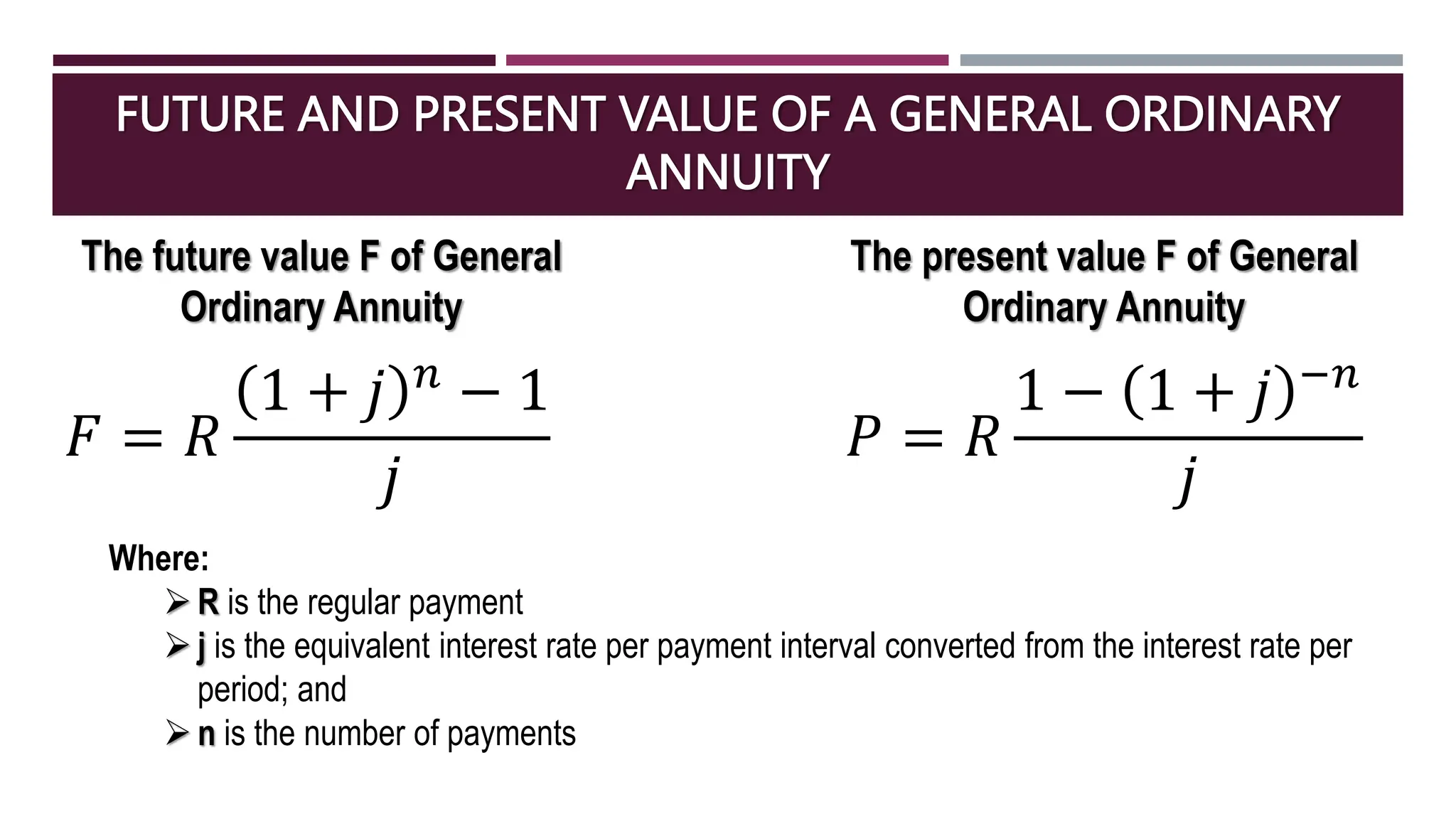
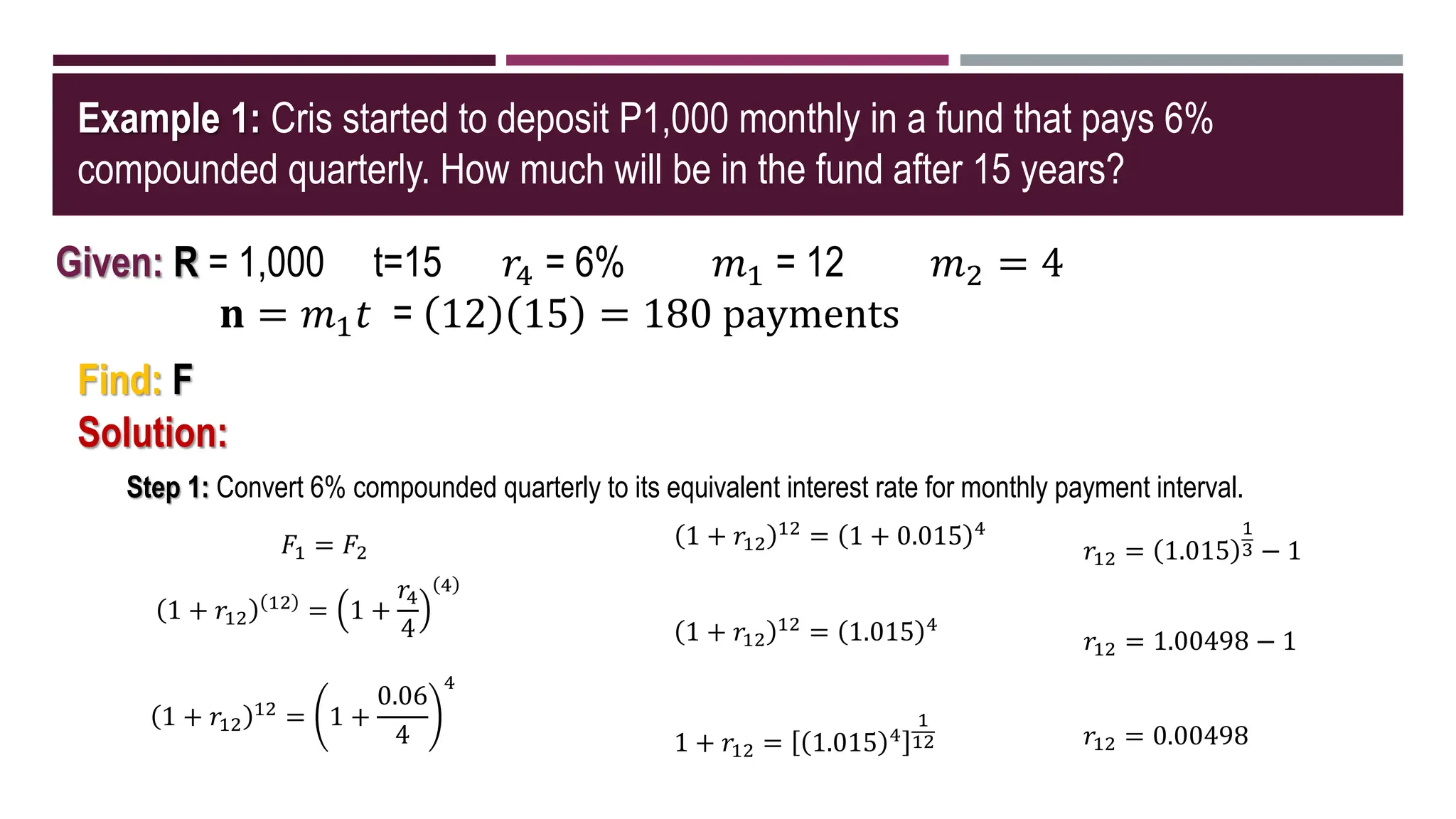
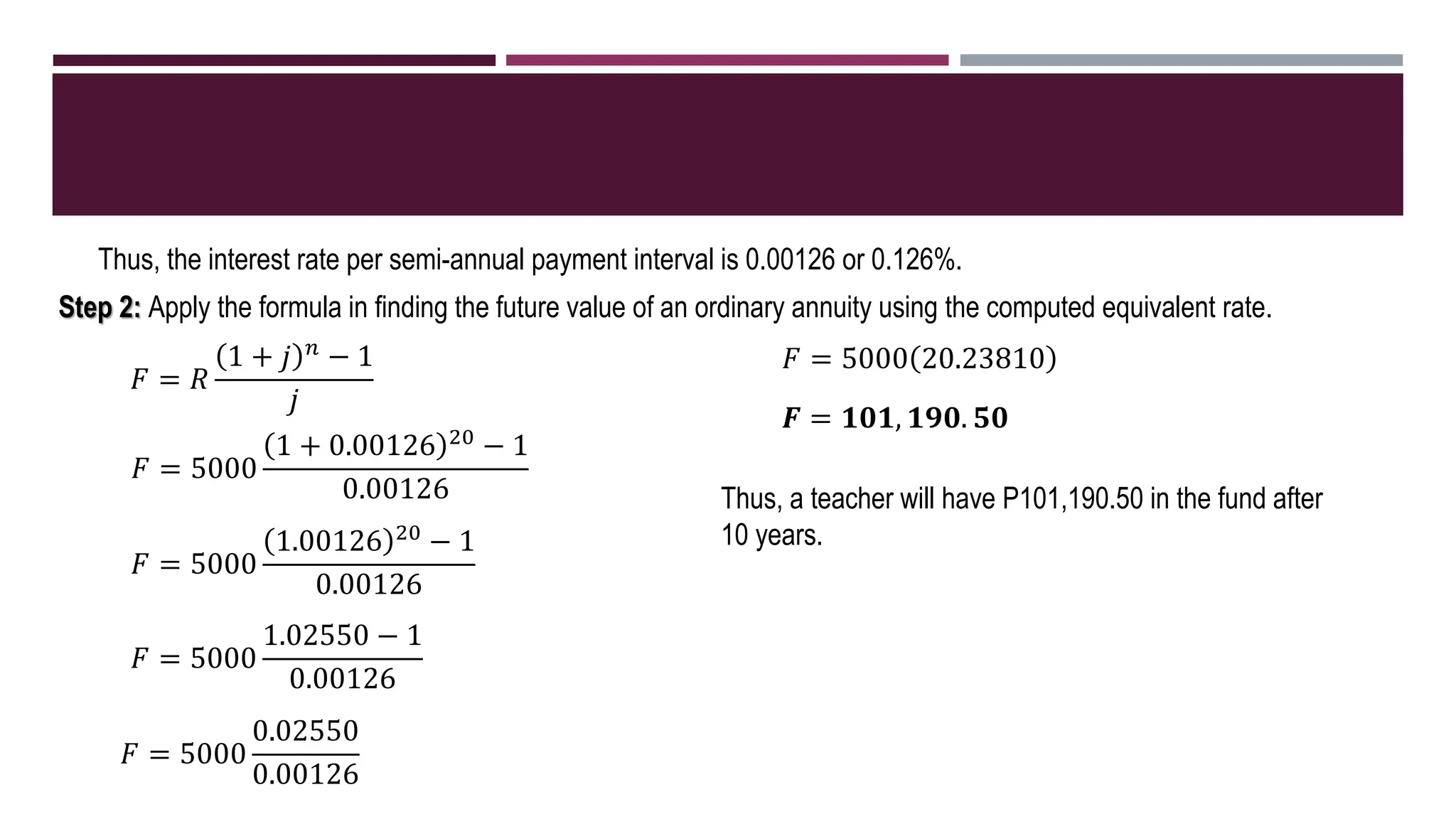
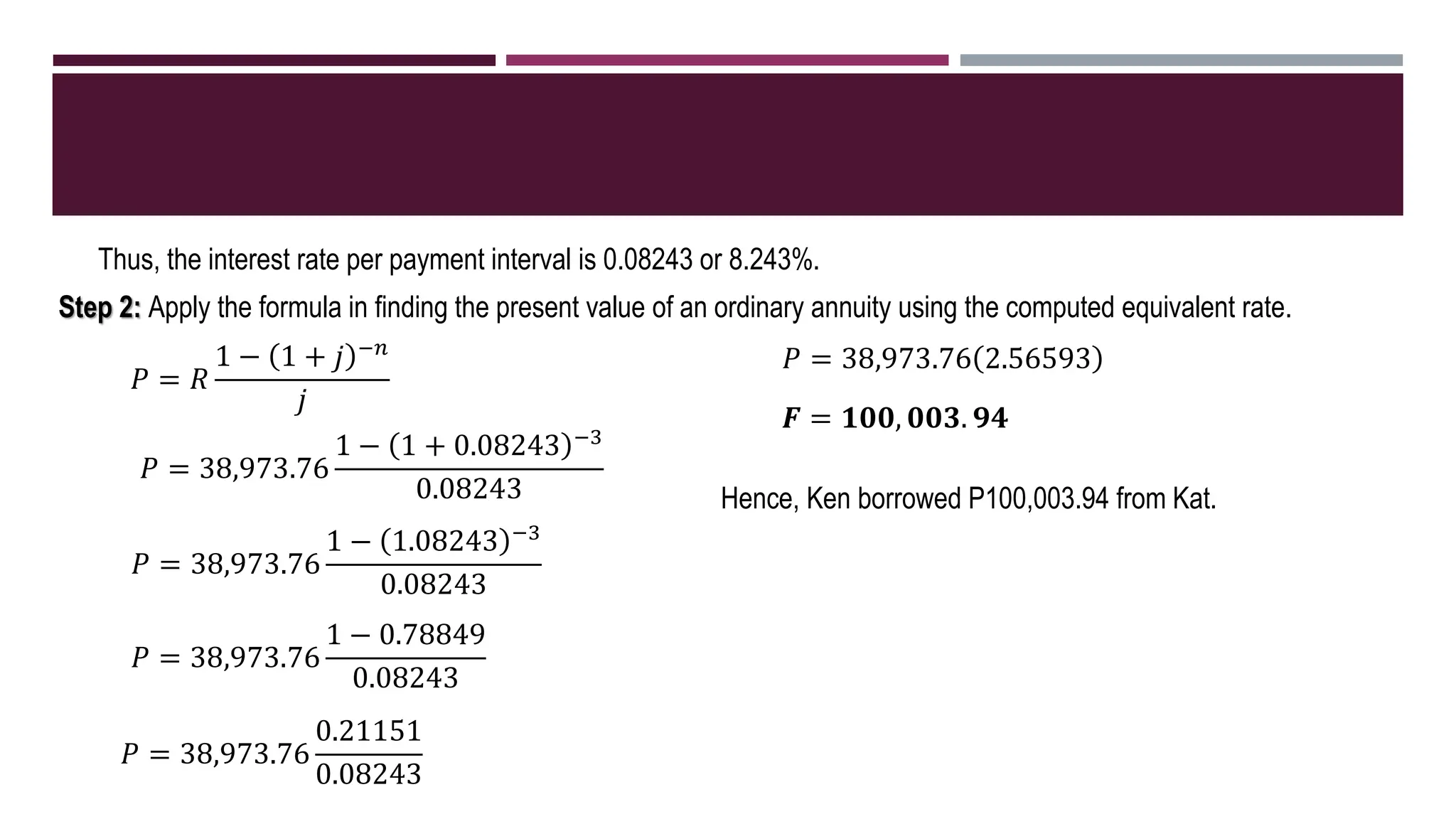
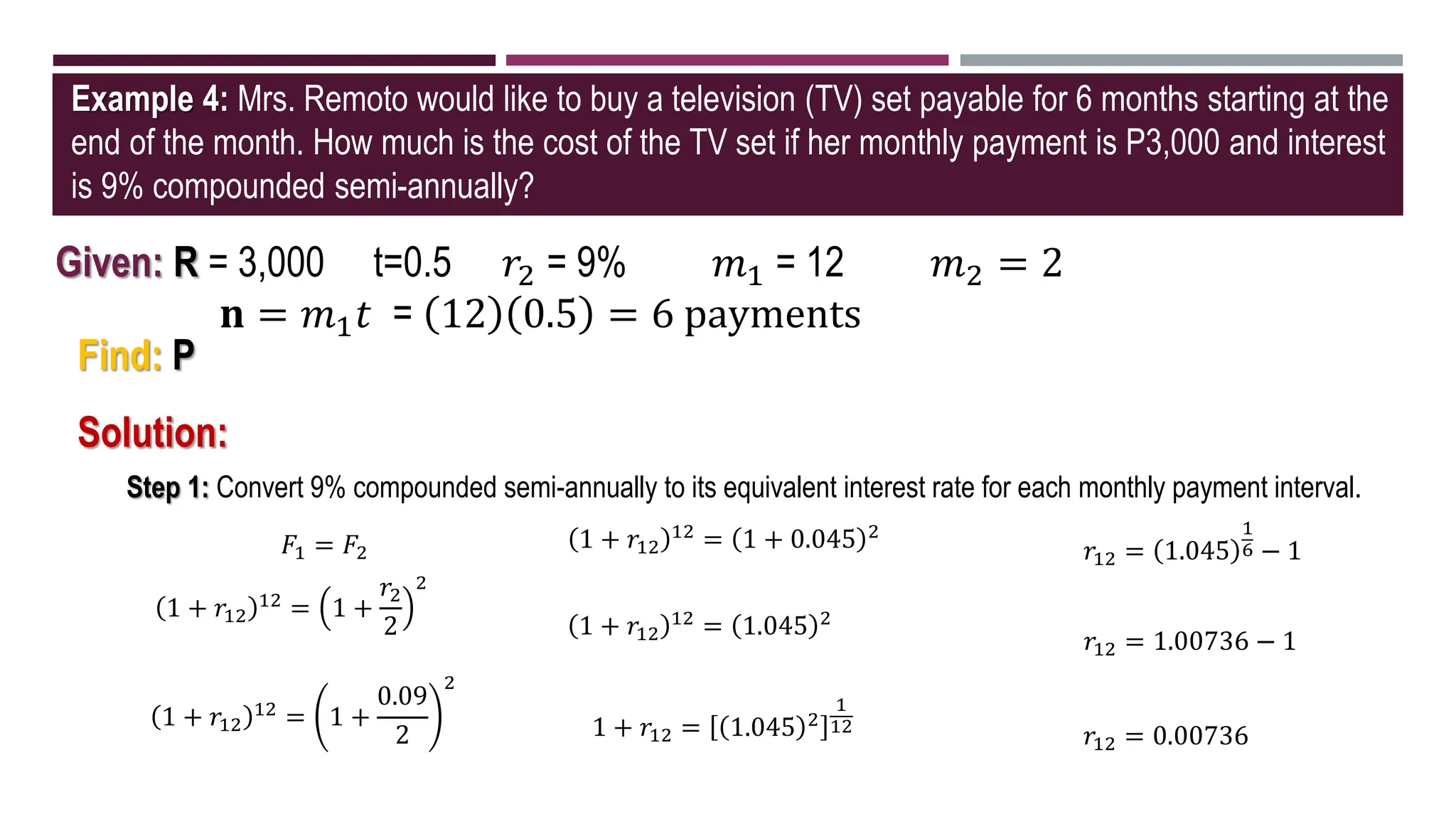
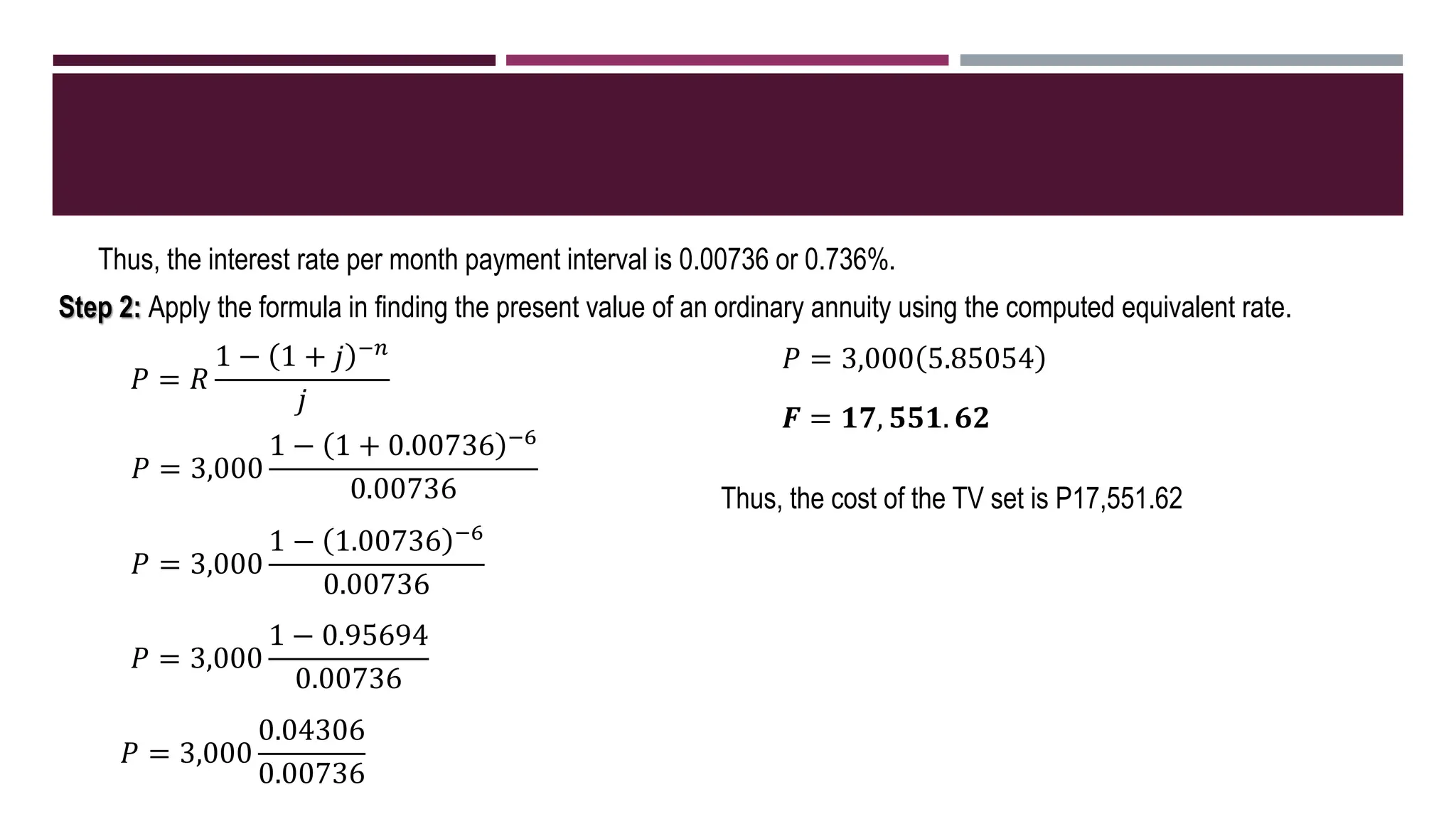
The document discusses general annuities where the payment interval is different from the interest compounding period. It provides formulas to calculate the future and present value of a general ordinary annuity. Examples are included to demonstrate how to convert the interest rate to the equivalent rate per payment interval and apply the formulas. The key steps are to convert the given interest rate to the equivalent rate per payment interval before using the annuity formulas.