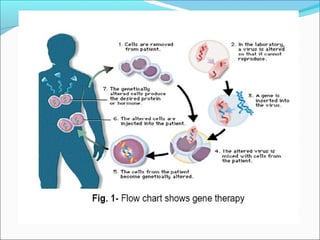
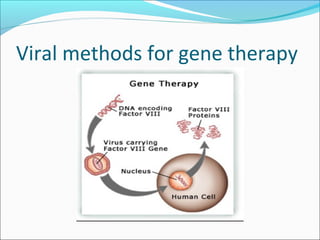
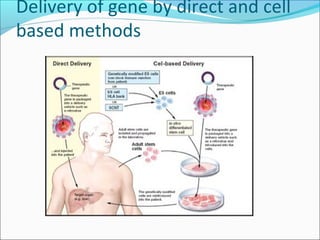
Gene therapy involves techniques that modify or manipulate genes to treat or prevent diseases. The first gene therapy treatment occurred in 1990 for severe combined immunodeficiency. There are four main approaches to gene therapy: inserting a normal gene to compensate for a defective one, replacing an abnormal gene with a normal one, repairing an abnormal gene, or altering gene regulation. Viruses are commonly used as vectors to deliver therapeutic genes into target cells, with retroviruses, adenoviruses, adeno-associated viruses, and herpes simplex viruses being some of the most widely used viral vectors, each with advantages and limitations.