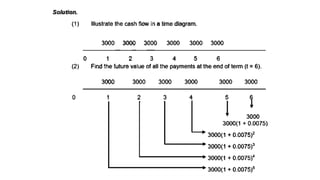
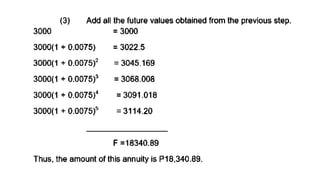
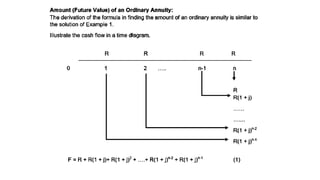
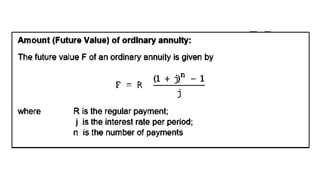
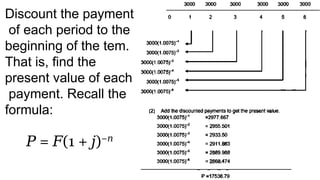
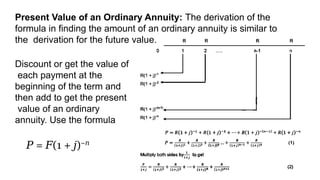
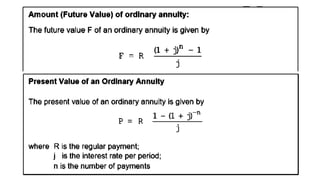
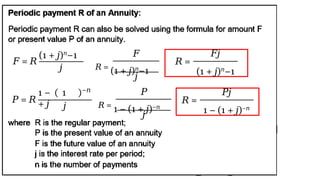
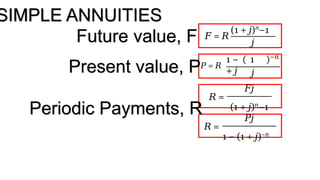
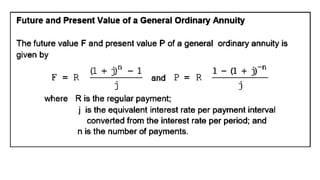
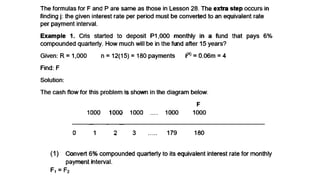
The document explains various types of annuities, including simple, ordinary, due, certain, and contingent annuities, along with definitions of key variables such as term, periodic payment, future value, and present value. It provides examples, particularly focusing on a scenario involving monthly deposits with a specified interest rate and the calculation of both future and present values. Additionally, it outlines the formulas used for determining the future and present values of ordinary annuities.