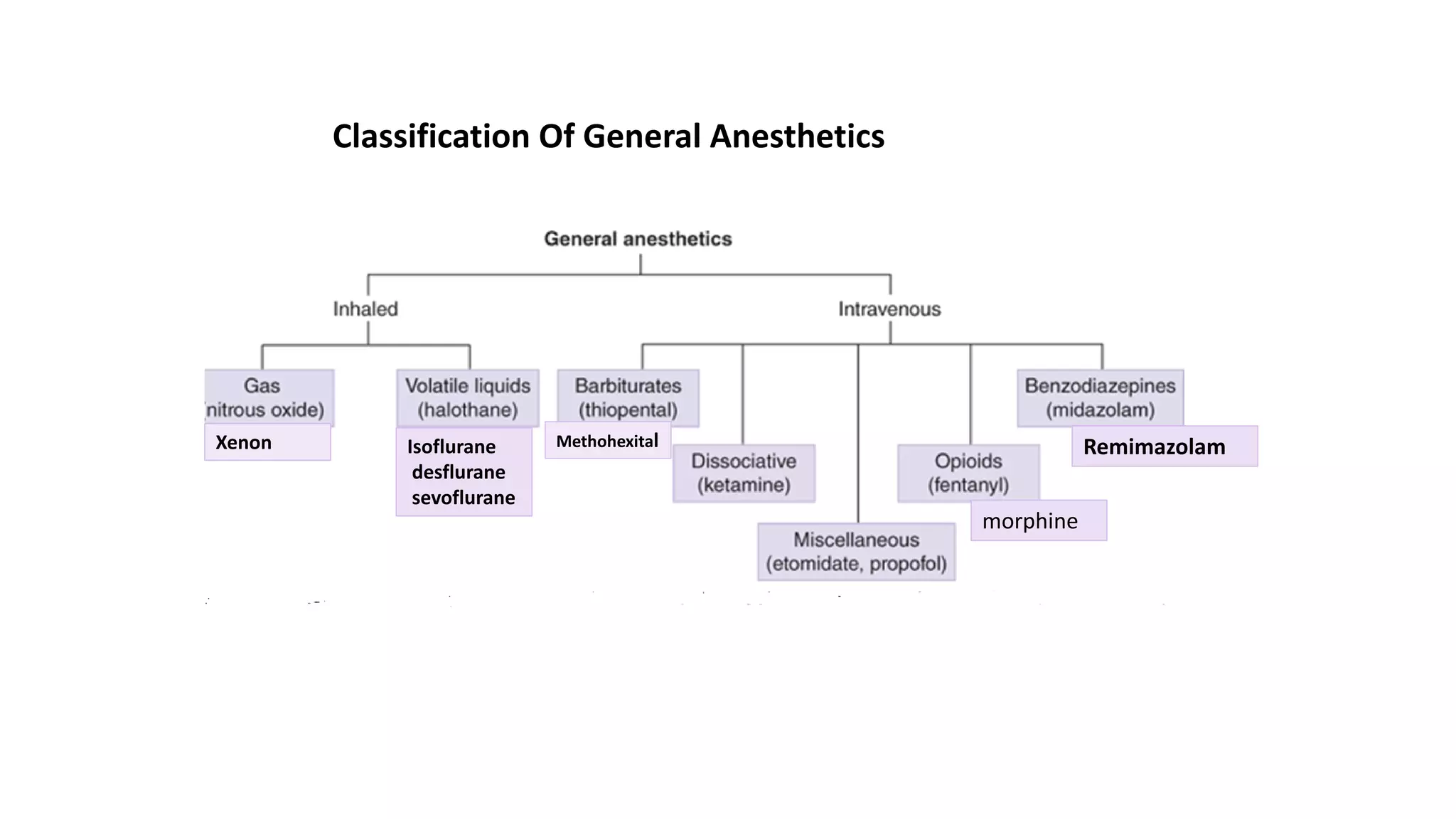
General anesthetics are drugs used during surgery to induce unconsciousness, analgesia, and muscle relaxation. They work by blocking NMDA receptors or enhancing GABA receptors in the central nervous system. There are two main types - general anesthetics that are gases administered by inhalation (nitrous oxide, xenon), and volatile liquids administered by inhalation (halothane, isoflurane, desflurane, sevoflurane). These drugs work by passing through four stages - analgesia, loss of consciousness, surgical anesthesia with loss of reflexes, and a dangerous stage of respiratory depression. The ideal general anesthetic is potent, inexpensive, minimally soluble in tissues, stable, and lacks side effects like cardiotoxicity.



![Mechanisms of anesthesia
1- Blocking the NMDA and glutamate controlled channels.
▪ Glutamate or NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptors in the CNS are activated by the excitatory AA
neurotransmitter glutamic acid.
➢ Agonists: This activation opens the channel, allowing K+ to flow to the extra cellular fluid and Na and
Ca++ to flow into the nerve cell. The increased intracellular [Ca++] activates the liberation of the
(NO), which causes alertness (consciousness).
➢ Antagonists: Ketamine blocks NMDA receptors, causes CNS depression (anesthesia)
2- Activation of the inhibitory GABA receptor controlled channel.
▪ Binding of GABA (inhibitory transmitter) to their receptors will open the Cl- channel, leading to the
influx of Cl- and hyper- polarization of the neuron.
o Halothane and isoflurane inhibit the synaptic destruction of GABA, thereby increasing the GABA-ergic
neurotransmission.
o Benzodiazepines and barbiturates: Enhance GABA opening Cl channels γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
o Benzodiazepines and barbiturates produce anesthesia, by enhancing of GABA opening of the chloride
channel
3- Inhaled anesthetics are also known to enhance the major inhibitory receptors in the spinal cord, the
glycine receptors.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/generalanesthesia-220301234449/75/General-anesthetics-Medicinal-Chemistry-III-4-2048.jpg)