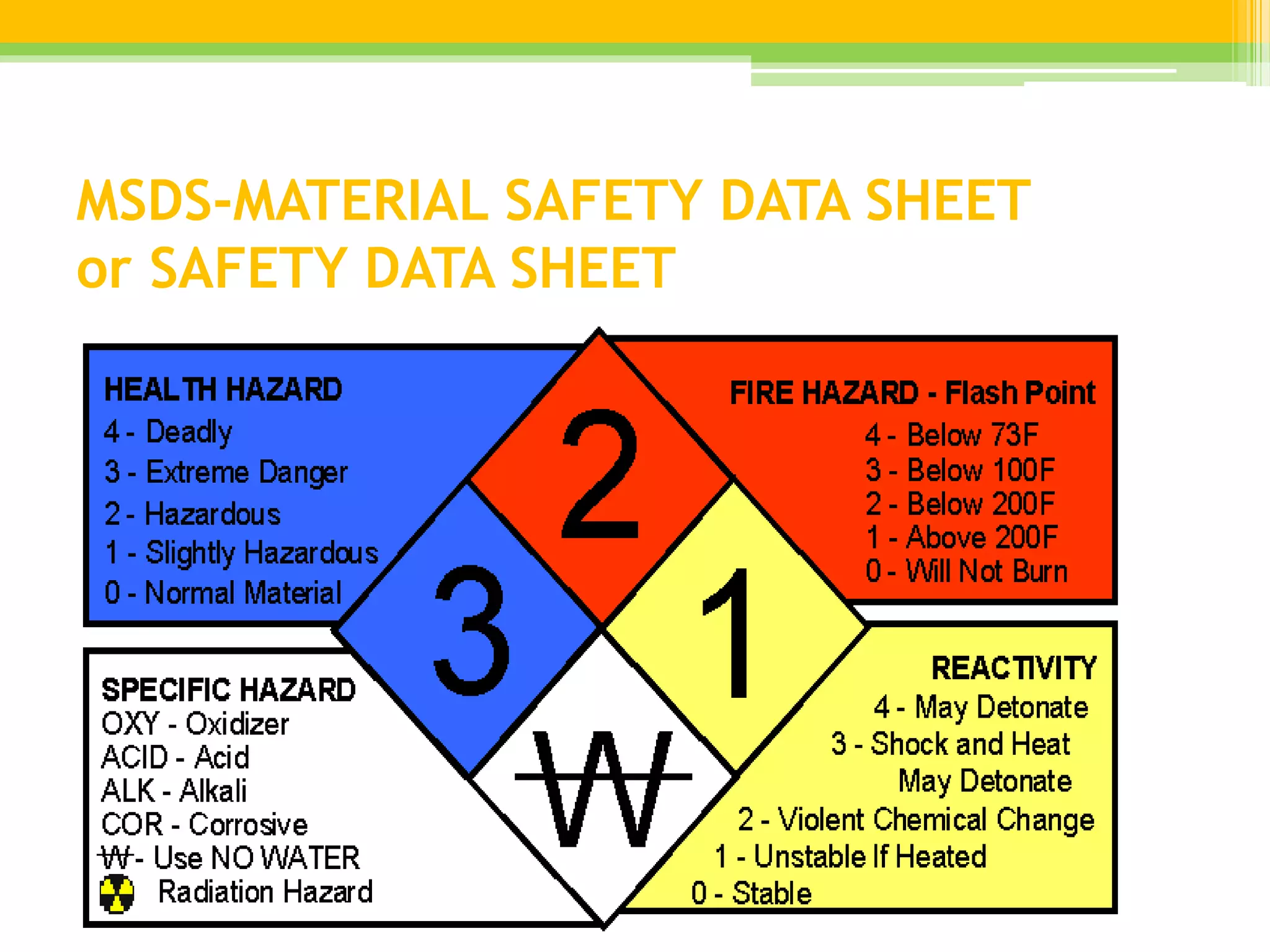
A Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) provides vital information on health risks and safe handling of chemicals. It outlines essential details including chemical identity, health effects, exposure limits, and necessary first aid measures. Manufacturers are required to create and maintain these sheets, ensuring accessibility for employees to promote a safe working environment.