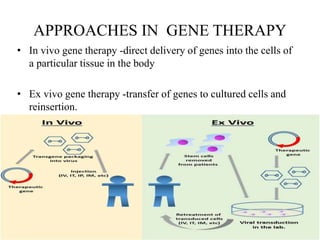
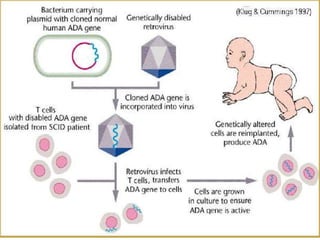
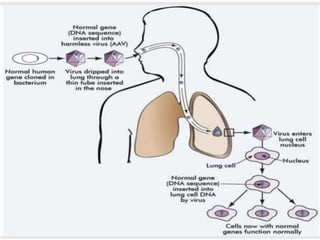
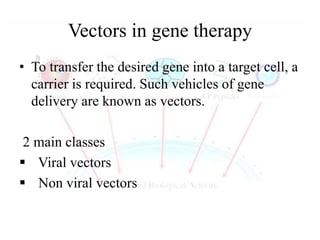
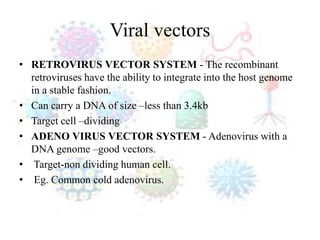
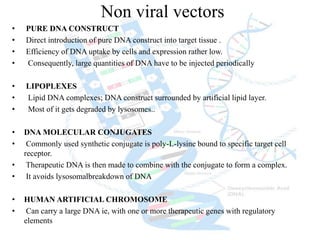
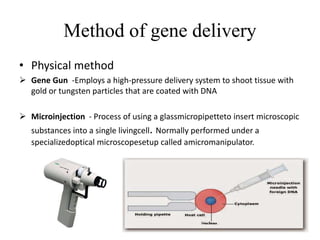
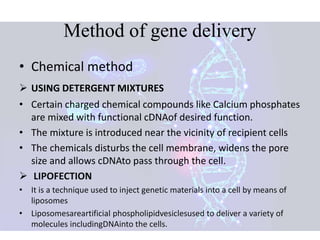
Gene therapy involves introducing genes into cells to treat or cure diseases. It works by correcting defective genes that cause illnesses. The first approved human gene therapy trial took place in 1990 in the US and treated a patient with ADA-SCID. There are two main types of gene therapy - somatic cell gene therapy, which treats genes in body cells but is not inherited, and germline gene therapy, which treats genes in reproductive cells and can be passed to offspring. Gene therapy approaches include in vivo delivery of genes directly into tissues and ex vivo therapy involving culturing and modifying cells outside the body before reinsertion. Viral and non-viral vectors are used to transport therapeutic genes into target cells.