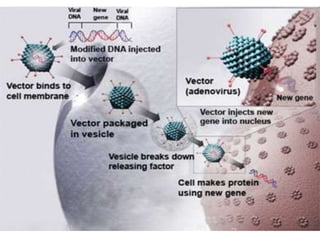
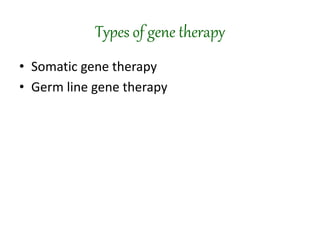
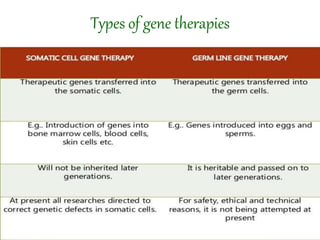
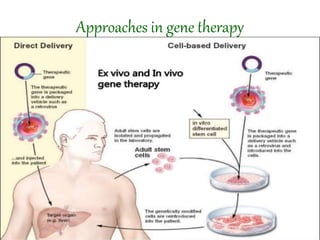
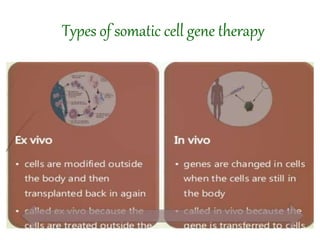
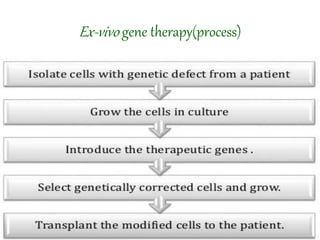
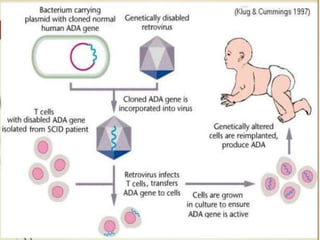
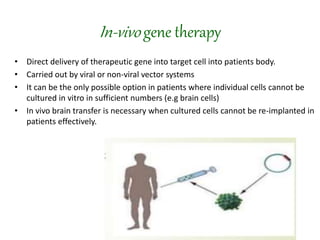
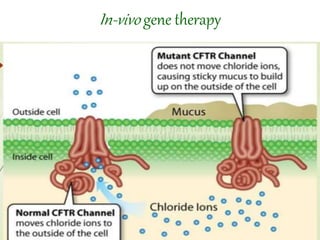
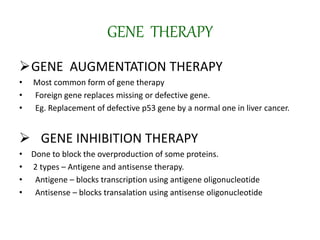
Gene therapy involves introducing genes into cells to treat or prevent disease. It works by delivering a therapeutic gene into a patient's target cells using a vector. This can replace an abnormal gene with a healthy one, inactivate a mutated gene, or introduce a new gene to fight disease. There are two main types - somatic gene therapy only affects treated cells while germline gene therapy results in permanent changes that can be inherited. Approaches include ex vivo gene therapy, which modifies cells outside the body before transplant, and in vivo gene therapy through direct delivery. While gene therapy holds promise to cure genetic diseases, it faces challenges like short-lived effects and safety risks.