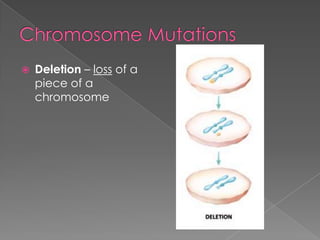
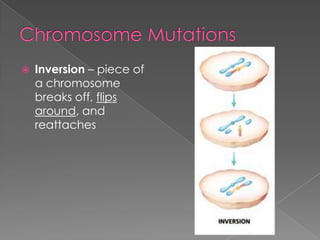
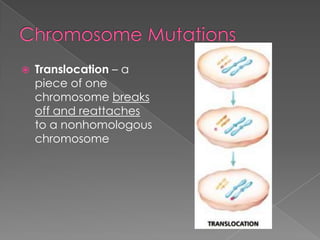
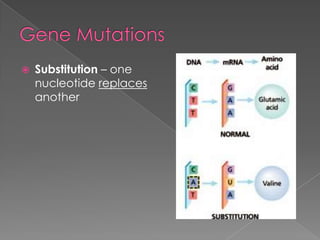
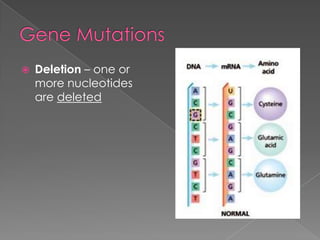
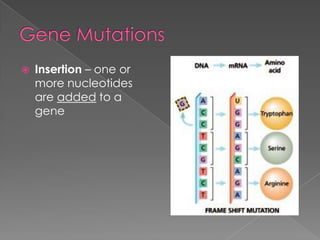
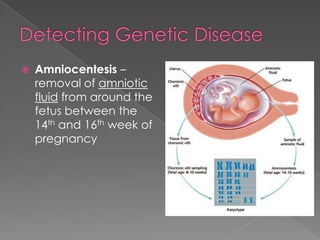
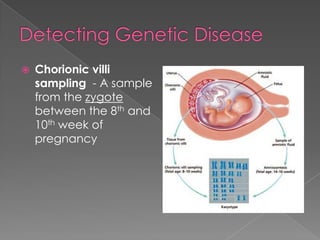
A mutation is a change in a gene that can be inherited if it occurs in a sex cell. Mutations can have positive, negative, or neutral effects. There are several types of mutations, including deletions, inversions, translocations, and point mutations such as substitutions, deletions, and insertions. Genetic screening through tests such as amniocentesis and chorionic villi sampling can detect over 200 genetic disorders in fetuses. Genetic counseling informs individuals about genetic disorders that may affect their offspring.