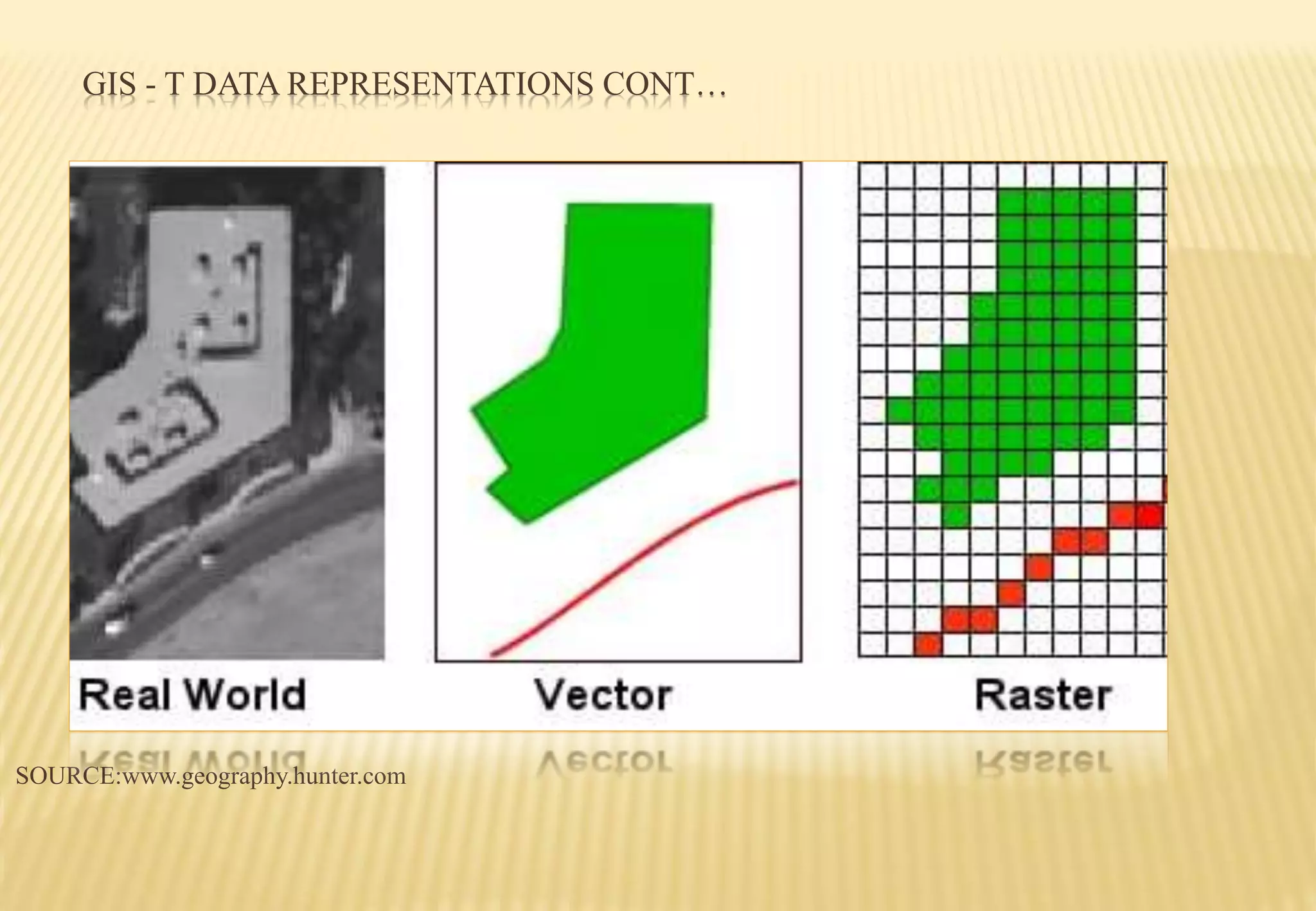
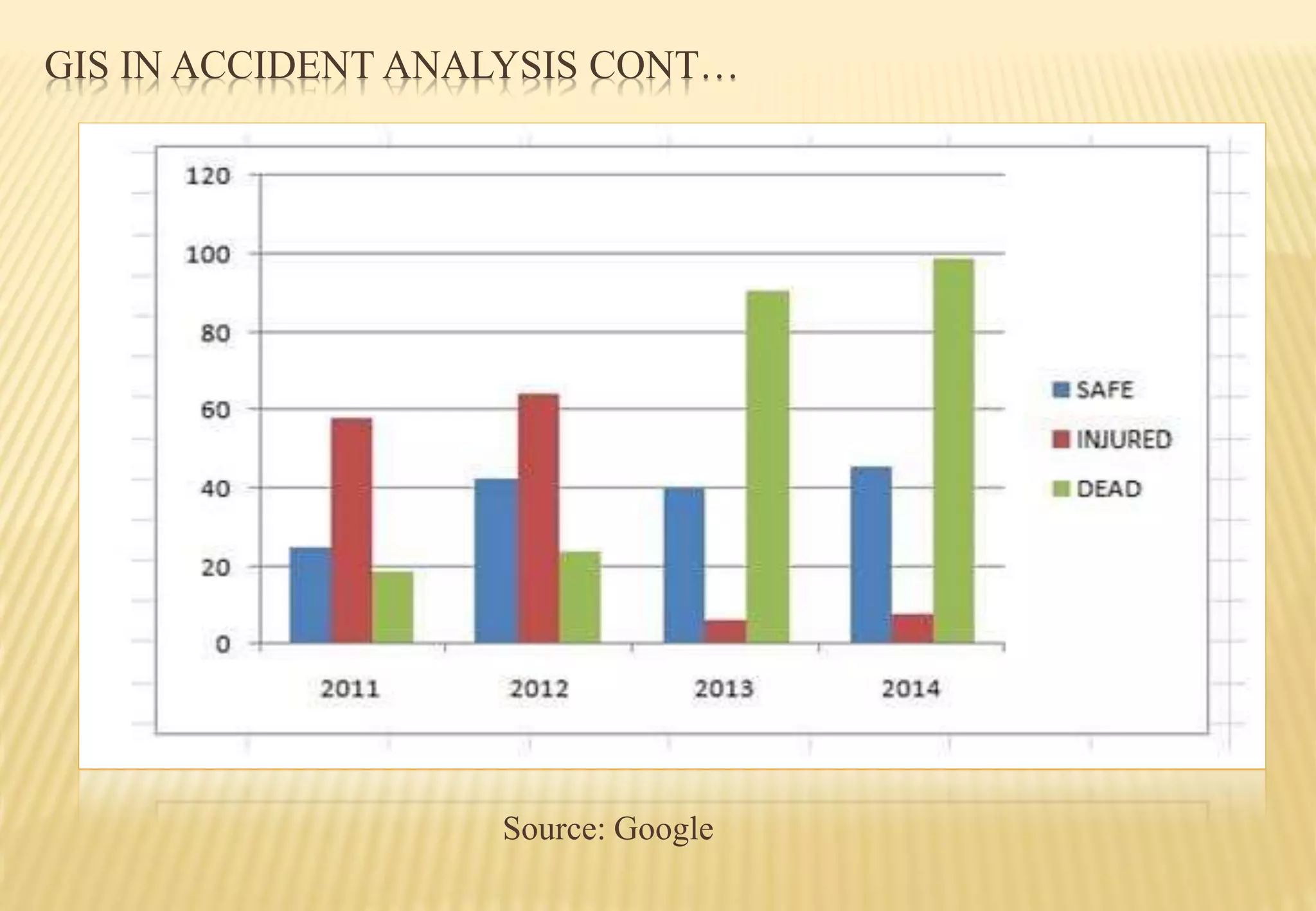
This document discusses the use of geographical information systems (GIS) in transportation planning. It begins by introducing GIS and how it can help with transportation systems. GIS is then categorized into three areas: data representation, analysis and modeling, and applications. Examples of GIS applications in transportation include highway management, accident analysis, route planning, and traffic modeling. The document also outlines some challenges of GIS in transportation and concludes that GIS is a key tool for analysis and decision making in public and private transportation planning.