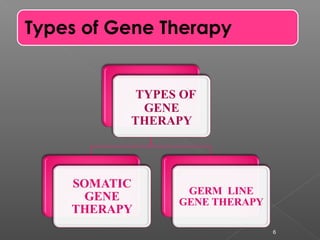
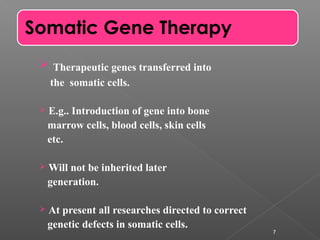
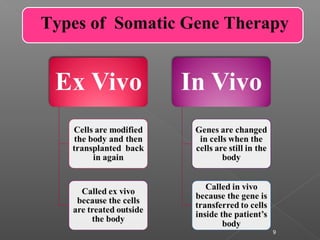
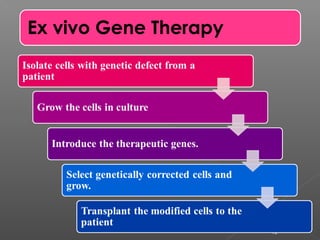
The document discusses gene therapy, which involves inserting normal genes into patients to replace abnormal genes that cause diseases. The first approved gene therapy experiment occurred in 1990 when a 4-year-old girl with severe combined immunodeficiency was treated. There are two main types of gene therapy - somatic cell gene therapy, which treats cells in the body but is not inherited, and germ line gene therapy, which treats eggs and sperm and can be inherited but has safety and ethical concerns. Viruses are commonly used as vectors to deliver therapeutic genes directly to tissues or cells can be removed and treated ex vivo before being returned to the body. While gene therapy holds promise, it also faces challenges and risks that require further research.