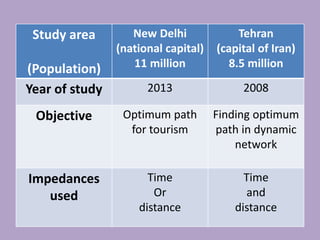
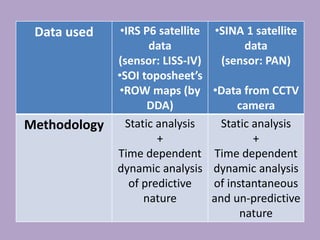
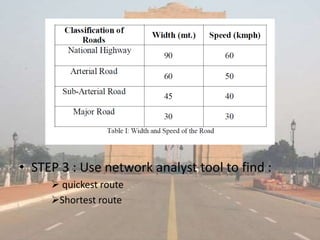
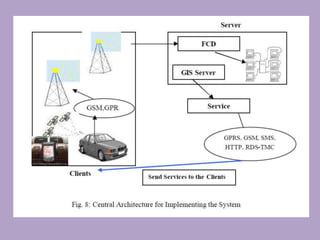
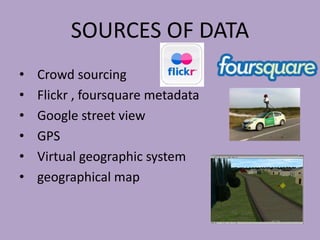
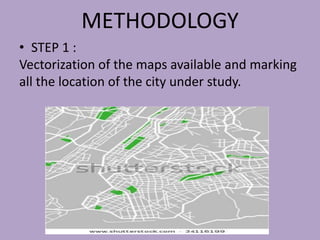
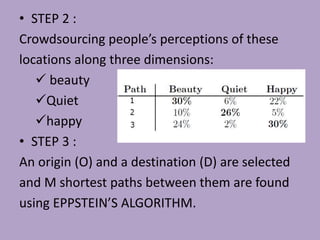
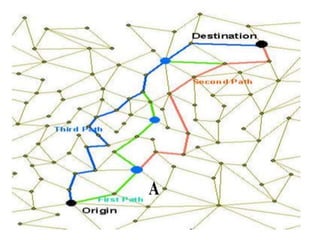
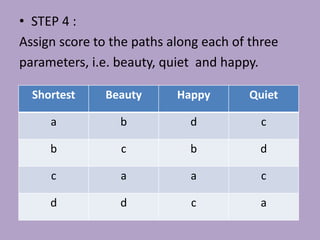
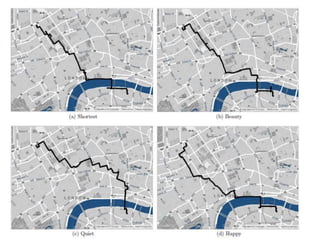
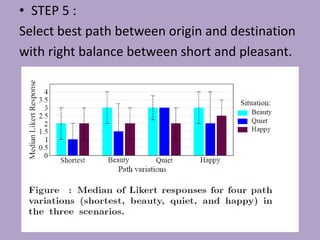
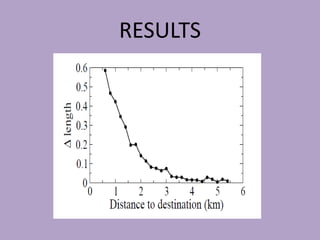
This document discusses network analysis and finding optimal paths. It presents two case studies - one analyzing optimum tourism paths in New Delhi using time and distance as impedances, and one finding optimal paths in Tehran's dynamic road network using real-time traffic data. Both used GIS software and network analysis tools. The document also proposes using crowd-sourced data on locations' beauty, quietness and happiness to recommend routes that balance shortest distance with pleasantness.









![REFERENCES
• Research paper “The shortest path to happiness : Recommending
Beautiful, Quiet and Happy routes in the city” by Yahoo labs [Barcelona,
(Spain)] and University of Torino (Italy).
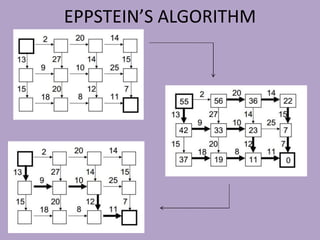
• http://www.isi.edu/natural-language/people/epp-cs562.pdf (for
eppstein’s algorithm).
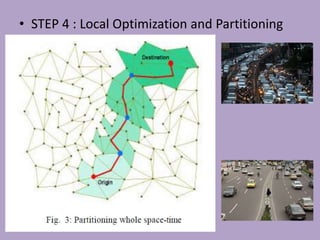
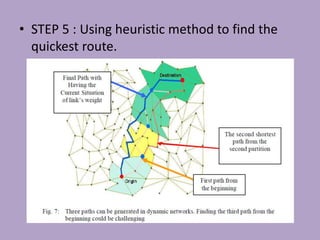
• IDOSI published “New Method for Finding Optimal Path in Dynamic
Networks” (world applied sciences journal 3 (supple 1) 2008)
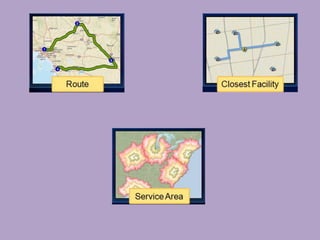
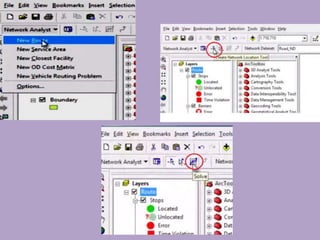
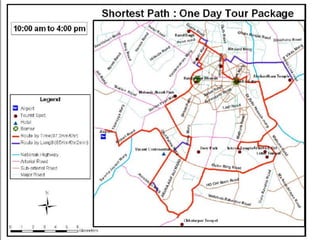
• “identification of optimum path for tourist places using GIS based network
analysis” (IJARSGG (2013) Vol. 1, No. 2, 34-38)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/network-analysis-for-shortest-optimum-path-160216081950/85/Network-analysis-for-shortest-optimum-path-28-320.jpg)
