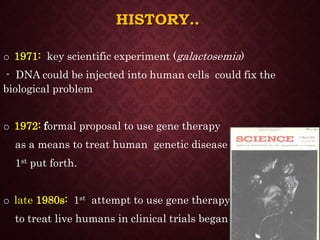
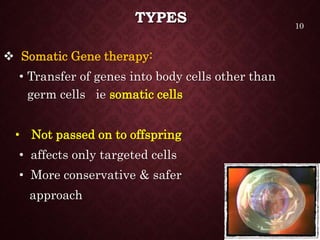
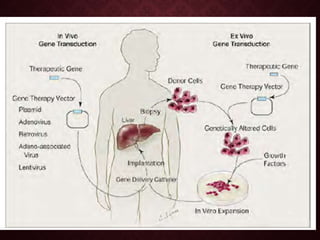
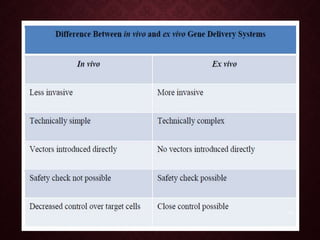
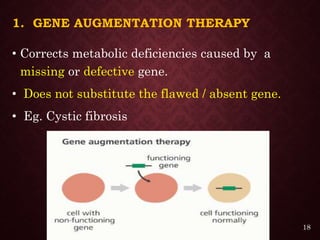
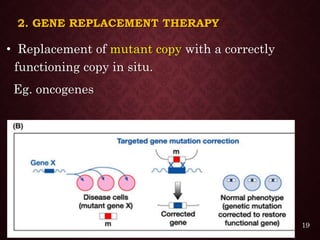
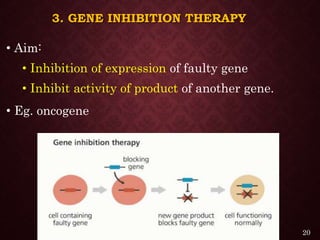
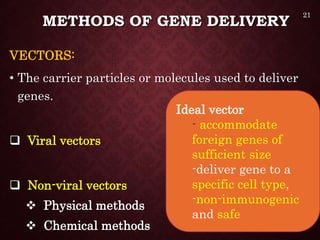
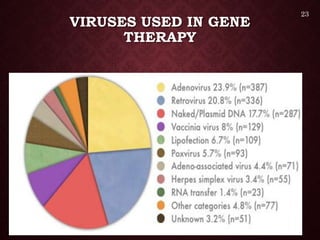
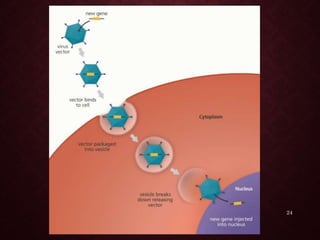
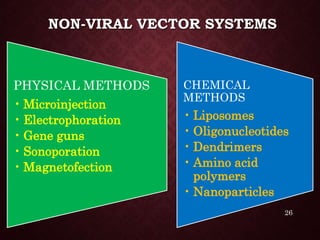
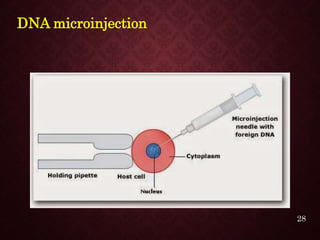
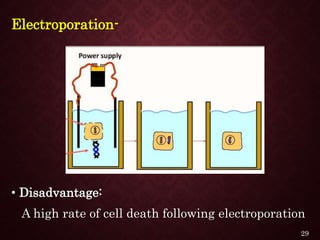
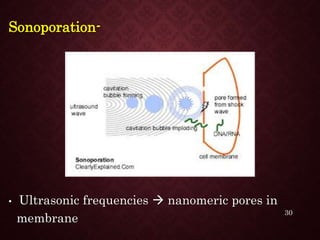
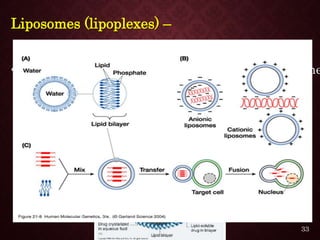
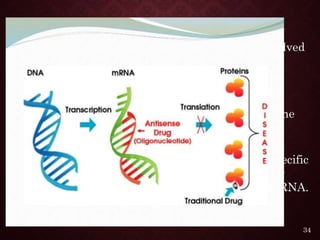
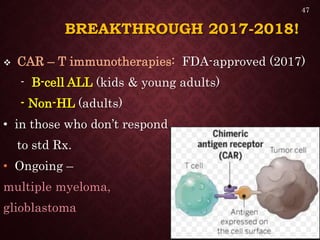
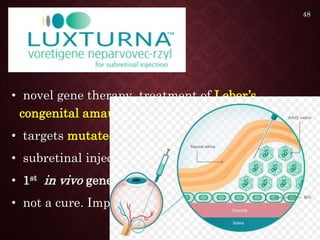
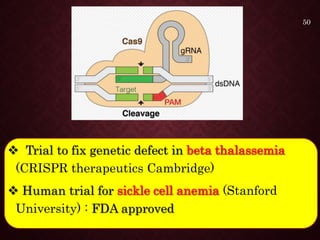
Gene therapy involves introducing genetic material into cells to treat or prevent disease. It has the potential to cure genetic disorders by correcting the underlying genetic defect. There are two main types - somatic gene therapy, which affects only targeted cells and is safer, and germline gene therapy which can permanently alter the genes and be passed to offspring. Recent advances include FDA-approved CAR-T immunotherapies for cancer and the first gene therapy approved for an inherited retinal disease. Challenges remain regarding delivery methods, safety, and ethical issues.