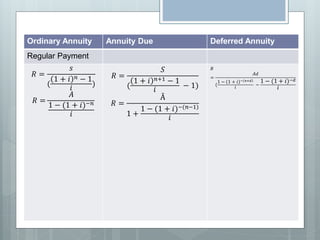
This document defines and explains different types of annuities, including ordinary annuity, annuity due, and deferred annuity. It provides formulas to calculate the present value and regular payments of each type of annuity. Key details include that ordinary annuity payments are made at the end of each interval, annuity due payments are made at the beginning of each interval, and deferred annuity payments begin at a later time.








![Ordinary Annuity Annuity Due Deferred Annuity
Payments made at the end
of each interval.
Payments made at the beginning of
each interval.
Is an annuity in which
the first payment is
made at some later
time.
The amount of an ordinary
annuity, S:
-Is the value at the end of
the term.
-Is the value on the last
payment date.
-is the sum of the
accumulated payments at
the end of the term.
𝑺 = 𝑹[
𝟏 + 𝒊 𝒏 − 𝟏
𝒕
]
𝑺 = 𝑹[
𝟏 + 𝒊 𝒏+𝟏
− 𝟏
𝒕
− 𝟏]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/annuity-191011064015/85/Annuity-9-320.jpg)
![Ordinary Annuity Annuity Due Deferred Annuity
The present value
of annuity denoted
by A:
- Is the value
one period
before the first
payment.
- -is a sum of
discounted
payments at
the beginning
of the terms
𝑨 = 𝑹[
𝟏−(𝟏+𝒊)−𝒏
𝒊
]
𝑨 = 𝑹[𝟏 +
𝟏−(𝟏+𝒊)−(𝒏−𝟏)
𝒊
]
𝑨 = 𝑹[
𝟏−(𝟏+𝒊)−(𝒏+𝒅)
𝒊
-
𝟏−(𝟏+𝒊)−(𝒅)
𝒊
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/annuity-191011064015/85/Annuity-10-320.jpg)