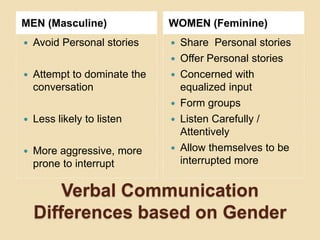
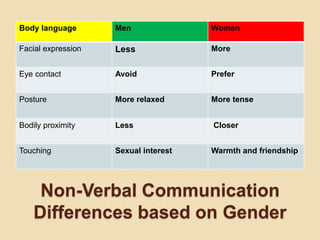
The document discusses the distinctions between sex and gender, emphasizing that sex is a biological classification while gender is a socially constructed role. It outlines various verbal and non-verbal communication differences between men and women, attributing these to brain structure and socialization. The document advocates for understanding and respecting these differences to enhance effective communication and conflict resolution.









![ “The real issue [in workplace conflict] is
lack of gender intelligence. We need to
appreciate and respect the differences
between men and women; to anticipate
them and respond appropriately to them.”
- John Gray
Author, Men are from Mars, Women are from Venus
MANAGING COMMUNICATION CONFLICT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gender-basedcomm-150105191757-conversion-gate01/85/Gender-based-communication-12-320.jpg)


