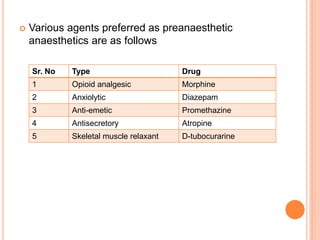
The document discusses general anesthetics and their stages and classifications. It describes the four stages of general anesthesia: analgesia and amnesia, delirium or excitement, surgical anesthesia, and medullary paralysis. It classifies general anesthetics based on their route of administration as volatile/inhalational (ether, halothane, cyclopropane, nitrous oxide) or non-volatile/intravenous (barbiturates, ketamine). It outlines the properties of ideal general anesthetics and discusses advantages and disadvantages of specific anesthetics. It also discusses pre-anesthetic medications that are used prior to anesthesia administration.