This document provides information on gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), including its definition, diagnosis, management, risks, prevention, and postpartum follow up. Some key points:
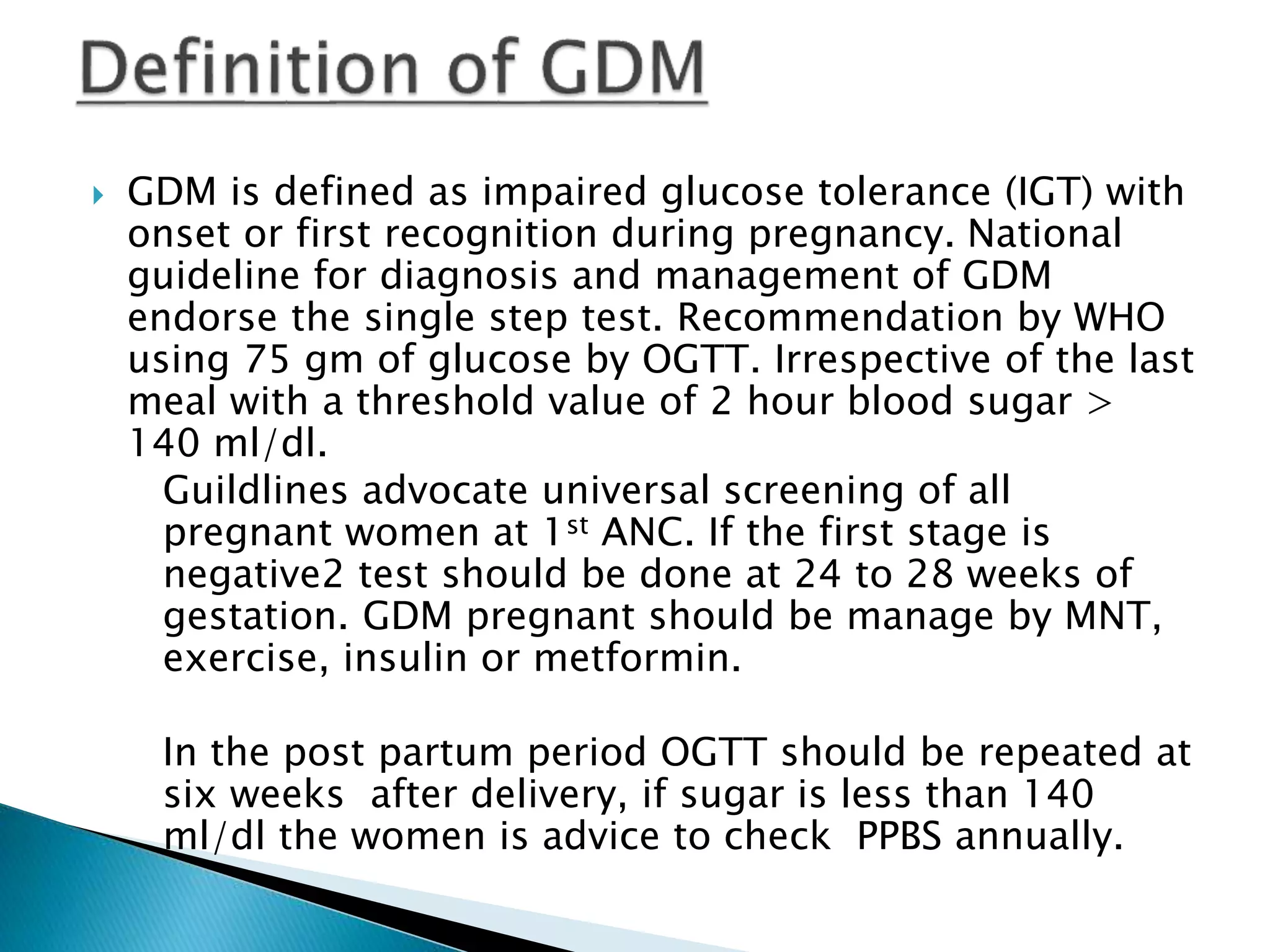
- GDM is glucose intolerance that begins during pregnancy. Screening is recommended for all pregnant women, with a diagnosis made if the 2-hour glucose tolerance test result is over 140 mg/dL.
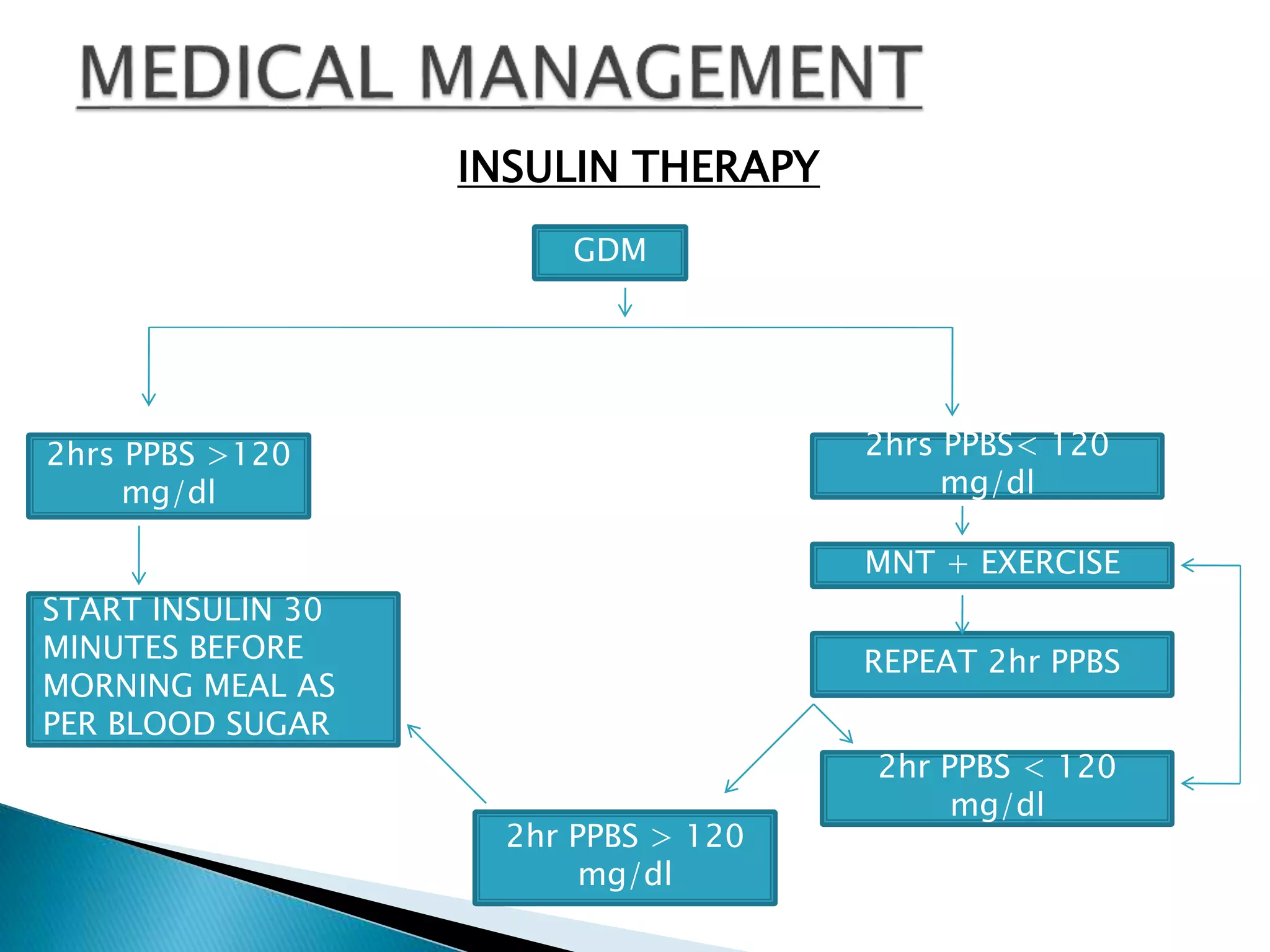
- Risks of untreated GDM include complications for both mother and baby. Lifestyle changes like diet and exercise as well as possible medication can help control blood sugar levels and minimize risks.
- After delivery, women should receive follow up testing to determine if prediabetes or diabetes has developed. Ongoing monitoring