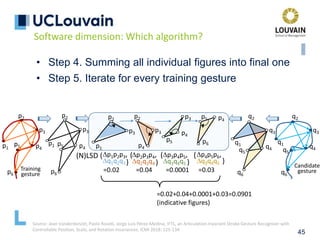
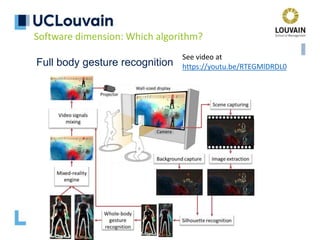
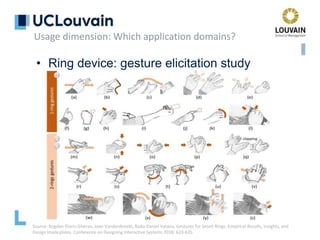
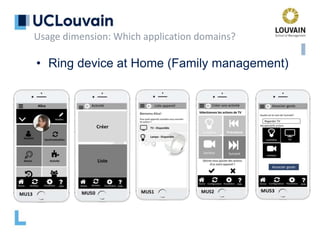
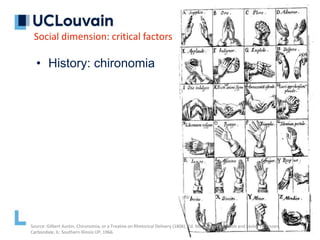
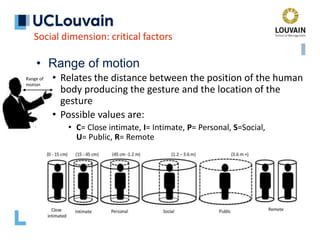
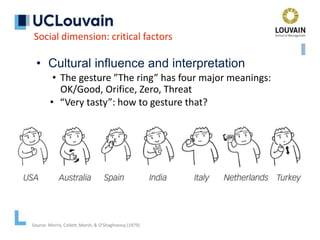
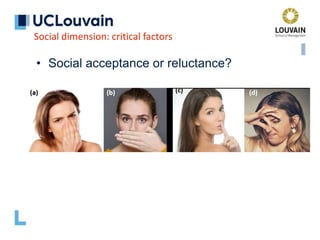
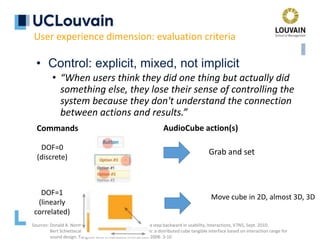
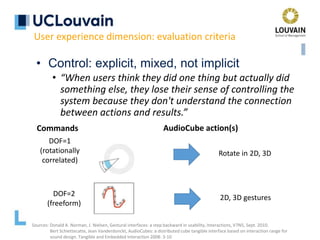
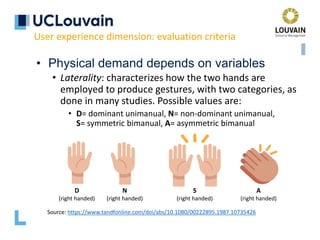
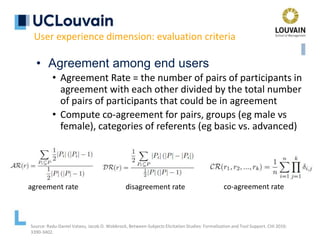
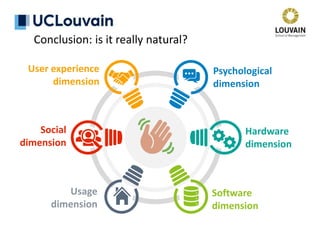
The document summarizes Jean Vanderdonckt's upcoming lecture on gestural interaction. It will cover the psychological, hardware, software, usage, social and user experience dimensions of gestural interaction. On the psychological dimension, it discusses definitions of gestures and theories of gesture types. On the hardware dimension, it outlines paradigms of contact-based and contact-less gesture interaction. On the software dimension, it provides an overview of gesture recognition algorithms such as Rubine, Siger, LVS and nearest neighbor classification.










![• McNeil’s interpretation of Kendon’s continuum (1994)
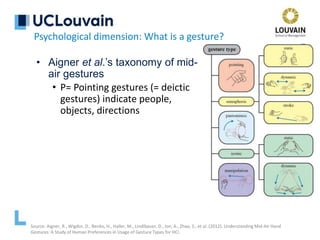
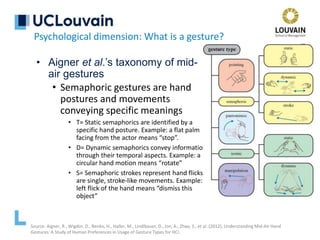
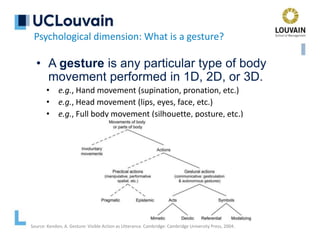
Psychological dimension: What is a gesture?
Gesticulation
Speech-framed gestures
Pantomimes
Emblems
Signs
“Adam Kendon once
distinguished gestures
of different kinds along
a continuum that I
named “Kendon's
Continuum”, in his
honor.” [McNeill, 1992]
Source: D. McNeill. Hand and Mind: What Gesture Reveals about Thought. University Chicago Press, 1992
Kendon, A., Do gestures communicate? A review. Research on Language and Social Interaction 27, 1994, 175-200
Mandatory presence
of speech
Optional presence
of speech
Mandatory presence of
speech frames
Optional absence
of speech
Mandatory absence
of speech](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanderdonckt-francquichair-20feb2020-210501183614/85/Gestural-Interaction-Is-it-Really-Natural-13-320.jpg)
![• McNeil’s interpretation of Kendon’s continuum (1994)
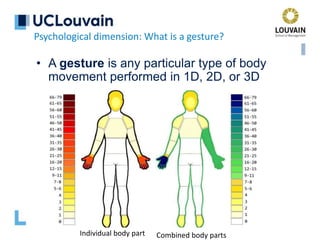
Psychological dimension: What is a gesture?
Gesticulation
Speech-framed gestures
Pantomimes
Emblems
Signs
Source: D. McNeill. Hand and Mind: What Gesture Reveals about Thought. University Chicago Press, 1992
Kendon, A., Do gestures communicate? A review. Research on Language and Social Interaction 27, 1994, 175-200
Mandatory presence
of speech
Optional presence
of speech
Mandatory presence of
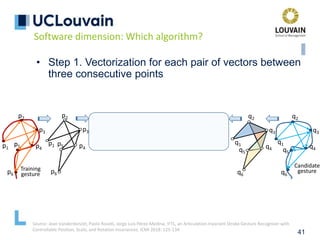
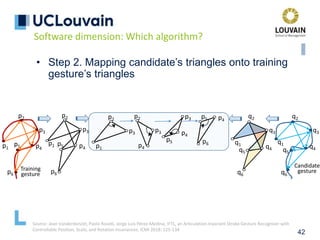
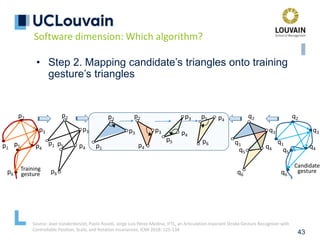
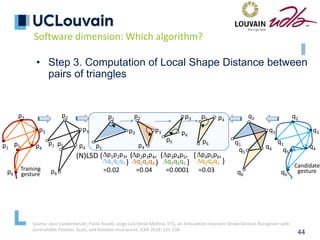
speech frames
Optional absence
of speech
Mandatory absence
of speech
“As one moves along Kendon’s
Continuum, two kinds of
reciprocal changes occur. First,
the degree to which speech is an
obligatory accompaniment of
gesture decreases from
gesticulation to signs. Second, the
degree to which a gesture shows
the properties of a language
increases.”
[McNeill, 1992]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanderdonckt-francquichair-20feb2020-210501183614/85/Gestural-Interaction-Is-it-Really-Natural-14-320.jpg)














![36
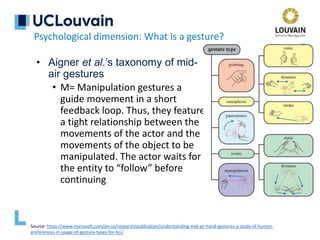
Nearest-Neighbor-Classification (NNC)
• Pre-processing steps to ensure invariance
• Re-sampling
• Points with same space between: isometricity
• Points with same timestamp between: isochronicity
• Same amount of points: isoparameterization
• Re-Scaling
• Normalisation of the bounding box into [0..1]x[0..1] square
• Rotation to reference angle
• Rotate to 0°
• Re-rotating and distance computation
• Distance computed between candidate gesture and
reference gestures (1-NN)
Software dimension: Which algorithm?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanderdonckt-francquichair-20feb2020-210501183614/85/Gestural-Interaction-Is-it-Really-Natural-36-320.jpg)
![37
Nearest-Neighbor-Classification (NNC)
• Two families of approaches
• “Between points” distance
• $-Family recognizers: $1, $3, $N, $P, $P+,
$V, $Q,…
• Variants and optimizations: ProTractor,
Protactor3D,…
• “Vector between points” distance
• PennyPincher, JackKnife,…
[Vatavu R.-D. et al, ICMI ’12]
[Taranta E.M. et al, C&G ’16]
Software dimension: Which algorithm?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanderdonckt-francquichair-20feb2020-210501183614/85/Gestural-Interaction-Is-it-Really-Natural-37-320.jpg)