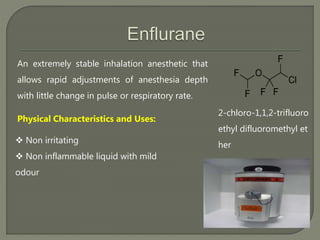
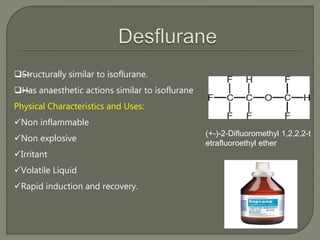
This document describes several inhalational anesthetic agents including halothane, ether, enflurane, isoflurane, desflurane, and sevoflurane. It discusses their physical and chemical properties, mechanisms of action, advantages, and disadvantages. The key points are:
- These agents work by altering the function of ion channels in the central nervous system to produce effects like unconsciousness and amnesia.
- They have various cardiovascular, respiratory, and other systemic effects depending on the specific agent.
- While rapid induction and recovery are advantages for some agents, others have greater risks of toxicity like hepatitis or sensitizing the heart to arrhythmias. Agent selection depends on balancing risks and benefits for each patient.