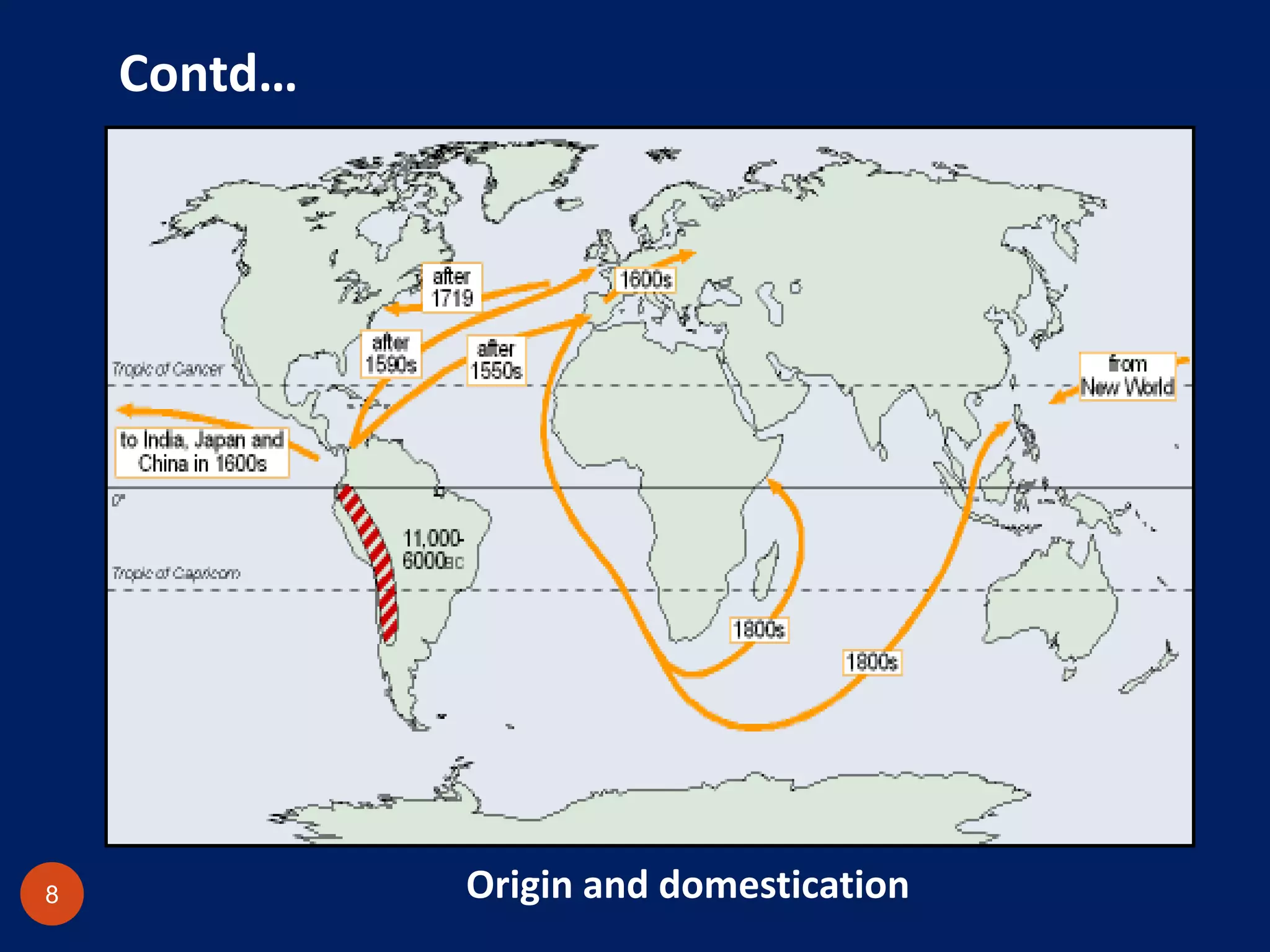
Potato is an important food crop that originated in South America. There are over 2000 species in the genus Solanum, with approximately 200 being tuber-bearing species like the cultivated potato (Solanum tuberosum). Wild potato species are a valuable genetic resource for breeding resistance to diseases and pests into cultivated varieties. Important wild species used in potato breeding include S. demissum, S. bulbocastanum, and S. stenotomum. Major international gene banks like the CIP in Peru conserve potato germplasm and provide access for breeding programs worldwide.