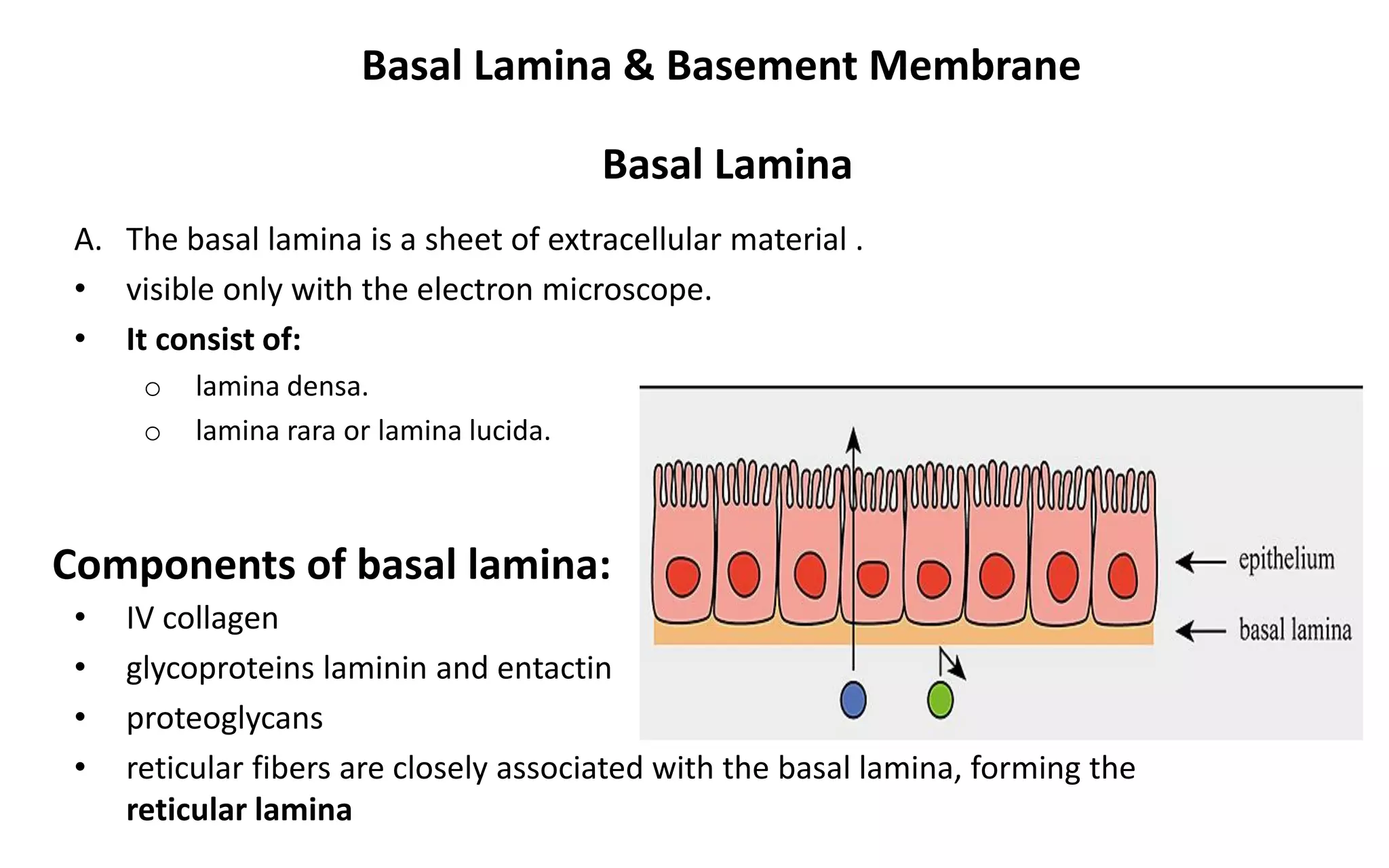
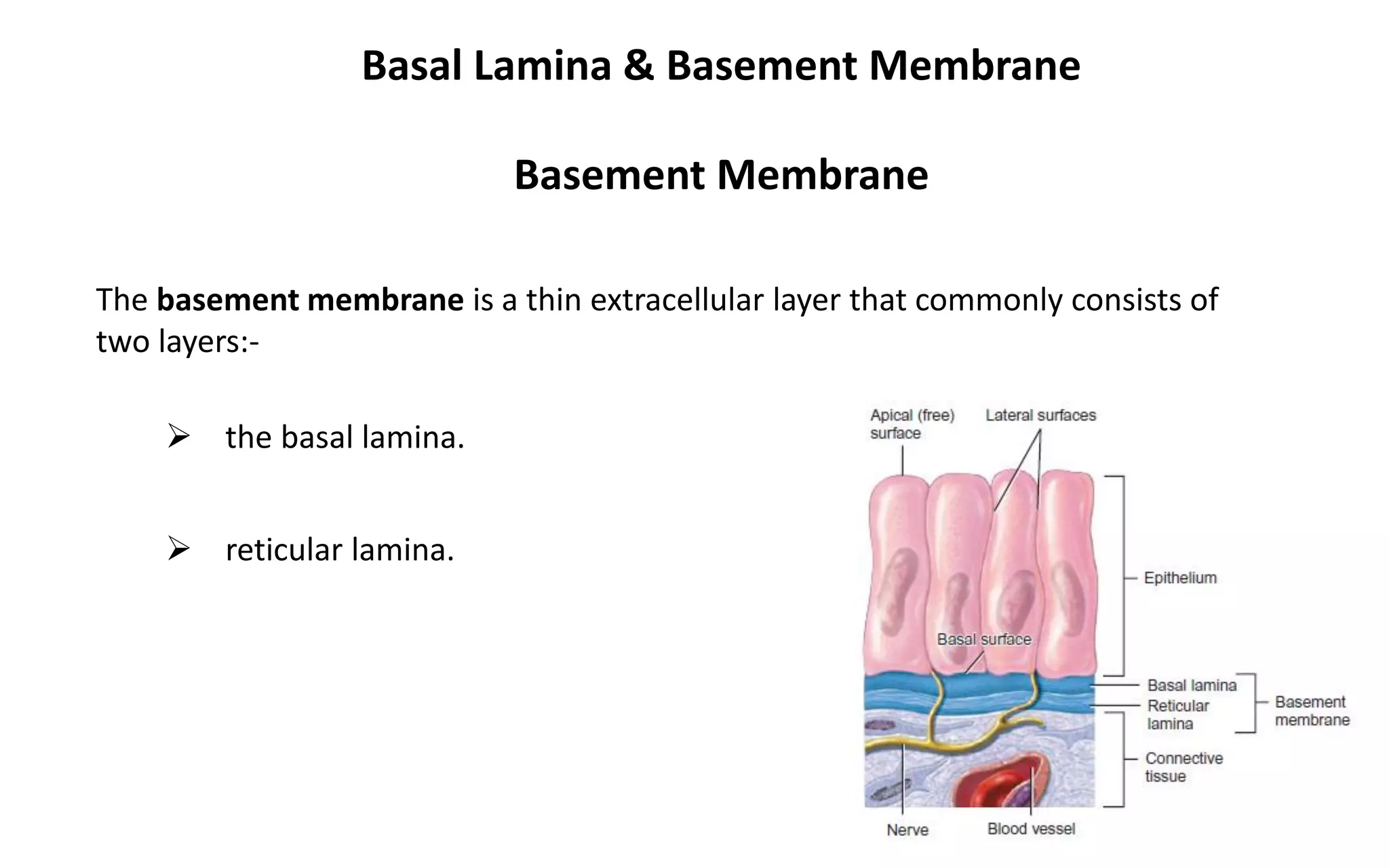
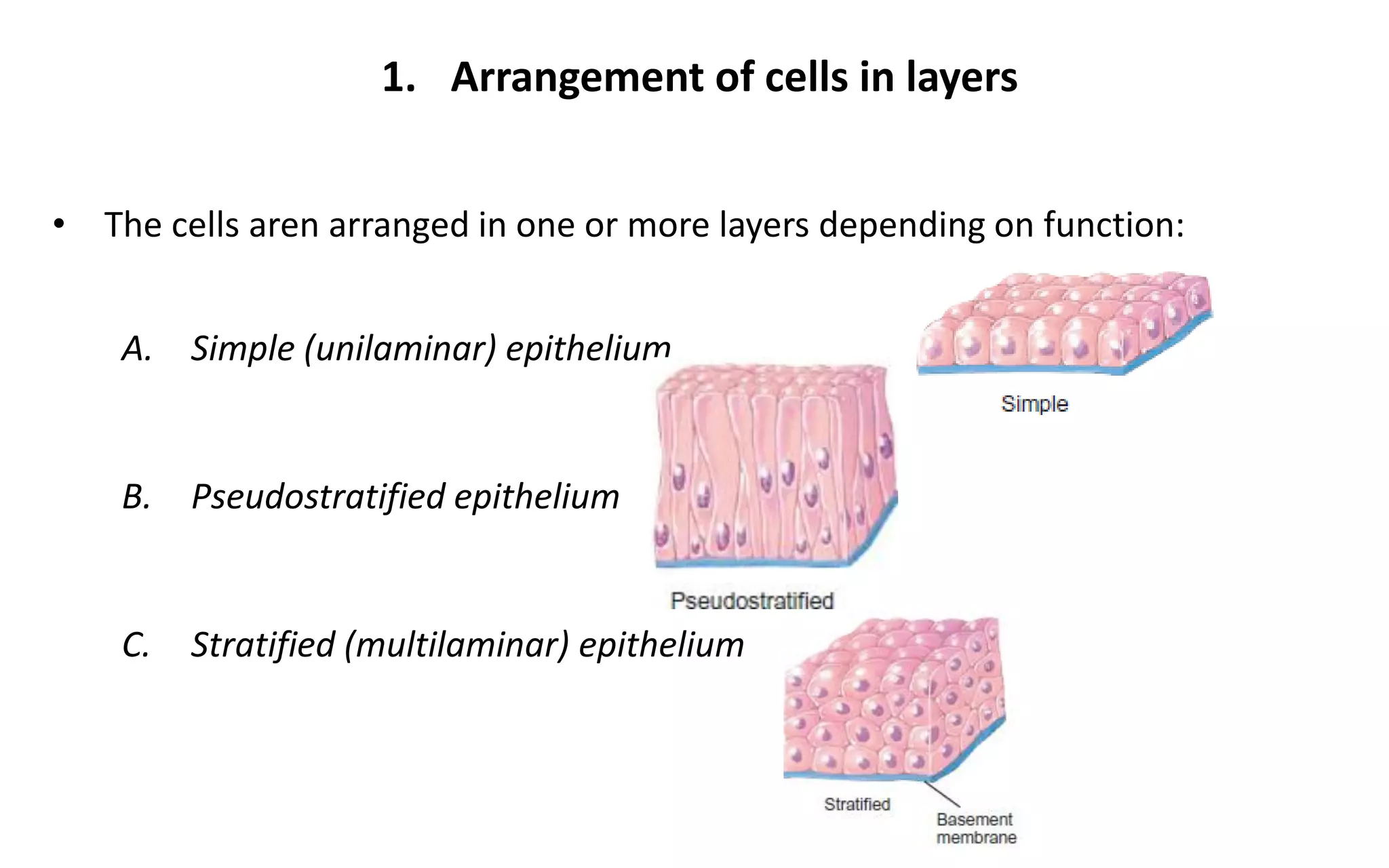
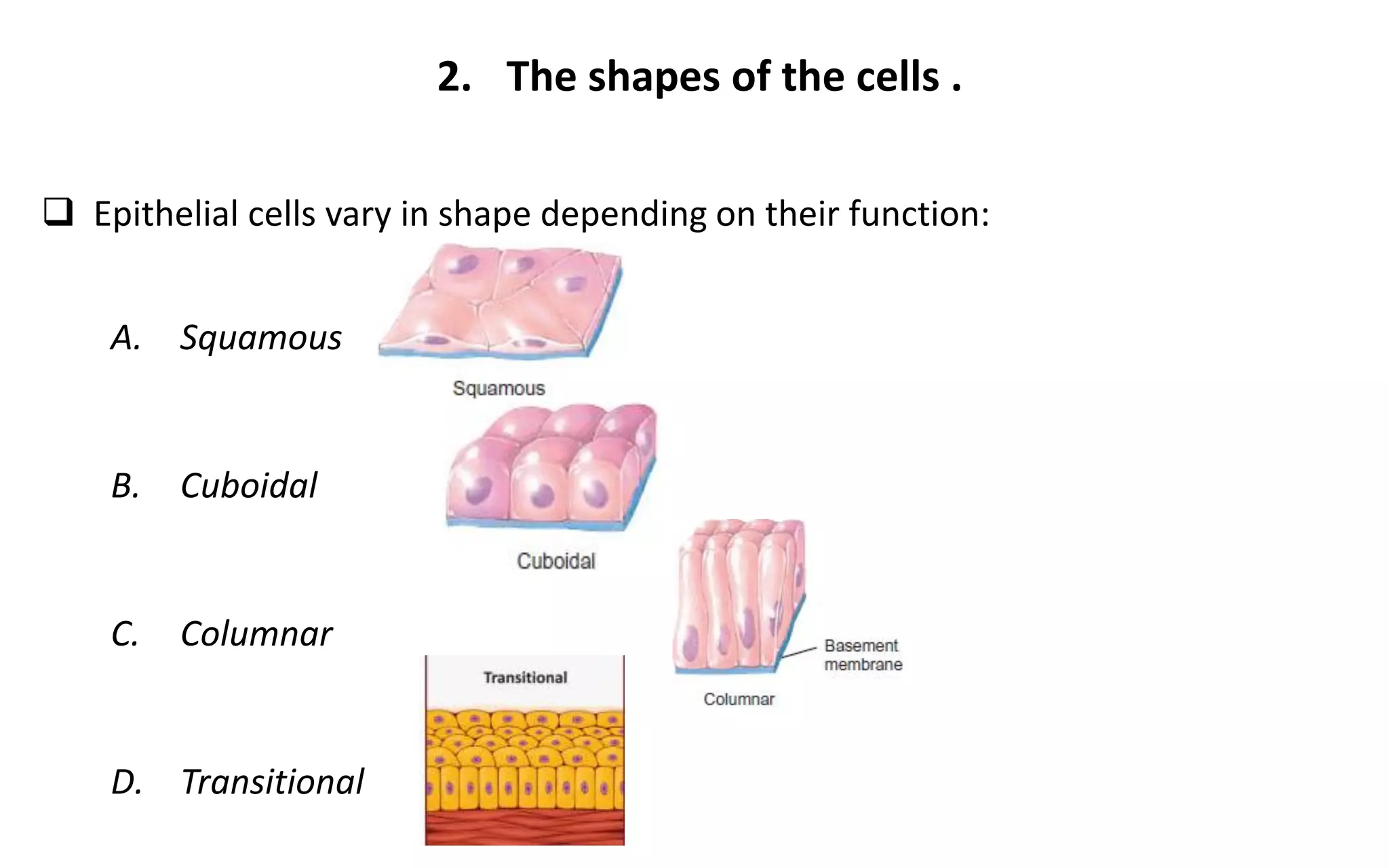
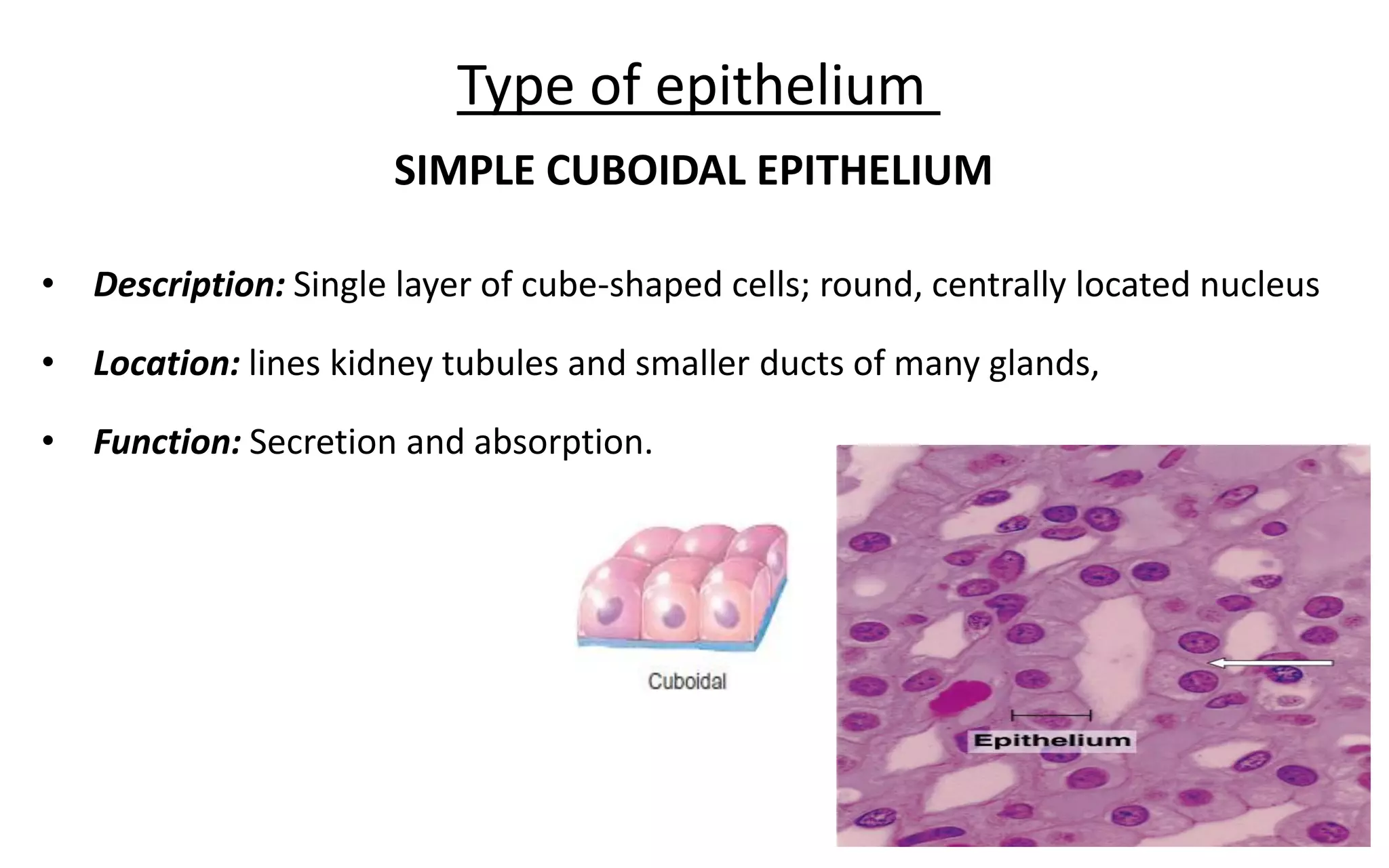
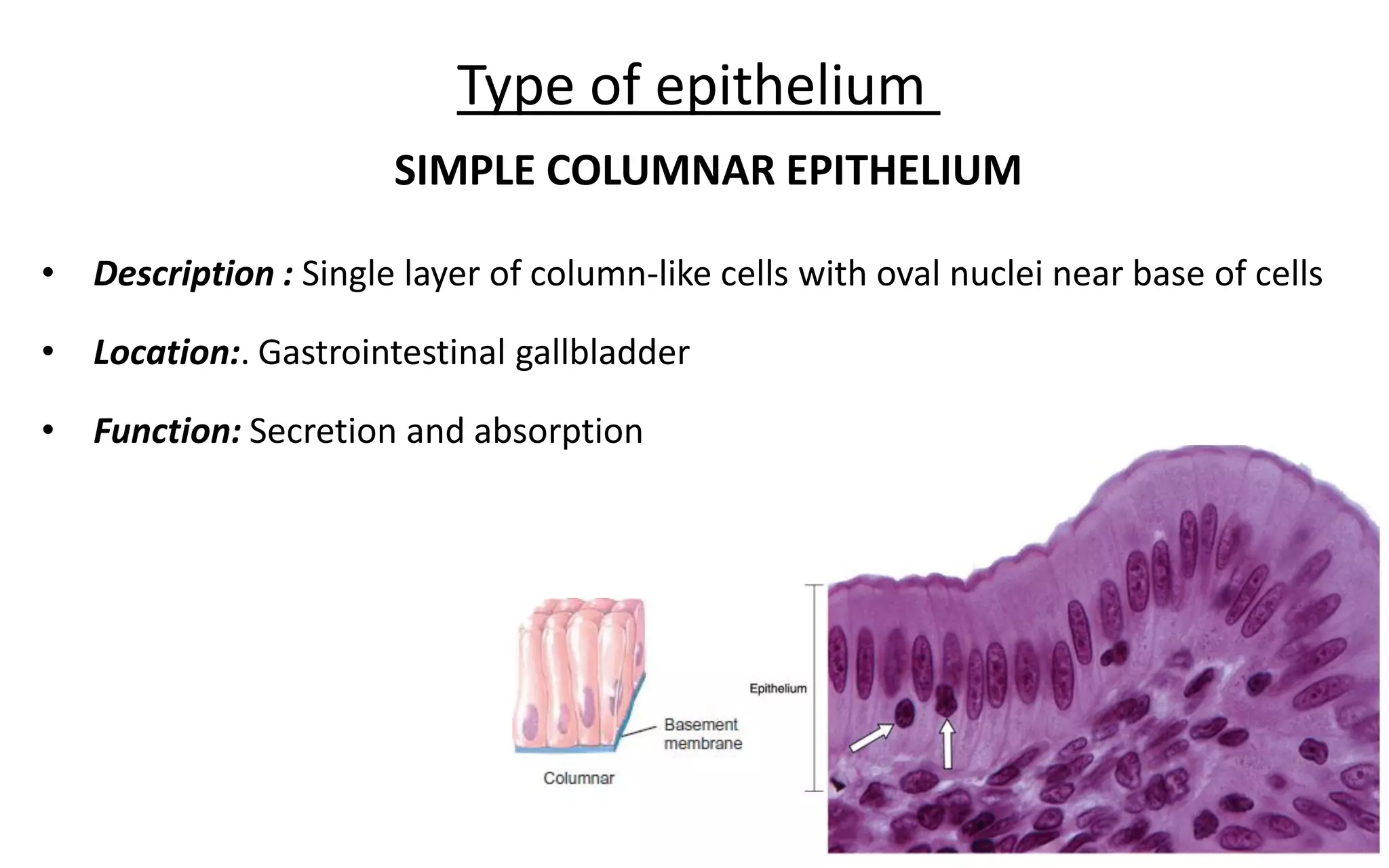
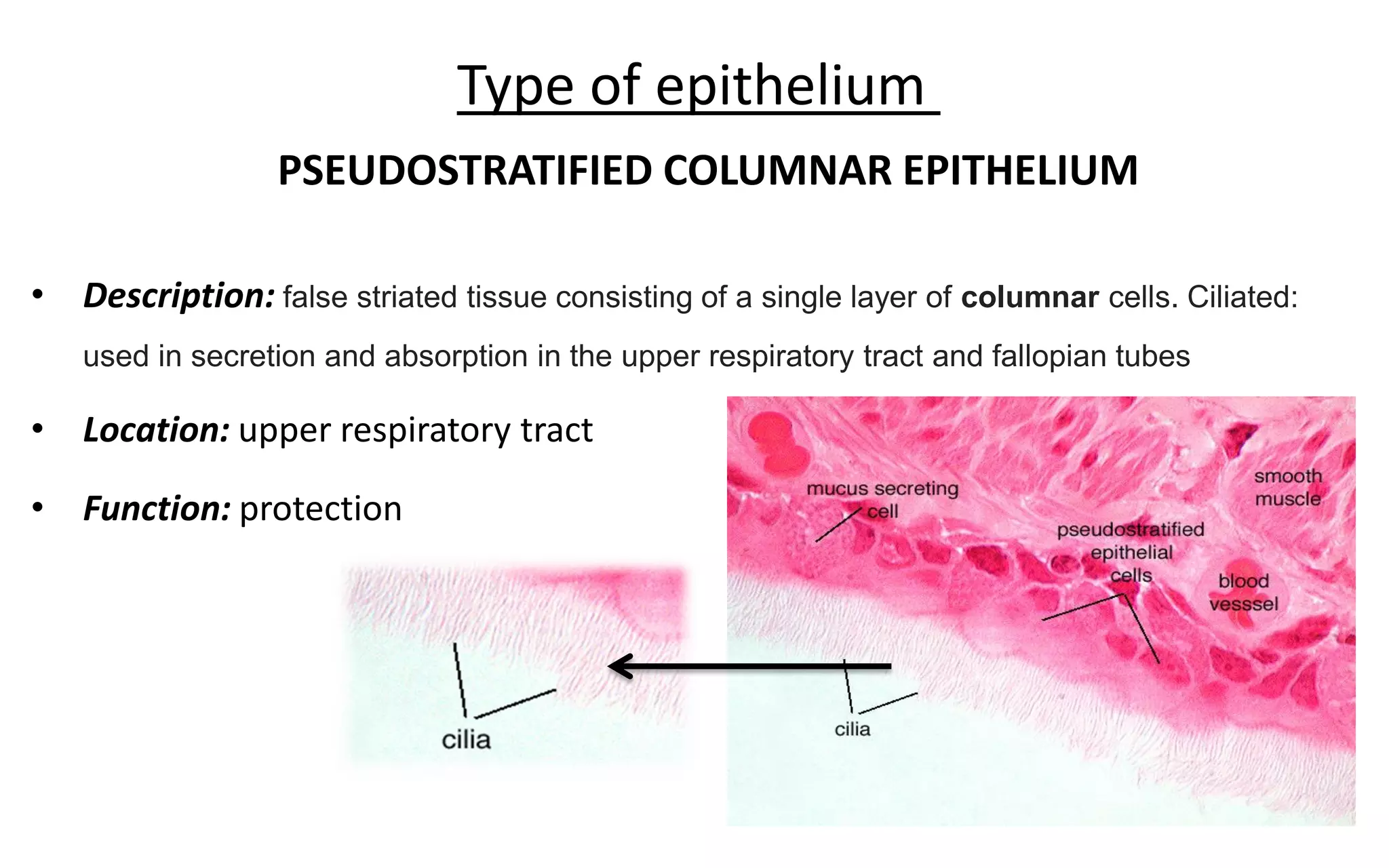
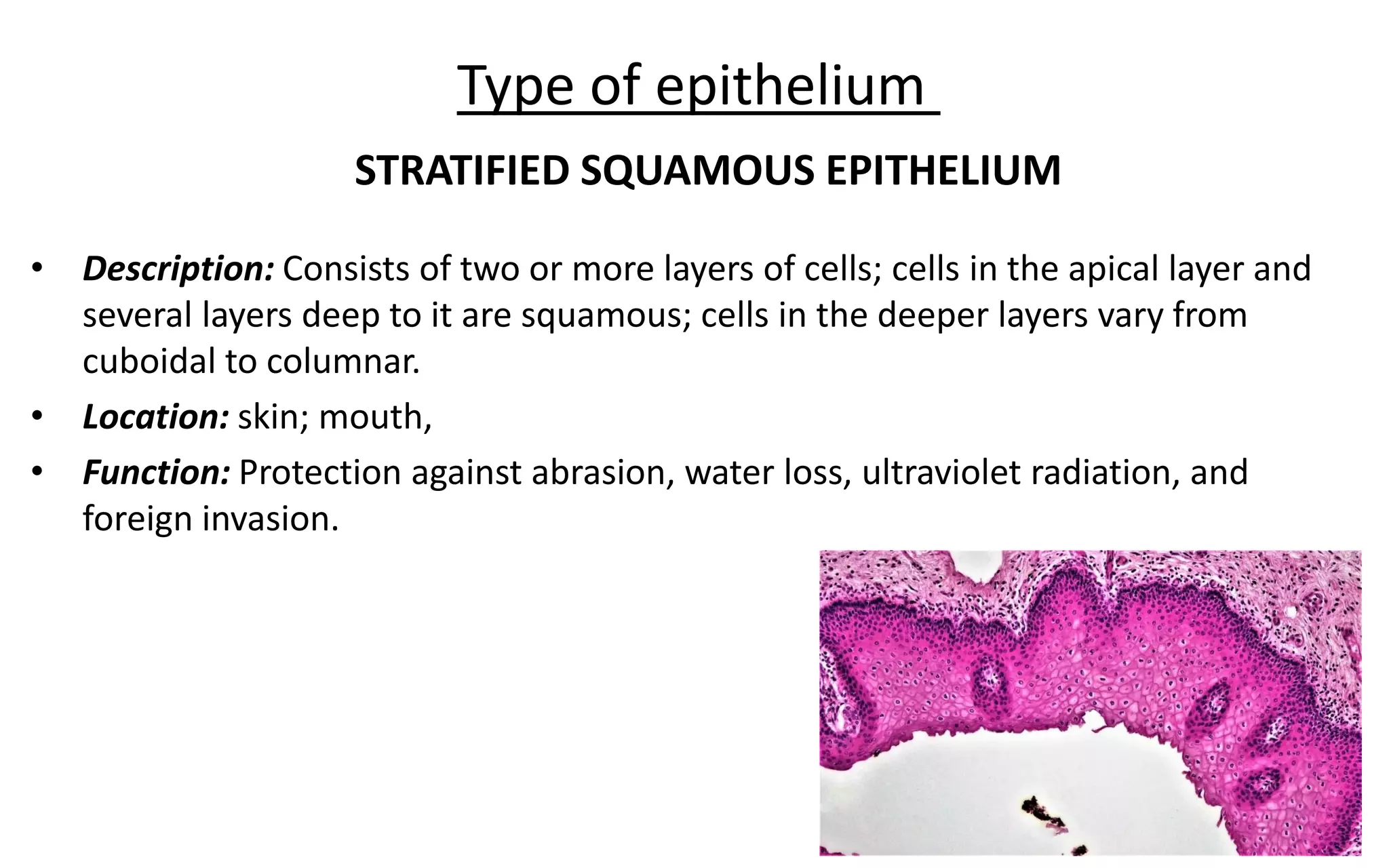
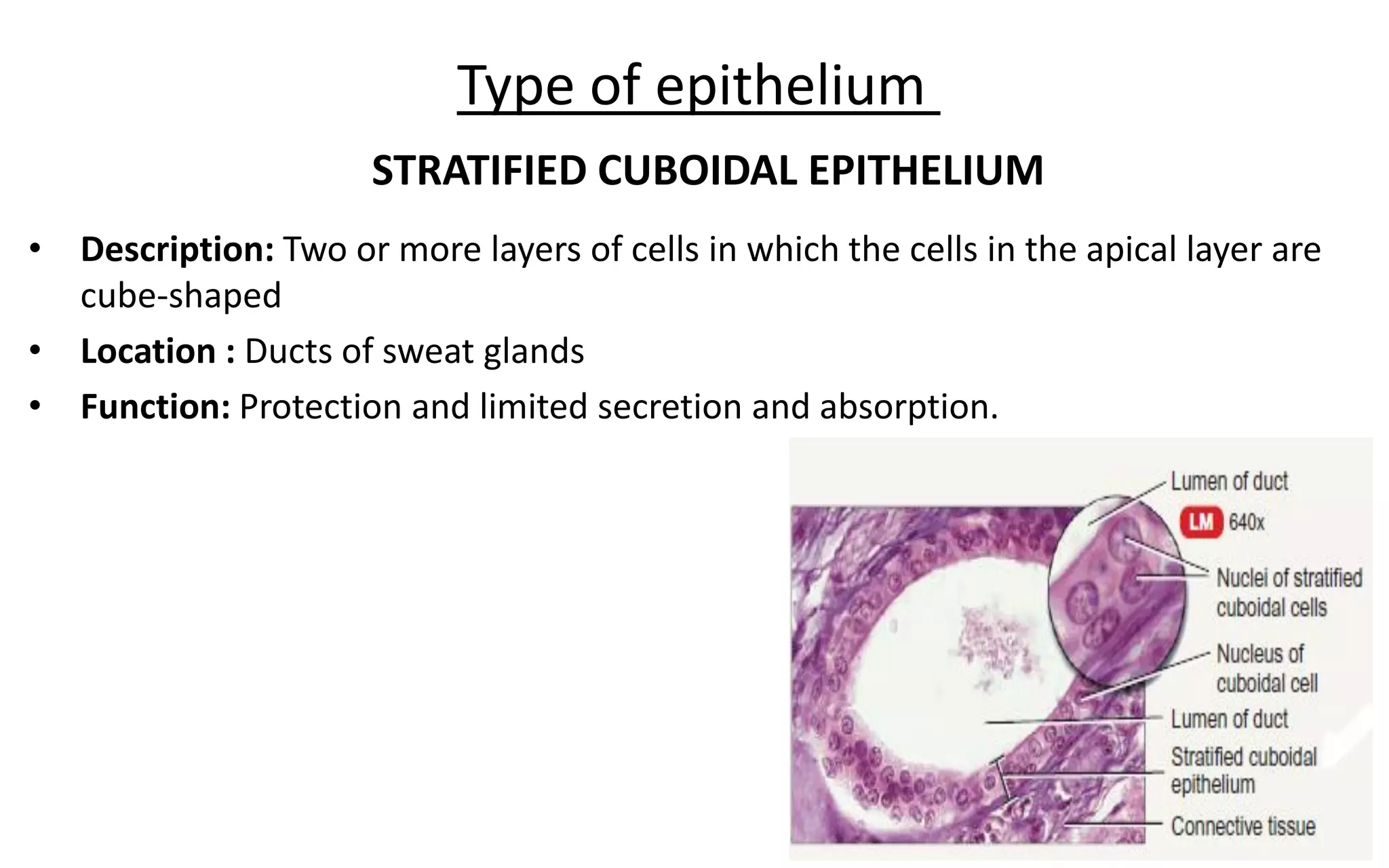
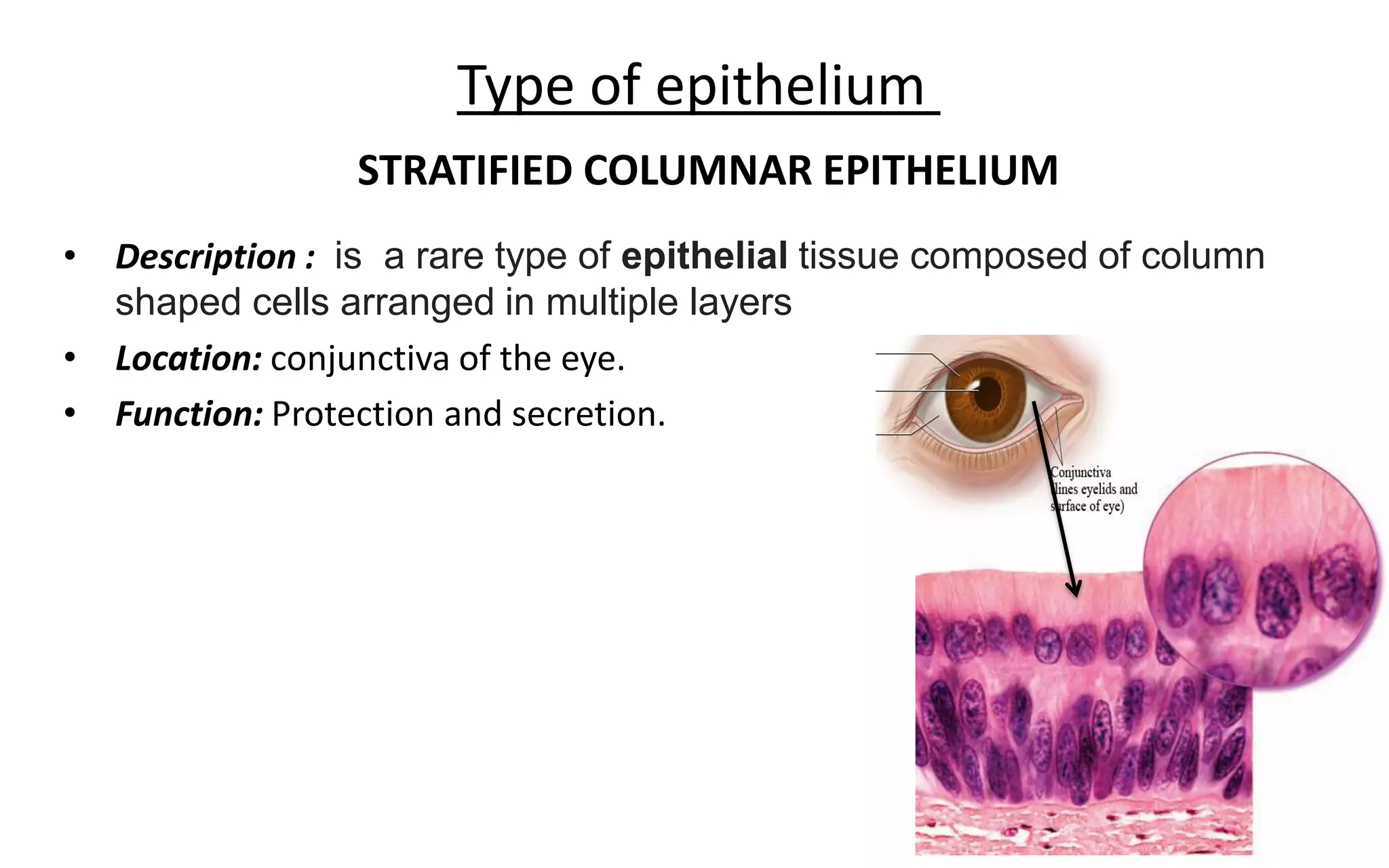
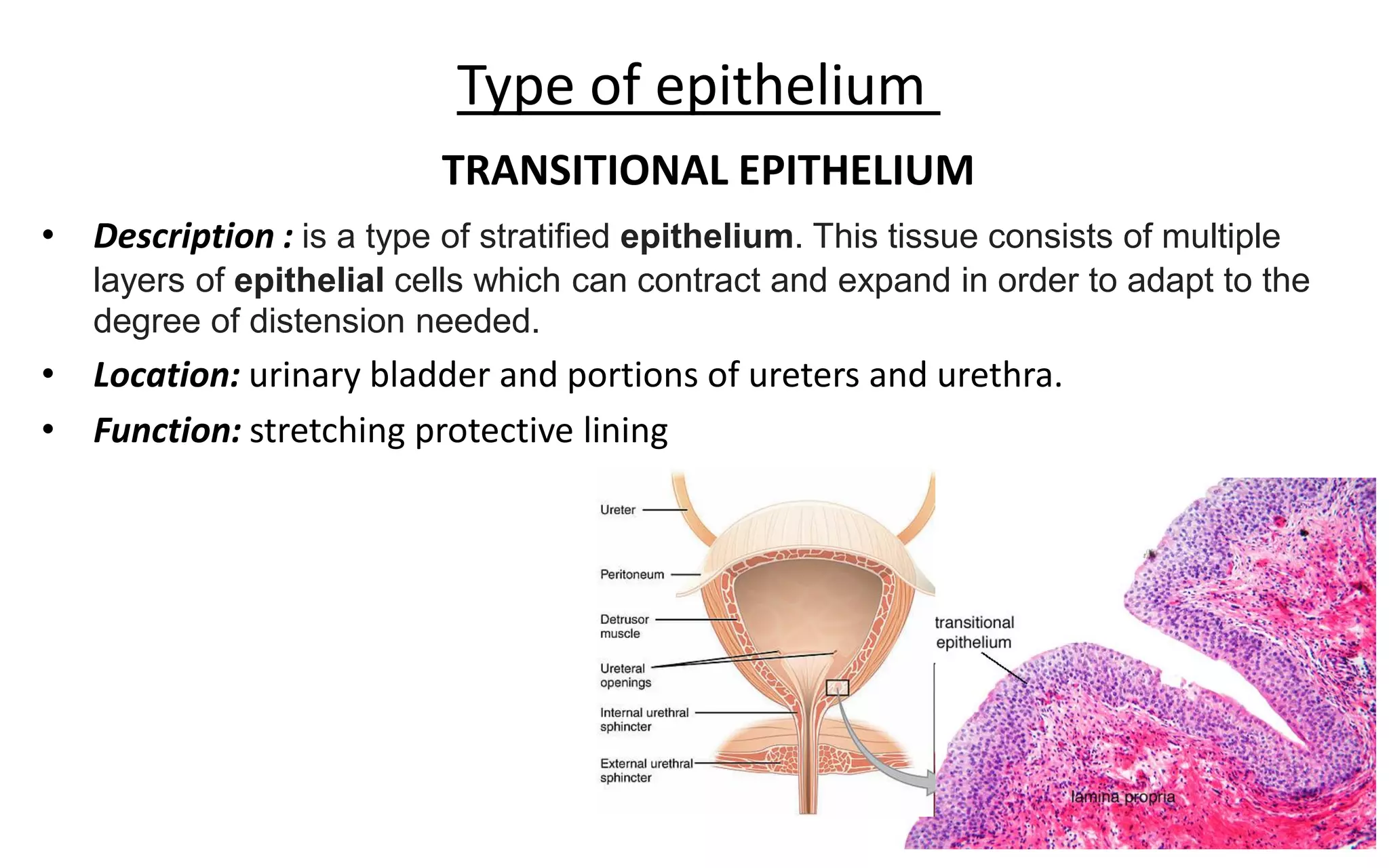
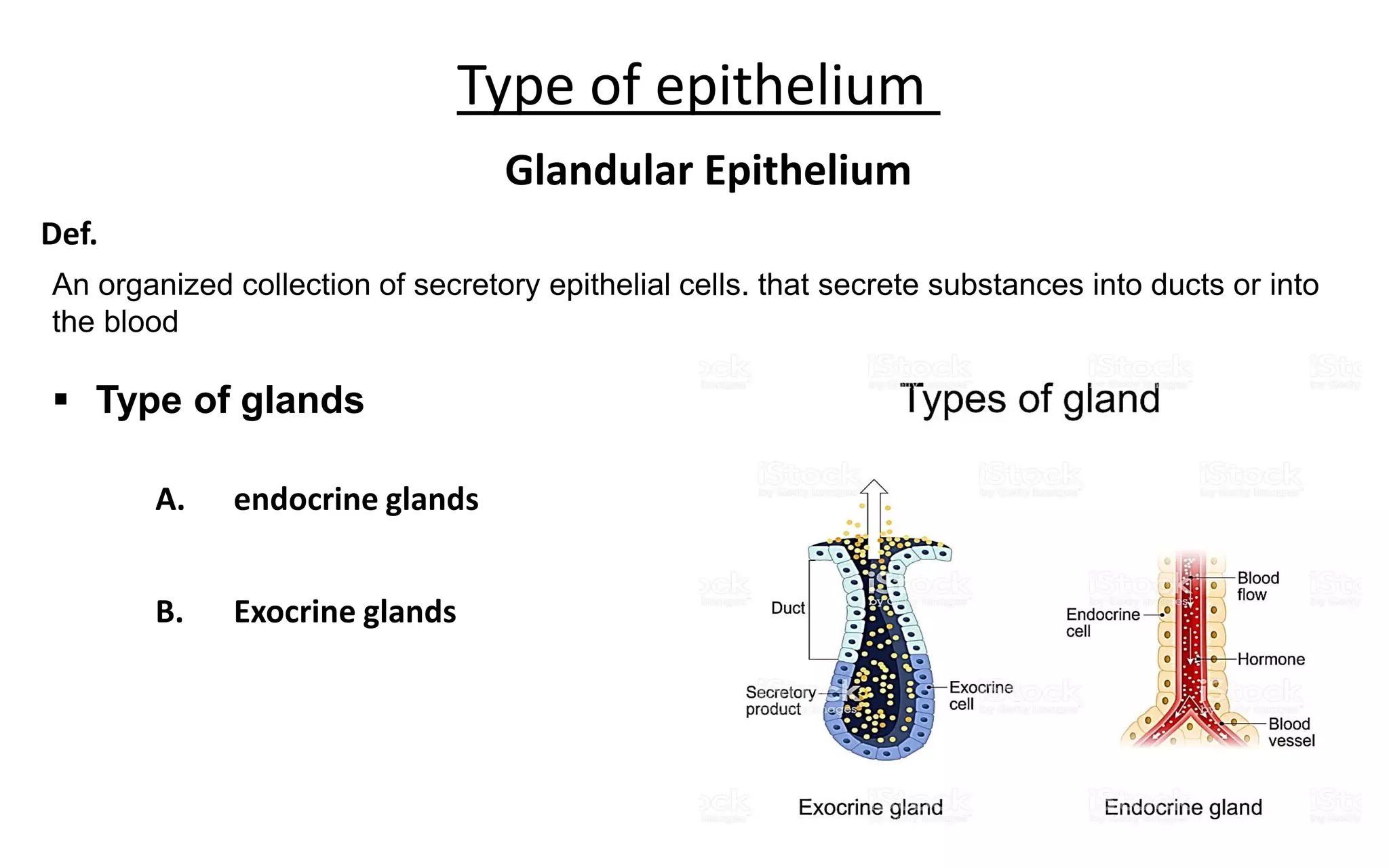
There are 4 main types of tissues in the body: epithelial, connective, nervous, and muscular. Epithelial tissue forms the outer layers of the skin and lines body cavities and organs. It has several important functions like protection, secretion, and absorption. Epithelial tissue is classified based on cell shape and layer arrangement into simple, stratified, and glandular epithelium, each with distinct characteristics and locations in the body.