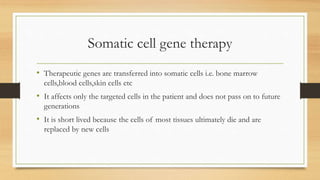
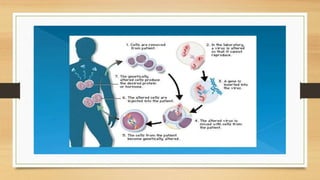
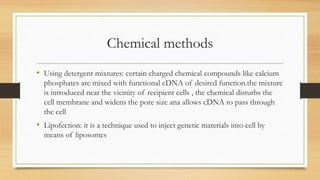
Gene therapy aims to treat diseases by introducing normal genes into cells containing defective genes. The first approved gene therapy occurred in 1990 and treated ADA-SCID. There are two main types of gene therapy - germline modifies heritable genes while somatic only affects treated cells. Viral and non-viral vectors are used to deliver genes, with retroviruses and adenoviruses commonly used viral vectors. Recent advances include gene therapies reducing symptoms for blindness and Parkinson's disease.