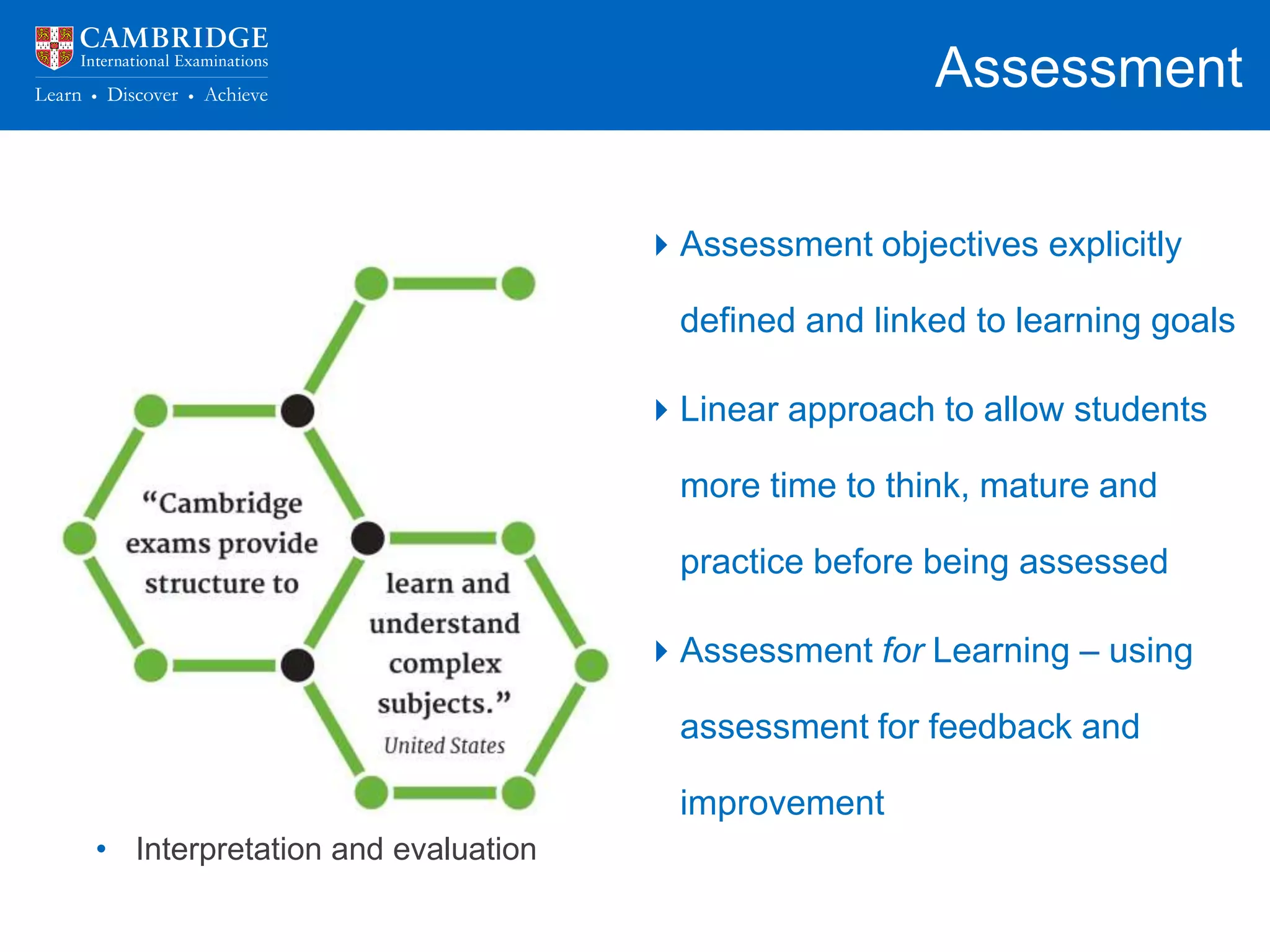
The document discusses how schools can prepare students for success in higher education. It notes that schools are responsible for not just getting students into university, but ensuring they are equipped to succeed once there. It then lists the key skills and abilities universities look for, such as content knowledge, independent learning, and higher-order thinking. The rest of the document outlines how schools can develop these skills through flexible curriculums, experiential learning, aligned pedagogy and assessment, and connections to universities and industry. It emphasizes the importance of assessment practices that encourage deep learning over memorization and the application of knowledge.