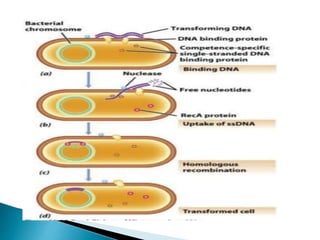
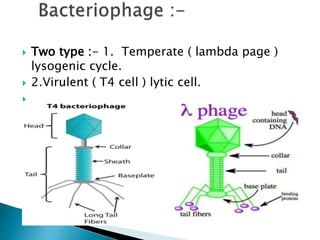
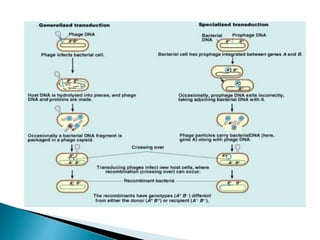
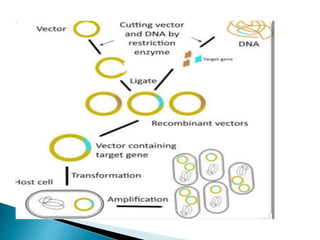
Bacterial transformation is a process of horizontal gene transfer where bacteria take up naked DNA from their environment. The mechanism involves cell-free DNA from lysed bacteria being taken up by competent bacteria, where the single-stranded DNA integrates into the bacteria's genome. Transformation can be used for gene mapping by analyzing the frequency of co-transformation of marker genes, which is inversely proportional to the distance between genes. Bacteriophage transduction is another form of horizontal gene transfer where bacteriophage acts as a vector, transferring DNA from a donor bacterium to a recipient. Restriction enzymes were discovered as a bacterial defense mechanism against bacteriophage involving enzymes that cut DNA at specific recognition sequences.